The global antidiabetics market size was valued at USD 82.85 billion in 2023 and is anticipated to reach around USD 263.12 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 12.25% from 2024 to 2033.
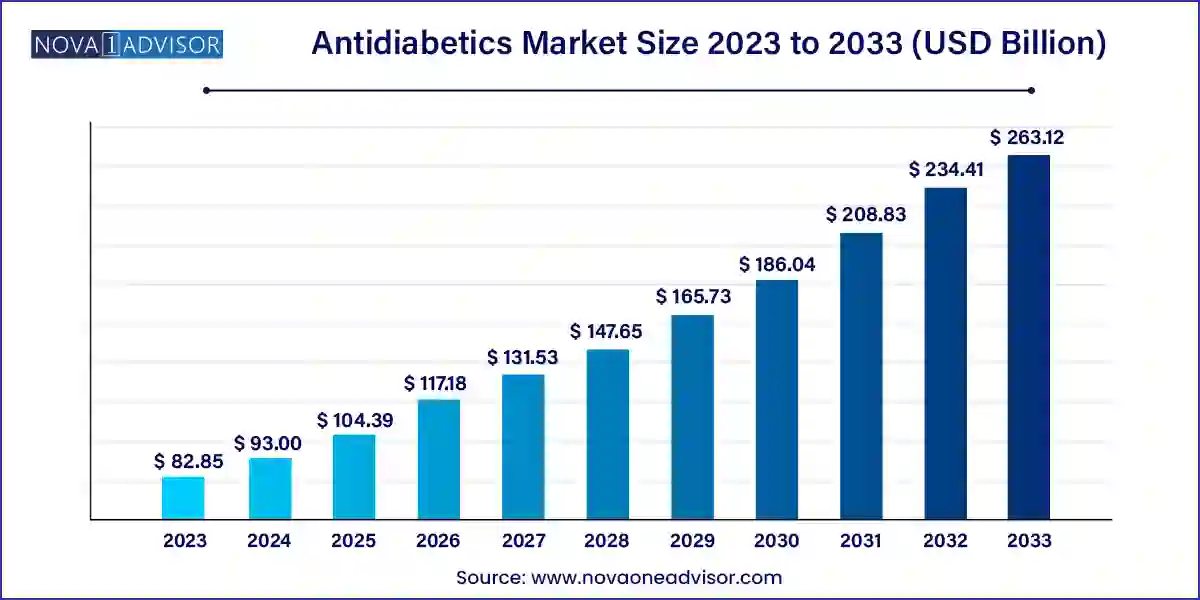
The U.S. antidiabetics market size was valued at USD 30.92 billion in 2023 and is projected to surpass around USD 98.37 billion by 2033, registering a CAGR of 12.27% over the forecast period of 2024 to 2033.
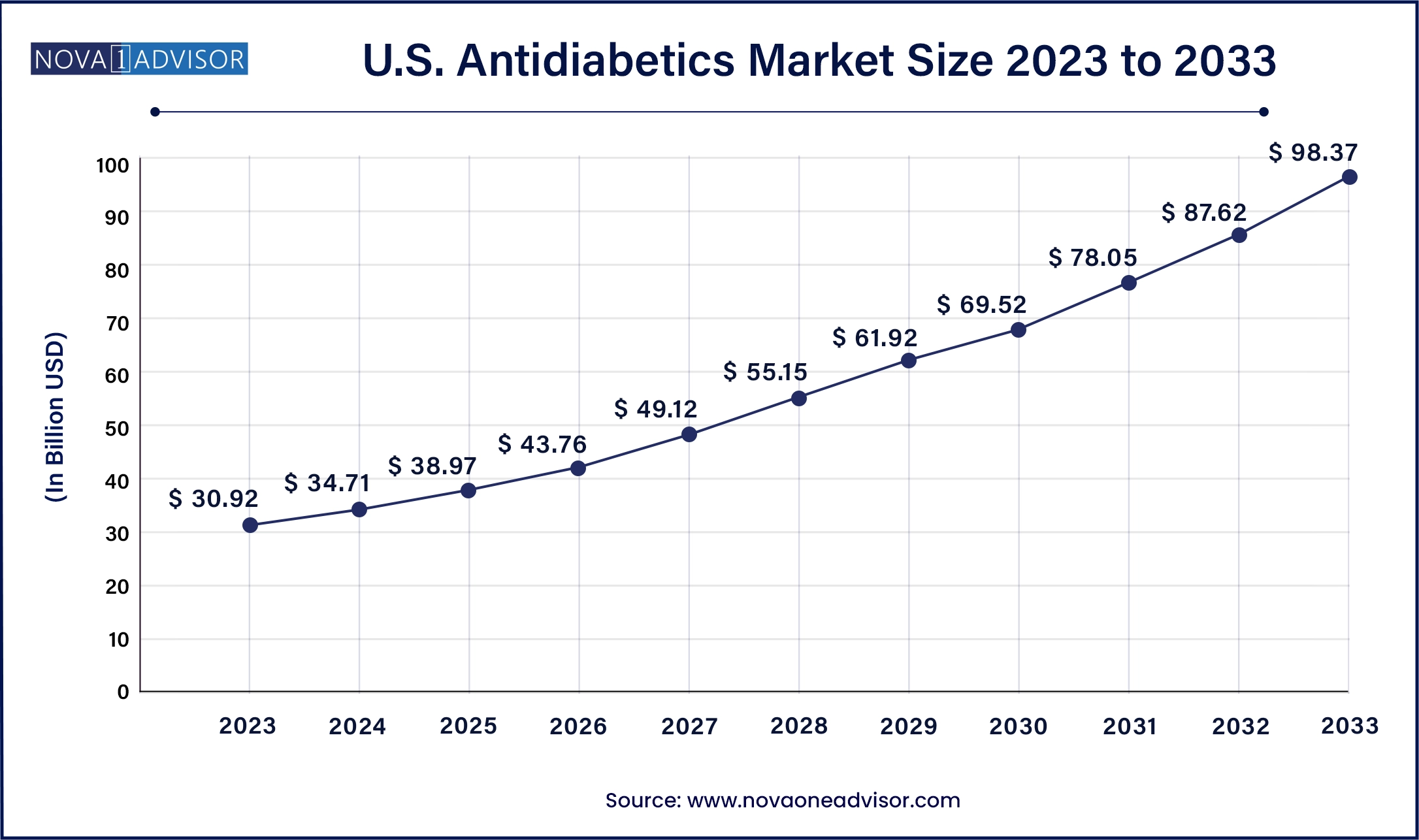
North America dominated the antidiabetics market, holding the largest share due to a high prevalence of diabetes, strong reimbursement frameworks, and the presence of major pharmaceutical players. The U.S., in particular, has one of the highest spending rates on diabetes care, driven by early diagnosis, aggressive management, and access to cutting-edge therapies. The widespread adoption of continuous glucose monitoring systems, smart insulin delivery devices, and health insurance coverage for new drug classes contributes to the region’s robust market performance. Moreover, the region is a hub for clinical trials, enabling faster drug approvals and commercial launches.
Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing region, projected to witness exponential growth over the next decade. The rise in urbanization, westernized diets, and genetic predisposition among populations in China, India, and Southeast Asia are contributing to a surge in diabetes cases. This has led to increased awareness campaigns, government health screenings, and an expansion of public-private healthcare collaborations. Furthermore, regional pharmaceutical companies are investing heavily in biosimilars and low-cost generics to cater to price-sensitive demographics. As access to diagnosis and treatment improves, Asia-Pacific is set to become a pivotal market in the global antidiabetics landscape.
