The hemoglobinopathies market size was exhibited at USD 10.52 billion in 2024 and is projected to hit around USD 34.76 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 12.7% during the forecast period 2025 to 2034.
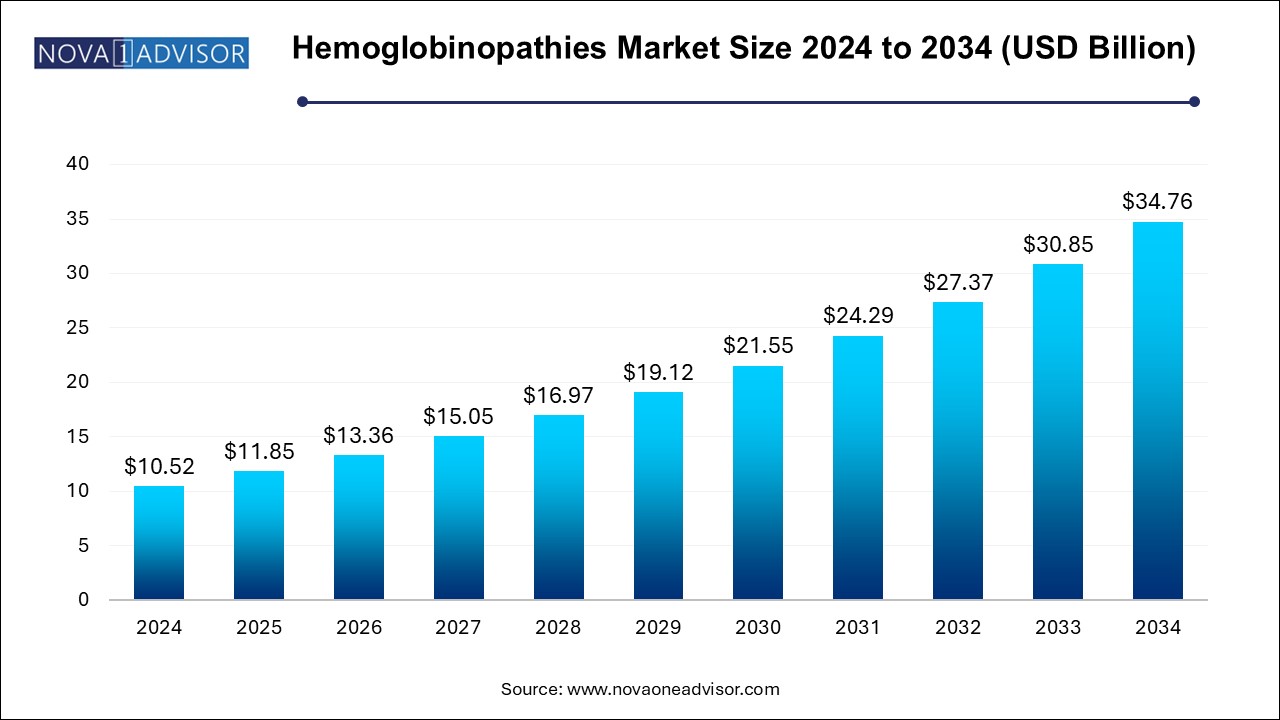
The U.S. hemoglobinopathies market size is evaluated at USD 3.0 billion in 2024 and is projected to be worth around USD 9.91 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 14.47% from 2025 to 2034.
North America held the largest revenue share of 38.0% of the market in 2024, driven by advanced healthcare systems, early adoption of novel therapies, and comprehensive insurance coverage. The U.S. maintains a large sickle cell disease patient population, strong advocacy networks, and well-funded research infrastructure. Companies such as Vertex Pharmaceuticals and bluebird bio are headquartered in the region, with several clinical trials and FDA approvals originating here.
The presence of Newborn Screening (NBS) programs across all U.S. states for SCD, coupled with Medicare and Medicaid coverage for transfusions and hydroxyurea, ensures consistent demand. Additionally, academic medical centers play a pivotal role in stem cell therapy access and clinical innovation.
Asia Pacific is expected to witness the fastest growth, primarily due to the high burden of beta-thalassemia and emerging healthcare reforms. Countries such as India, China, Thailand, and Indonesia report some of the highest global prevalence rates of thalassemia. As governments invest in mass screening, blood bank networks, and transplant infrastructure, treatment accessibility is improving.
Additionally, pharmaceutical companies are increasingly targeting these regions with low-cost generics, biosimilars, and mobile diagnostic tools. International collaborations, such as WHO’s support for hemoglobinopathy control in Southeast Asia, are accelerating regional adoption of screening and early intervention strategies.
