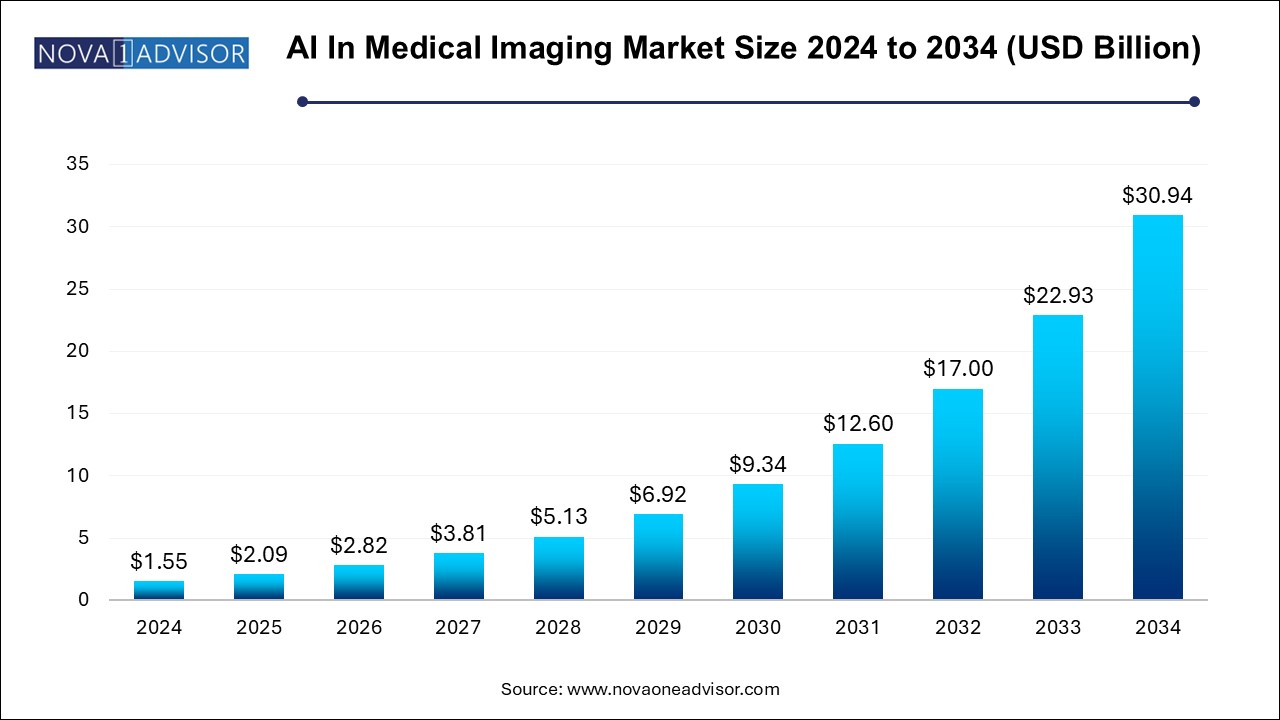
The AI in medical imaging market size was exhibited at USD 1.55 billion in 2024 and is projected to hit around USD 30.94 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 34.9% during the forecast period 2024 to 2034.
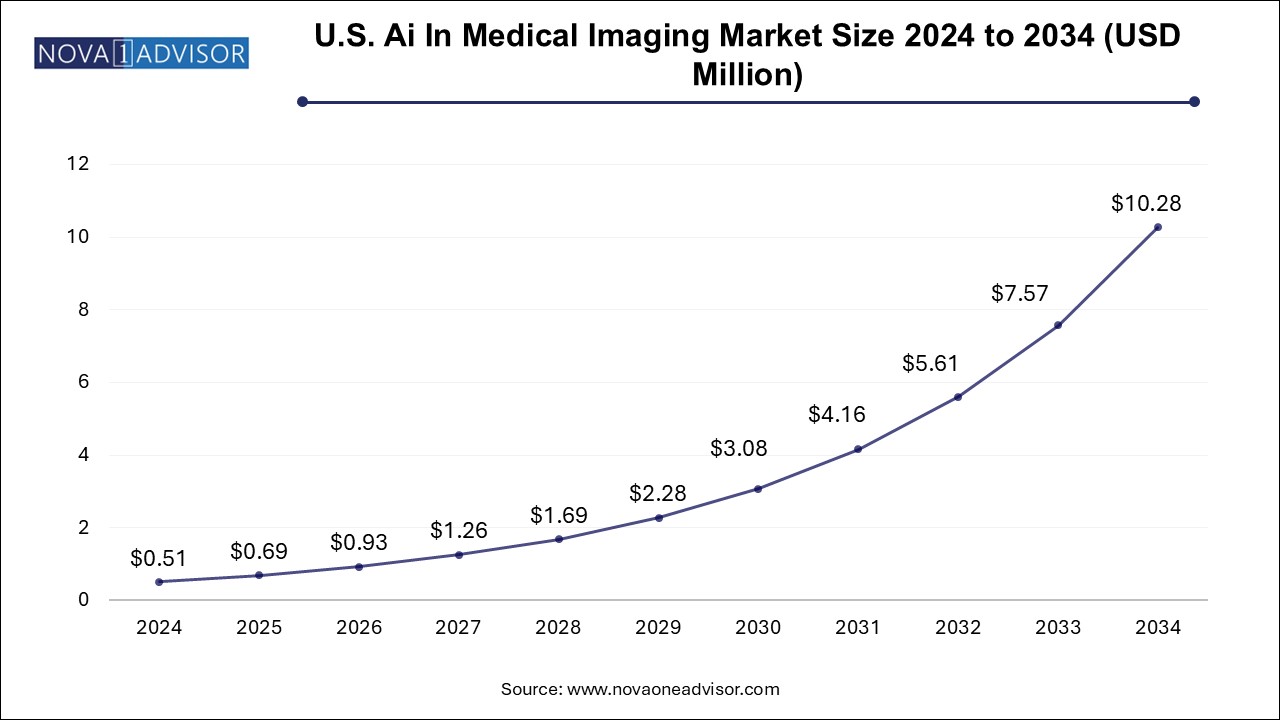
The U.S. AI in medical imaging market size is evaluated at USD 0.510 million in 2024 and is projected to be worth around USD 10.28 million by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 31.39% from 2025 to 2034.
