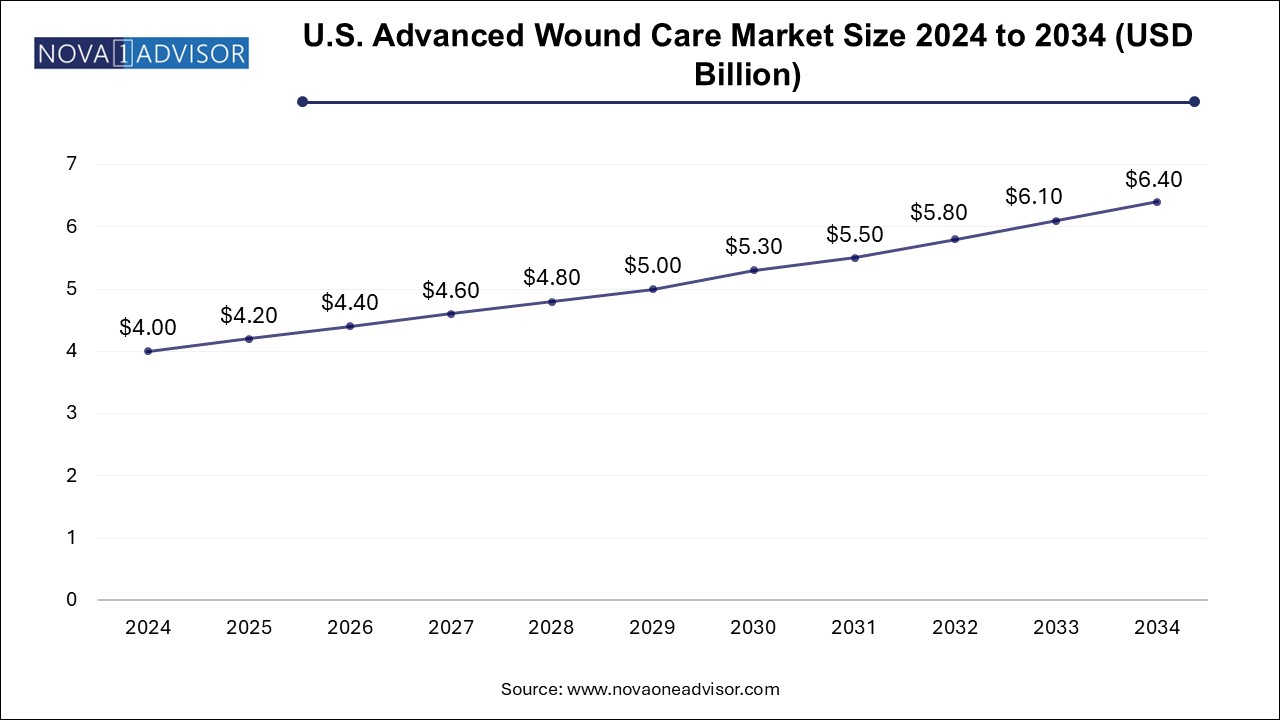
The advanced wound care market size was exhibited at USD 11.55 billion in 2024 and is projected to hit around USD 18.48 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 4.81% during the forecast period 2025 to 2034.