The hemoglobinopathies market refers to the diagnosis, treatment, and management of inherited blood disorders caused by abnormal hemoglobin production or structure. Hemoglobinopathies primarily include thalassemia, sickle cell disease (SCD), and other rare hemoglobin (Hb) variants such as HbC, HbE, and HbD. These disorders result in chronic anemia, pain crises, organ damage, and reduced life expectancy, significantly burdening healthcare systems—especially in regions with high prevalence.
The market for hemoglobinopathies is gaining momentum due to increasing disease awareness, supportive governmental and non-governmental policies, advanced genetic testing, and new therapeutic options. The rise in birth prevalence in Asia, Africa, and the Middle East, combined with the growth of targeted therapy, bone marrow transplantation, and gene therapy, is shifting the treatment paradigm from palliative to potentially curative.
Traditionally, disease management relied heavily on blood transfusions and chelation therapy. However, innovations in hydroxyurea formulations, disease-modifying agents, and hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) have broadened the treatment landscape. In parallel, the surge in pre-implantation genetic diagnosis (PGD) and prenatal screening reflects the increased role of preventive strategies and carrier screening in high-risk populations.
As pharmaceutical and biotech firms focus on gene-editing tools like CRISPR-Cas9 and lentiviral vectors, the future of hemoglobinopathies care may lie in single-administration curative therapies, minimizing lifetime treatment costs. A growing emphasis on equitable access, coupled with favorable regulatory policies for rare disease drugs, provides fertile ground for industry expansion.
Rise in Genetic Screening and Carrier Testing: Governments and NGOs are expanding prenatal and neonatal screening programs in high-risk regions.
Emergence of Gene Therapies: Clinical trials for CRISPR-based and lentivirus-mediated gene therapies show promise for long-term cure.
Increased Access to Bone Marrow Transplantation: Improved donor registries and reduced-intensity conditioning regimens are making HSCT more accessible.
AI in Hemoglobin Variant Detection: Advanced bioinformatics and AI models are streamlining variant interpretation in complex genotyping.
Growing Focus on Orphan Drug Development: Regulatory incentives such as priority review and market exclusivity are encouraging innovation.
Decentralization of Diagnostic Infrastructure: Portable electrophoresis and rapid genetic kits are expanding diagnostics to rural areas.
Telemedicine in Disease Monitoring: Digital health tools are supporting follow-ups for transfusion schedules and hydroxyurea adherence.
Multidisciplinary Care Models: Integration of hematologists, psychologists, and pain specialists is improving quality of life outcomes.
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 11.85 Billion |
| Market Size by 2034 | USD 34.76 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2025 to 2034 | CAGR of 12.7% |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025-2034 |
| Segments Covered | Type, Diagnosis, Therapy, Region |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) | Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Regional scope | North America; Europe; Asia Pacific; Latin America; MEA |
| Key Companies Profiled | Sangamo Therapeutics; bluebird bio, Inc.; Global Blood Therapeutics, Inc.; Pfizer, Inc.; Emmaus Life Sciences, Inc.; Prolong Pharmaceuticals, LLC; Celgene Corporation; Bioverativ Inc.; Gamida Cell; Novartis AG |
One of the primary drivers of the hemoglobinopathies market is the high global prevalence and health burden associated with thalassemia and sickle cell disease. The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that over 5% of the global population carries a gene for hemoglobin disorder. Sickle cell disease alone affects over 20 million people worldwide, and over 300,000 babies are born annually with severe hemoglobinopathies.
Countries in sub-Saharan Africa, the Middle East, India, and Southeast Asia report some of the highest birth prevalence rates, often compounded by poor access to early diagnosis and care. In high-income countries, migration from endemic regions is expanding the patient pool and increasing awareness and screening efforts.
The growing need for early identification and lifelong management creates significant market potential for diagnostic tools and disease-modifying therapies. As disease awareness increases and national healthcare systems prioritize rare and inherited disorders, the demand for effective and affordable care strategies is projected to rise.
A major restraint hampering market growth is the limited access to advanced therapies—such as bone marrow transplantation and gene therapy—in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs), where the disease burden is highest. Despite the existence of potentially curative treatments, financial, logistical, and infrastructural barriers prevent widespread access.
Even where standard of care includes blood transfusions and iron chelation therapy, poor healthcare infrastructure leads to delays in diagnosis, inadequate transfusion protocols, and non-compliance with chelation regimens, increasing complications and mortality. Gene therapy trials and commercial treatments, while promising, remain out of reach for the vast majority of patients due to costs exceeding $1 million per treatment.