North America is the global leader in the AI in medical imaging market, owing to a combination of advanced healthcare infrastructure, strong R&D capabilities, and supportive regulatory frameworks. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved more than 500 AI-enabled medical devices as of early 2025, many of which are imaging-focused. This regulatory clarity has allowed vendors to innovate and commercialize products rapidly.
The presence of major AI developers like IBM Watson Health, Aidoc, Zebra Medical Vision, and Arterys, as well as imaging equipment OEMs such as GE Healthcare and Siemens Healthineers with regional R&D hubs, fuels continued growth. U.S. academic medical centers and teleradiology providers are also adopting AI tools for research, education, and clinical service delivery.
Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing region, driven by increasing demand for imaging services, a rising middle class, and rapid digitization of healthcare systems. Countries like China, India, Japan, and South Korea are witnessing massive investments in AI startups, public health diagnostics, and smart hospital infrastructure. China’s “Healthy China 2030” initiative and India’s digital health mission are creating conducive environments for AI adoption in diagnostics.
AI is being used in tuberculosis screening, stroke detection, breast cancer diagnosis, and prenatal ultrasound across urban and rural areas. Domestic tech giants like Alibaba, Ping An, and Lunit are developing region-specific AI models optimized for local demographics and imaging protocols. With large population datasets, supportive governments, and cost-effective engineering talent, Asia-Pacific is expected to become a global AI hub in imaging.
The AI in medical imaging market represents one of the most transformative innovations in healthcare, where artificial intelligence is enhancing diagnostic precision, accelerating clinical workflows, and augmenting decision-making across radiology and imaging departments. Leveraging deep learning algorithms, computer vision, and natural language processing (NLP), AI is reshaping how imaging data produced from CT, MRI, X-rays, ultrasounds, and nuclear imaging modalities is processed, interpreted, and integrated into patient care.
Medical imaging data is voluminous and complex, often requiring detailed examination across hundreds of slices or scans. AI algorithms are capable of rapidly analyzing these datasets with high accuracy, highlighting abnormalities, quantifying disease progression, and even predicting future complications. In scenarios like stroke detection, pulmonary embolism, or early breast cancer, AI can identify anomalies in seconds, far faster than traditional radiologist workflows.
The increasing demand for imaging due to aging populations, chronic diseases, and expanded access to healthcare has resulted in rising workloads for radiologists globally. AI addresses this bottleneck by automating routine tasks, flagging critical findings, and facilitating triage, thereby improving throughput and reducing diagnostic errors. In parallel, AI applications in imaging are expanding into non-diagnostic areas like image acquisition enhancement, protocol standardization, and longitudinal data analytics.
With regulatory approvals accelerating, large-scale clinical validation growing, and partnerships forming between AI startups and global OEMs like GE Healthcare, Siemens Healthineers, and Philips, the AI in medical imaging market is poised for exponential growth. From research centers to rural clinics, AI-powered imaging is redefining the frontiers of precision medicine and diagnostic care.
Proliferation of FDA-Approved AI Imaging Tools: Regulatory bodies have begun approving AI tools for clinical use, validating their safety and effectiveness.
Integration with PACS and Radiology Information Systems (RIS): Seamless AI-PACS integration is streamlining adoption and improving workflow compatibility.
Growth in AI for Triage and Workflow Prioritization: AI tools are helping radiologists by flagging urgent cases, such as brain bleeds or pulmonary embolisms.
Expansion of AI in Point-of-Care Ultrasound (POCUS): AI is aiding non-radiologist clinicians in acquiring and interpreting ultrasound images at the bedside.
Advancements in Explainable AI (XAI): Efforts to make AI outputs interpretable are improving clinician trust and regulatory compliance.