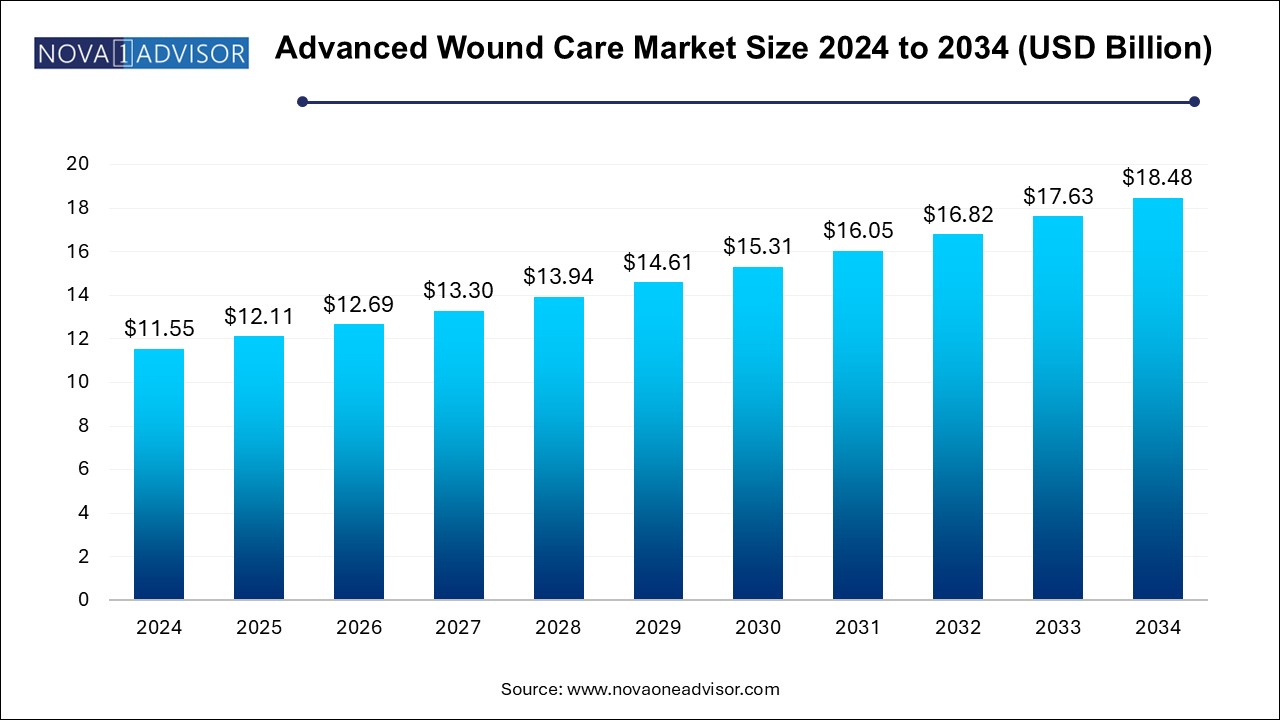
The U.S. advanced wound care market size is evaluated at USD 4.0 billion in 2024 and is projected to be worth around USD 6.4 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 4.36% from 2025 to 2034.
North America, particularly the United States, dominates the global advanced wound care market, supported by a well-established healthcare infrastructure, widespread insurance coverage, and early adoption of innovative wound care solutions. The U.S. sees high incidences of chronic wounds due to its aging population and rising prevalence of diabetes and obesity. The region is home to major players in the wound care industry, such as 3M, Smith & Nephew, and Johnson & Johnson, which continually innovate and invest in advanced therapies.
Additionally, favorable reimbursement policies under Medicare and private insurers support access to high-end products like bioengineered skin substitutes and negative pressure wound therapies. Hospitals and outpatient clinics across the region are increasingly adopting evidence-based wound care protocols, and growing public awareness ensures strong product demand.
Asia Pacific is emerging as the fastest-growing region, driven by rising healthcare investments, growing awareness of wound management, and a large patient population suffering from diabetes and trauma-related injuries. Countries such as China, India, Japan, and South Korea are experiencing rapid healthcare modernization, leading to greater adoption of advanced wound care protocols in both public and private sectors.
Government initiatives aimed at improving diabetic care, the establishment of wound care centers in urban hospitals, and the emergence of local wound care product manufacturers are contributing to regional momentum. While affordability remains a barrier in some countries, the expansion of insurance schemes and growing medical tourism—particularly in wound and burn treatment—are expected to further fuel market growth.
The advanced wound care market has emerged as a vital segment within the global medical devices and healthcare solutions industry, playing a critical role in the management of acute and chronic wounds. Unlike traditional wound care products such as gauze and cotton, advanced wound care products are designed to promote faster healing, maintain a moist wound environment, and reduce the risk of infection. These innovations are particularly significant in addressing complex wounds such as diabetic foot ulcers, pressure ulcers, venous leg ulcers, and surgical wounds, which often resist healing through conventional treatments.