Bridging this gap requires massive investment in local diagnostics, trained personnel, insurance reforms, and tiered pricing models to ensure that life-saving innovations benefit the most vulnerable populations.
The most transformative opportunity in the hemoglobinopathies market lies in emerging gene therapies and genome editing technologies. Biotech firms are actively developing and testing single-administration treatments that can potentially eliminate the need for chronic therapies and transfusions.
For example, therapies such as lovotibeglogene autotemcel (Lovo-cel) for sickle cell disease and betibeglogene autotemcel (Zynteglo) for transfusion-dependent beta-thalassemia represent a leap in curative intervention. CRISPR-Cas9 editing of the BCL11A gene to reactivate fetal hemoglobin is another promising strategy under clinical evaluation.
Regulatory designations like “Breakthrough Therapy” and “Orphan Drug” status in the U.S. and Europe offer expedited pathways and financial incentives for companies innovating in this space. While upfront costs remain high, the potential to reduce lifetime disease management expenses is attracting payer interest, laying the groundwork for a shift from palliative care to durable cures.
Sickle Cell Disease dominated the hemoglobinopathies market, accounting for the largest patient population and highest healthcare utilization. It is particularly prevalent in sub-Saharan Africa, the Middle East, and parts of India. In the U.S., SCD is a leading genetic disorder among African Americans, creating consistent demand for diagnostics, pain management, hydroxyurea, and transfusions.
Because SCD results in recurrent vaso-occlusive crises, strokes, and organ complications, it has received significant attention from pharmaceutical innovators. Ongoing clinical trials for gene therapies, biologics like voxelotor and crizanlizumab, and novel pain modulators further underscore its central role in the hemoglobinopathies landscape.
Thalassemia is the fastest-growing segment, largely due to improved survival, expanding carrier screening, and increasing healthcare access in Asia and the Middle East. Transfusion-dependent beta-thalassemia (TDT) and intermediate thalassemias require lifelong care, creating a sustained need for transfusion services, chelation drugs, and curative bone marrow transplants. Public health initiatives, such as mandatory premarital screening in Gulf countries and genetic counseling programs in India, are boosting diagnostic volumes and driving early intervention.
Blood tests were the most commonly used diagnostic modality across all hemoglobinopathies, particularly in low-resource settings where access to advanced molecular testing remains limited. CBC, reticulocyte count, and peripheral smear remain first-line tools for anemia and hemoglobinopathy suspicion, followed by confirmatory tests.
Genetic testing is the fastest-growing diagnostic segment, driven by the need for prenatal screening, definitive diagnosis, and therapy planning—especially for bone marrow transplantation or gene therapy eligibility. Pre-implantation genetic diagnosis (PGD) is gaining traction among families with prior affected children. Technologies such as next-generation sequencing (NGS), multiplex PCR, and capillary electrophoresis are being integrated into diagnostic algorithms to improve variant detection and differentiation.
The sickle cell disease segment held the largest revenue share of 63.0% of the hemoglobinopathies market in 2024, remaining the backbone of care in thalassemia and severe sickle cell cases. Transfusions alleviate anemia, suppress ineffective erythropoiesis, and reduce complications. However, risks of alloimmunization, iron overload, and infection transmission necessitate strict monitoring and iron chelation support.
Gene therapy is projected to be the fastest-growing therapeutic segment, with several pipeline candidates moving toward regulatory approval and commercialization. Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation, previously limited to matched sibling donors, is now expanding through haploidentical transplants and gene-modified autologous cells. Regulatory approvals, pricing negotiations, and long-term follow-up results will define the trajectory of these transformative therapies.
In February 2025, Vertex Pharmaceuticals and CRISPR Therapeutics submitted their BLA for exa-cel, a CRISPR-based gene therapy for SCD and TDT, marking a significant milestone in genome editing-based treatments.
In December 2024, bluebird bio’s Zynteglo received expanded coverage approval in the U.S. for beta-thalassemia, after demonstrating durable transfusion independence in long-term data.
In November 2024, India’s Ministry of Health launched a national carrier screening program targeting 100 million individuals over five years, focusing on tribal and rural populations.
In August 2024, Agios Pharmaceuticals presented Phase 2 data for mitapivat, an oral activator of pyruvate kinase, showing improved hemoglobin levels in non-transfusion-dependent thalassemia.
In June 2024, Bio-Rad Laboratories released a next-gen capillary electrophoresis platform for multiplex hemoglobin variant detection, reducing test time by 40%.
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2034. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the hemoglobinopathies market
By Type
By Diagnosis
By Therapy
By Regional