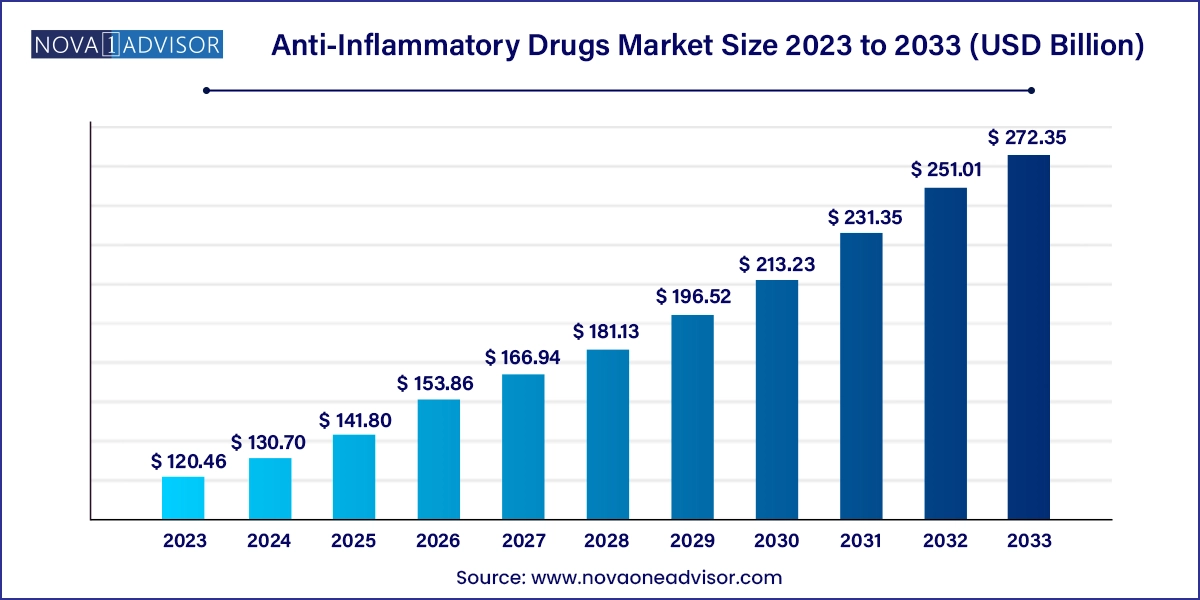
The global anti-inflammatory drugs market size was valued at USD 120.46 billion in 2023 and is anticipated to reach around USD 272.35 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 8.5% from 2024 to 2033.
The anti-inflammatory drugs market encompasses a wide array of pharmaceuticals designed to alleviate inflammation and its associated symptoms. This market is driven by several factors, including the increasing prevalence of inflammatory conditions such as arthritis, asthma, and inflammatory bowel disease worldwide. The aging population, particularly in developed regions, adds to this demand as older individuals are more susceptible to chronic inflammatory ailments. Furthermore, advancements in drug development technologies have led to the introduction of innovative anti-inflammatory therapies, expanding the market's offerings. Additionally, heightened awareness regarding the importance of early diagnosis and treatment of inflammatory diseases among both patients and healthcare providers is fostering market growth. With a continuous influx of research and development efforts aimed at addressing inflammation-related disorders, the anti-inflammatory drugs market is poised for further expansion in the coming years.
The global Anti-inflammatory Drugs Market represents a vital segment within the pharmaceutical industry, driven by the growing burden of inflammatory disorders and a rising geriatric population. Inflammatory diseases such as arthritis, asthma, inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) continue to pose a significant public health challenge. Anti-inflammatory drugs aim to reduce inflammation, alleviate pain, and restore normal physiological functions in patients. The therapeutic efficacy of these drugs in both acute and chronic inflammatory conditions has made them essential in both hospital and outpatient settings.
In 2024, the market is characterized by increasing adoption of biologic therapies, rising demand for personalized medicine, and a surge in investment in research and development activities aimed at innovating new classes of anti-inflammatory agents. The market is largely composed of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), corticosteroids, and anti-inflammatory biologics, with biologics gaining substantial attention for their targeted mechanisms and lower side effect profiles.