Chronic wounds are increasingly prevalent due to the global rise in diabetes, obesity, cardiovascular diseases, and aging populations—each a contributing factor to impaired wound healing. In parallel, the surge in surgical procedures and trauma-related injuries has expanded the scope of acute wound management. Hospitals, outpatient clinics, and home healthcare settings are now widely adopting advanced wound care solutions that include foam dressings, hydrocolloids, hydrogels, alginates, collagen-based therapies, silver-infused antimicrobial dressings, and bioengineered skin substitutes.
The growth of this market is further driven by technology integration in wound care, including the use of telehealth for remote wound monitoring, smart dressings embedded with sensors, and the use of biomaterials and growth factors that actively participate in the healing cascade. With increasing regulatory approvals, expansion into emerging markets, and an emphasis on patient-centric care, the global advanced wound care market is expected to grow steadily through 2034
Growing Use of Antimicrobial and Silver-Based Dressings Amid Infection Control Priorities
Emergence of Smart Wound Dressings with Embedded Sensors for Moisture and pH Monitoring
Rise in Home Healthcare and Self-Managed Wound Care Driven by Aging Populations
Increased Investment in Bioengineered Skin Substitutes and Tissue Regeneration Technologies
Integration of Telemedicine in Wound Care for Remote Consultation and Progress Tracking
Personalized Wound Care Solutions Based on Patient Comorbidities and Healing Rates
Strong Demand for Advanced Products in Treating Diabetic Foot Ulcers and Venous Ulcers
Collaborations Between Biotech and Device Manufacturers to Develop Next-Gen Therapies
Widening Reimbursement Coverage for Advanced Wound Care in Developed Countries
Shift from Inpatient to Outpatient and Home-Based Wound Management Solutions
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 12.11 Billion |
| Market Size by 2034 | USD 18.48 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2025 to 2034 | CAGR of 4.81% |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025-2034 |
| Segments Covered | Product, Application, End use, Region |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) | Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Regional scope | North America; Europe; Asia Pacific; Latin America; MEA |
| Key Companies Profiled | ConvaTec Group PLC; Smith & Nephew PLC; Mölnlycke Health Care AB; B. Braun Melsungen AG; 3M; URGO; Coloplast Corp.; Integra LifeSciences; Medline Industries, Inc. |
One of the most significant drivers of the advanced wound care market is the rising global incidence of chronic wounds, particularly diabetic foot ulcers, pressure ulcers, and venous leg ulcers. As per the International Diabetes Federation (IDF), over 537 million adults are currently living with diabetes—a figure projected to reach 643 million by 2030. Among these patients, approximately 15–25% will develop a diabetic foot ulcer at some point, and these wounds often take weeks or months to heal, putting them at high risk for infection, amputation, and death.
Advanced wound care solutions offer an effective alternative by actively supporting wound healing through moisture balance, oxygen permeability, and the delivery of antimicrobial or regenerative agents. In the case of diabetic foot ulcers, for example, foam dressings and collagen-based dressings have shown superior results in tissue regeneration and exudate management. The rising awareness of these benefits among healthcare providers, along with increased funding for diabetic care programs worldwide, is significantly fueling the demand for advanced wound therapies.
Despite clinical benefits, the high cost of advanced wound care products remains a critical barrier to widespread adoption, particularly in low-income countries and rural healthcare settings. Products such as silver-infused dressings, negative pressure wound therapy (NPWT) devices, and bioengineered skin substitutes are priced significantly higher than traditional gauze or saline-based treatments. The cost disparity becomes more pronounced in chronic care settings where repeated dressing changes and long treatment cycles are necessary.
Additionally, reimbursement policies for advanced wound care vary across countries, and in many regions, coverage is limited or absent altogether. This makes advanced therapies inaccessible to large segments of the population. Hospitals and clinics with budget constraints often continue to rely on conventional products, even in cases where modern alternatives may improve healing outcomes. Addressing these challenges requires not only innovation in cost-effective production but also concerted policy efforts to expand reimbursement schemes.
A promising opportunity lies in the expansion of advanced wound care solutions into the home healthcare segment, supported by demographic shifts and advances in digital health. As healthcare systems globally aim to reduce hospital stays and the associated risk of nosocomial infections, more wound care patients are being managed at home—especially those recovering from surgeries, burns, or chronic illnesses. This trend has been accelerated by the COVID-19 pandemic and the parallel rise in telemedicine.