Cloud-Based Imaging AI Platforms: AI-as-a-Service models allow hospitals to adopt AI without large capital investments in IT infrastructure.
Multimodal AI Combining Imaging with EMR/Lab Data: AI platforms are now synthesizing imaging with electronic health record (EHR) data for comprehensive clinical insights.
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 2.09 Billion |
| Market Size by 2034 | USD 30.94 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2024 to 2034 | CAGR of 34.9% |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2024-2034 |
| Segments Covered | Technology, Application, Modalities, End use, and Region |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) | Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Regional scope | North America; Europe; Asia Pacific; Latin America; MEA |
| Key Companies Profiled | GE HealthCare; Microsoft; Digital Diagnostics Inc.; TEMPUS; Butterfly Network, Inc.; Advanced Micro Devices, Inc.; HeartFlow, Inc.; Enlitic, Inc.; Canon; Medical Systems USA, Inc.; Viz.ai, Inc., EchoNous, Inc.; eartVista Inc.; Exo Imaging, Inc.; Nano-X Imaging Ltd. |
Deep learning dominates the AI in medical imaging market due to its superior performance in image recognition, segmentation, and classification tasks. Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) and U-Net architectures are extensively used to process high-resolution imaging data such as CT, MRI, and mammograms. These models learn from thousands of annotated cases to detect anomalies like tumors, hemorrhages, and fractures. Vendors such as Aidoc, Zebra Medical Vision, and Arterys have developed deep learning models that are now FDA-approved for clinical use across various modalities.
However, Natural Language Processing (NLP) is the fastest-growing technology segment. NLP is used to extract insights from radiology reports, clinical notes, and pathology records, often unstructured in nature. When combined with imaging, NLP enables the creation of rich patient profiles for clinical decision support. It also plays a role in auto-generating structured reports, identifying missed findings in retrospective analysis, and supporting clinical trial matching. As imaging becomes increasingly integrated with EHRs, NLP’s ability to synthesize narrative and quantitative data is becoming invaluable.
Neurology has emerged as the dominant application segment due to the prevalence of conditions like stroke, dementia, multiple sclerosis, and traumatic brain injury, which all rely heavily on MRI and CT imaging. AI tools have demonstrated impressive accuracy in identifying ischemic strokes, brain hemorrhages, gliomas, aneurysms, and other critical findings. Stroke triage algorithms have been particularly impactful, reducing door-to-needle time for thrombolysis or thrombectomy procedures. Companies like Viz.ai and RapidAI have built large neurology-focused AI product portfolios that are now being adopted in stroke centers globally.
On the other hand, cardiology is the fastest-growing application segment. AI-powered echocardiography, cardiac MRI, and CT angiography tools are gaining traction in detecting valvular heart disease, coronary artery stenosis, myocardial infarction, and left ventricular dysfunction. These tools assist cardiologists in quantifying ejection fraction, identifying perfusion defects, and planning interventions. With cardiovascular disease being the leading cause of death worldwide, early detection and risk stratification through imaging are becoming strategic priorities, and AI is at the forefront of this transformation.
X-ray imaging dominates the market in terms of volume and AI adoption, primarily because of its widespread availability, cost-effectiveness, and utility across various conditions. AI algorithms for chest X-rays are used for detecting pneumonia, tuberculosis, pleural effusion, lung nodules, rib fractures, and cardiomegaly. Chest X-rays are often the first imaging modality used in emergency and outpatient settings, making AI-assisted diagnosis highly scalable and impactful.
Meanwhile, ultrasound is the fastest-growing modality in AI applications. The expansion of point-of-care ultrasound (POCUS) and handheld devices has democratized access to sonographic imaging across emergency rooms, rural clinics, and ambulances. AI tools now assist in probe guidance, image quality assessment, and anatomical landmark identification, enabling even novice users to perform scans accurately. Applications include obstetric monitoring, cardiac assessments, trauma evaluations, and liver disease staging. Vendors such as Butterfly Network and Clarius are integrating AI directly into devices to make ultrasound a smart, autonomous diagnostic tool.
Hospitals represent the largest end-use segment, especially tertiary and academic medical centers that have the infrastructure, IT support, and budgets to adopt AI imaging platforms. These institutions are typically early adopters, using AI for a range of tasks including emergency triage, inpatient monitoring, and surgical planning. Integration with hospital PACS, EHR, and RIS systems is typically more feasible in these environments, and AI can be leveraged to reduce bottlenecks and improve patient flow.
However, diagnostic imaging centers are the fastest-growing end users of AI imaging technologies. These centers face high volumes and competition, making speed and accuracy critical differentiators. AI tools offer productivity gains through auto-triage, faster reporting, and error reduction, making them attractive to private imaging facilities. As reimbursement models evolve to favor outcomes and efficiency, imaging centers are expected to invest more in AI platforms that improve turnaround and diagnostic precision.
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2034. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the AI in medical imaging market
By Application
By Modalities
By End Use
By Regional