The rising global prevalence of autoimmune disorders is a key factor driving demand. According to the World Health Organization, autoimmune diseases affect approximately 5–8% of the population globally, a figure that continues to increase. The growing inclination towards over-the-counter (OTC) medications for managing mild inflammatory symptoms and the expansion of online pharmacies are reshaping how patients access these medications. Furthermore, lifestyle-related inflammatory diseases such as obesity-induced inflammation and metabolic syndromes are gaining prominence, further expanding the scope of the market.
Rising Popularity of Anti-inflammatory Biologics: Biologics, including monoclonal antibodies and cytokine inhibitors, are increasingly used to treat autoimmune and inflammatory diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis and Crohn’s disease.
Expansion of OTC NSAIDs and Corticosteroids: Increased self-medication and consumer preference for readily available drugs are boosting the growth of OTC segments, especially in developed nations.
Growing Use of Digital Health Platforms: The emergence of digital pharmacies and mobile apps for prescription renewals is simplifying access to anti-inflammatory drugs and improving patient adherence.
Pipeline Expansion and Regulatory Approvals: Major pharmaceutical companies are investing heavily in R&D for next-generation anti-inflammatory drugs, with multiple new drugs receiving FDA and EMA approvals in recent years.
Combination Therapies and Personalized Treatment Regimens: A focus on tailoring treatments based on individual inflammatory responses is leading to combination therapies involving biologics, corticosteroids, and NSAIDs.
Geographical Shift in Market Growth: While North America continues to dominate, Asia-Pacific is witnessing the fastest growth due to rising healthcare infrastructure and increasing disease awareness.
Chronic Disease Management Initiatives: Government health programs in multiple countries are incorporating anti-inflammatory therapies in their public health management strategies.
| Report Attribute | Details |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 130.70 Billion |
| Market Size by 2033 | USD 272.35 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2024 to 2033 | CAGR of 8.5% |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Forecast Period | 2024 to 2033 |
| Segments Covered | Drug Class, Treatment, Route of Administration, Sales Channel , Distribution channel and Region |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) | Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Report Coverage | Revenue forecast, company ranking, competitive landscape, growth factors, and trends |
| Key Companies Profiled | Pfizer, Inc., GlaxoSmithKline plc, Johnson & Johnson Services Inc., Merck & Company, Inc., Novartis AG, Amgen, Inc., AstraZeneca plc, Eli Lily and Company, AbbVie Inc., F. Hoffmann-La Roche AG, Bristol Myers Squibb Company, Biogen Inc., Sun Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd, Mylan, Inc., Aurobindo Pharma Limited, and Dr. Reddy’s Laboratories among others. |
One of the strongest drivers in the anti-inflammatory drugs market is the increasing prevalence of chronic inflammatory diseases, especially among the aging population. Diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, asthma, ulcerative colitis, and psoriasis are becoming more common as life expectancy increases. According to the CDC, over 54 million adults in the U.S. alone suffer from arthritis, a number expected to grow with the aging baby boomer demographic. Chronic inflammation is also linked to a range of lifestyle-related conditions such as type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and certain cancers, leading to increased demand for long-term anti-inflammatory treatment. This expanding patient base places significant demand on healthcare systems and propels the adoption of both prescription and OTC anti-inflammatory medications.
Despite robust demand, the market is constrained by the side effect profiles of many anti-inflammatory medications. NSAIDs are widely known for their potential to cause gastrointestinal bleeding, ulcers, and cardiovascular risks when used long-term. Corticosteroids, while highly effective, can cause osteoporosis, weight gain, diabetes, and mood disorders. Even biologics, despite being more targeted, can suppress the immune system and lead to an increased risk of infections. These safety concerns necessitate rigorous patient monitoring, reduce medication adherence, and deter physicians from long-term prescriptions in certain demographics, particularly the elderly and immunocompromised. Regulatory warnings and drug recalls in the past have further heightened scrutiny and hesitancy regarding certain drug classes.
A major opportunity in the market is the emergence of biosimilars to high-cost anti-inflammatory biologics. Biologics such as adalimumab (Humira) and etanercept (Enbrel) dominate the market but are prohibitively expensive for many patients. The expiration of patents and subsequent regulatory pathways in regions like the U.S., Europe, and Japan have allowed pharmaceutical companies to develop and commercialize cost-effective biosimilars. These alternatives maintain comparable safety and efficacy to their originators and can significantly improve access to biologic therapies in lower-income regions and among cost-sensitive populations. The growing adoption of biosimilars is expected to reduce healthcare costs and catalyze growth in emerging markets.