Advanced wound dressings that require less frequent changes, deliver controlled medication release, or are equipped with wearable sensors for pH, moisture, or infection status are increasingly suitable for home use. These smart dressings, combined with mobile apps and remote physician monitoring, are transforming how wounds are assessed and managed. Companies that can develop user-friendly, affordable, and telehealth-compatible products are well-positioned to tap into this rapidly expanding opportunity space.
Moist wound dressings, including foam, hydrocolloid, film, hydrogel, alginate, and collagen dressings, dominate the global advanced wound care product segment. These dressings create and maintain an optimal moist wound environment, which promotes autolytic debridement, reduces pain, and accelerates granulation tissue formation. Foam dressings, in particular, are widely used due to their versatility in absorbing high levels of exudate, making them ideal for treating pressure ulcers, venous leg ulcers, and post-operative wounds. Their ease of use and extended wear time make them suitable for both inpatient and home care settings.
Film and hydrocolloid dressings are preferred for superficial wounds, blisters, and surgical sites, while collagen and hydrogel dressings are increasingly used in chronic wound care settings due to their biocompatibility and regenerative support. Collagen dressings are particularly effective in non-healing wounds and diabetic ulcers. Meanwhile, the biomaterials segment—which includes skin substitutes and growth factor-based products—is the fastest-growing category. These products are gaining traction for their role in tissue regeneration, especially in non-healing or complex wound cases such as burns and full-thickness ulcers.
Chronic wounds, especially diabetic foot ulcers, pressure ulcers, and venous leg ulcers, account for the largest share of the advanced wound care market by application. These wounds typically exhibit slow healing due to underlying pathologies and comorbid conditions, and they frequently require long-term management. Advanced products like foam, alginate, and collagen dressings are routinely used in chronic wound care protocols, along with antimicrobial agents to manage infection risks. The market growth in this segment is further supported by a surge in global diabetes rates and aging populations, which are more susceptible to chronic wounds.
On the other hand, surgical and traumatic wounds under the acute wound category represent the fastest-growing segment. As the volume of elective and emergency surgeries rises worldwide, the demand for advanced solutions that promote quick healing, minimize scarring, and reduce post-operative complications is escalating. These wounds benefit from antimicrobial dressings, skin substitutes, and growth factor-infused therapies that reduce healing time. Additionally, trauma-related injuries from accidents and burns—especially in low- and middle-income regions—are contributing to increased demand in this segment.
Based on end use, the hospital segment dominated the market with the largest revenue share of 46.0% in 2024. These facilities rely heavily on a wide range of dressings, antimicrobial products, and negative pressure devices to treat wounds in a controlled clinical setting. Hospitals also act as key channels for introducing new wound care technologies and protocols, supported by in-house specialists and surgical units.
Meanwhile, home healthcare is the fastest-growing end-use segment, driven by demographic trends favoring aging-in-place, coupled with healthcare system shifts toward outpatient care models. As elderly populations increase, so does the incidence of mobility-limiting conditions that require chronic wound care at home. Furthermore, the pandemic normalized the use of teleconsultation and at-home wound assessments, which have since been adopted more broadly. Companies offering easy-to-use, long-lasting dressings and smart monitoring tools are seeing high demand in this segment.
March 2025: Smith & Nephew launched a next-generation silver-impregnated foam dressing with sustained antimicrobial release, targeting post-surgical infections and chronic wound management.
February 2025: 3M Health Care introduced a line of breathable film dressings with integrated digital sensors for moisture monitoring, aimed at high-risk ulcer patients in home settings.
January 2025: ConvaTec Group completed the acquisition of a biotech firm specializing in growth factor-based wound healing agents, strengthening its position in the biomaterials segment.
December 2024: Mölnlycke Health Care expanded its global wound care R&D center in Sweden to accelerate the development of advanced dressings and digital wound care solutions.
November 2024: Coloplast launched a pilot program across European hospitals to introduce its AI-powered wound image analysis platform, designed to assist clinicians in dressing selection and wound progression tracking.
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2034. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the advanced wound care market
By Product
By Application
By End Use
By Regional