Anti-inflammatory biologics dominated the market due to their superior efficacy in managing chronic and autoimmune inflammatory conditions. Biologics target specific components of the immune response, such as tumor necrosis factor (TNF) or interleukins, thereby offering better symptom control with fewer systemic effects. Drugs like adalimumab, infliximab, and ustekinumab are widely prescribed for conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis, and Crohn’s disease. The rise in FDA approvals and biosimilar launches has further strengthened this segment. These treatments are often prescribed for patients who do not respond well to NSAIDs or corticosteroids.
On the other hand, NSAIDs represent the fastest-growing drug class due to their accessibility, affordability, and rapid relief of symptoms. NSAIDs like ibuprofen, naproxen, and diclofenac are available both OTC and via prescription, making them highly versatile. Their widespread use in managing pain, menstrual discomfort, fever, and minor injuries contributes to the expanding consumer base. The increasing trend of self-medication, particularly in developing countries, along with the proliferation of e-commerce platforms, has accelerated the growth trajectory of this segment.
Arthritis remains the dominant treatment segment, accounting for a large proportion of global anti-inflammatory drug use. The high prevalence of both rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis, especially in aging populations, ensures consistent demand. Biologics and NSAIDs are routinely used in combination to manage inflammation, swelling, and joint pain. The introduction of newer biologics tailored to specific patient profiles is also transforming arthritis treatment paradigms. Additionally, awareness campaigns by patient advocacy groups and access to early diagnosis have significantly contributed to the prominence of this segment.
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is the fastest-growing treatment area, propelled by increasing diagnostic rates and better disease management protocols. IBD, encompassing Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, often requires lifelong treatment. Anti-TNF agents and interleukin inhibitors have become mainstays in moderate to severe IBD management. Pharmaceutical companies are developing targeted therapies that minimize systemic exposure and adverse effects. As awareness improves and access to advanced therapies expands in countries like China and India, the IBD treatment segment is poised for rapid growth.
Oral administration dominates the market owing to its ease, patient compliance, and broad availability. NSAIDs and corticosteroids are primarily consumed in oral forms for acute and chronic conditions. The convenience of dosing without clinical supervision makes oral formulations the first-line option for many patients. Additionally, pharmaceutical innovations such as extended-release tablets and gastro-resistant coatings enhance tolerability and patient adherence, further consolidating the dominance of this segment.
Injection-based therapies are growing the fastest, especially due to the uptake of biologics, which are typically administered subcutaneously or intravenously. Biologics used for rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis, and IBD often require regular injections for optimal efficacy. The trend toward home-based injection therapies, auto-injectors, and self-administration pens is simplifying usage and driving adoption. Healthcare providers increasingly prescribe injectables for targeted delivery and rapid onset, making it a pivotal growth driver.
Hospital pharmacies remain the largest distribution channel, primarily due to their role in administering high-cost, biologic therapies and managing acute inflammation cases requiring inpatient care. Hospitals often stock specialized drugs not commonly available in retail pharmacies and serve as major centers for initiating treatment for conditions like multiple sclerosis or severe autoimmune diseases. Regulatory requirements and insurance coverage also guide many patients to hospital settings for these treatments.
Online pharmacies are experiencing the fastest growth, spurred by digital transformation, increased smartphone penetration, and patient preference for home delivery. Countries like the U.S., China, and India are witnessing a surge in online medicine purchases, especially for OTC NSAIDs and repeat prescriptions. The COVID-19 pandemic has further accelerated the adoption of online channels. Integration of e-prescriptions, telemedicine consultations, and AI-driven recommendations is redefining how patients access anti-inflammatory drugs.
Prescription-based sales dominate the market, particularly in the biologics and corticosteroids segments, where physician supervision is essential. Many anti-inflammatory treatments, especially for chronic or complex diseases, require detailed evaluation, monitoring, and dosage titration that cannot be accomplished through OTC channels. Prescription medications also receive broader insurance reimbursements, influencing patient and provider preferences.
Over-the-counter (OTC) drugs are the fastest-growing segment, driven by expanding consumer self-care trends and increasing regulatory approvals for NSAIDs and topical corticosteroids. OTC accessibility in supermarkets, convenience stores, and online platforms enhances affordability and reach. Many patients with mild symptoms prefer OTC solutions to avoid clinic visits, thus contributing significantly to market growth.
North America dominates the global anti-inflammatory drugs market, accounting for the largest market share due to a well-established healthcare infrastructure, high disease awareness, and access to advanced biologics. The U.S. contributes significantly, with substantial investments in R&D, favorable insurance coverage, and robust regulatory frameworks supporting innovation. The high prevalence of chronic diseases such as arthritis and COPD, coupled with a large aging population, fuels market demand. Additionally, the U.S. has witnessed strong adoption of biosimilars since the Biologics Price Competition and Innovation Act was implemented, improving affordability and access.
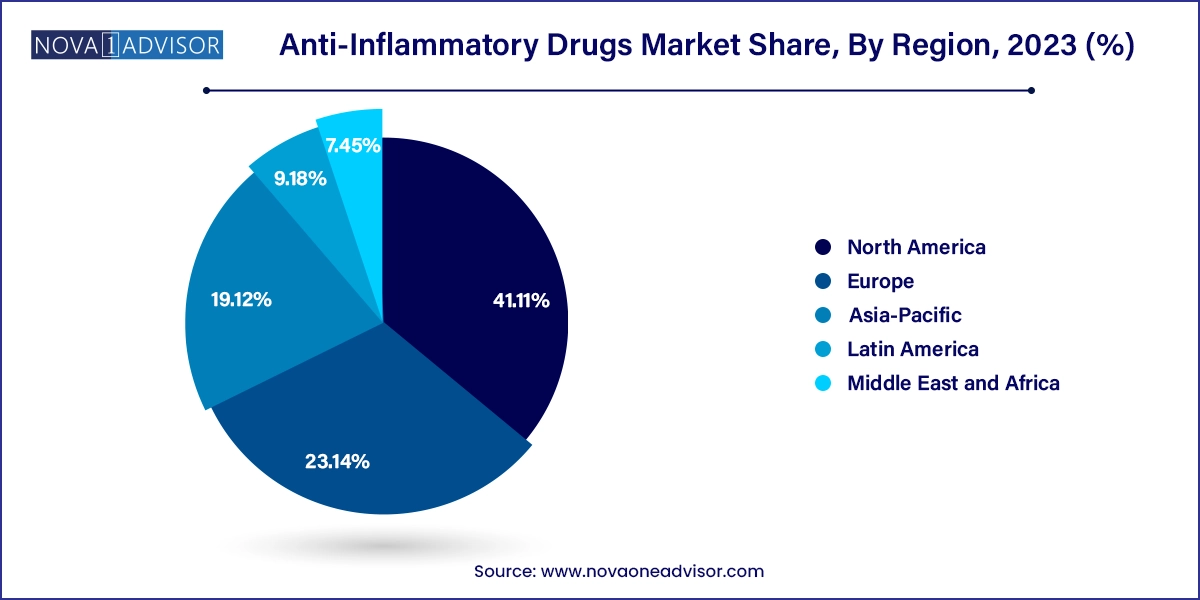
Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing regional market, driven by increasing healthcare spending, rapid urbanization, and expanding healthcare coverage in countries like China, India, and South Korea. Rising awareness of inflammatory diseases and improved diagnostic capabilities are prompting early treatment interventions. Governments in these regions are also promoting access to essential medicines and fostering pharmaceutical manufacturing hubs. The surge in e-commerce and online pharmacy adoption further accelerates the market's expansion in Asia-Pacific.
Pfizer and Samsung Bioepis (January 2025) announced FDA approval of SB17, a biosimilar to Stelara (ustekinumab), expanding biologic access for IBD and psoriasis patients in the U.S.
AbbVie (March 2025) launched a new subcutaneous formulation of Skyrizi (risankizumab) to enhance patient convenience for plaque psoriasis and Crohn’s disease treatment.
Johnson & Johnson (February 2025) invested $500 million into expanding its immunology drug pipeline, focusing on next-generation anti-inflammatory biologics.
Novartis (November 2024) received EMA approval for Cosentyx as a first-line treatment for axial spondyloarthritis, reflecting ongoing expansion into new inflammatory indications.
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2033. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the Anti-inflammatory Drugs market.
By Drug Class
By Treatment
By Route of Administration
By Distribution Channel
By Sales Channel
By Region