The global antidiabetics market has emerged as a dynamic segment of the healthcare industry, driven by a sharp rise in the prevalence of diabetes across the globe. Diabetes mellitus, a chronic metabolic disorder characterized by elevated blood glucose levels, has become a major public health concern, with the International Diabetes Federation (IDF) estimating over 530 million people affected worldwide as of 2023. Consequently, the demand for innovative, effective, and patient-centric treatment options is intensifying, creating substantial growth opportunities in the antidiabetics market.
Antidiabetics refer to the wide range of pharmacological agents used to manage blood sugar levels in diabetic patients. These include insulin formulations, oral hypoglycemics, and novel therapeutic agents such as GLP-1 receptor agonists and SGLT2 inhibitors. The industry has witnessed a transition from conventional therapies to next-generation biologics and combination regimens, further propelling the market growth. In addition to pharmaceutical advancements, government initiatives, rising healthcare expenditures, and growing awareness campaigns are supporting the expansion of this market.
The market’s scope encompasses various drug classes, administration routes, diabetes types, and distribution channels. The competition is fierce, with both global pharmaceutical giants and emerging biotech firms vying for market share. From insulin innovation to digital diabetes management solutions, the industry is also being shaped by the convergence of health tech and precision medicine. Collectively, these factors contribute to a multi-billion-dollar market that is poised for sustained growth in the coming decade.
Rising adoption of biosimilar insulin products to reduce treatment costs and enhance accessibility.
Growing preference for once-weekly injectable GLP-1 receptor agonists, improving patient adherence.
Increased R&D investments in oral insulin delivery systems, targeting needle-free administration.
Integration of digital health tools and continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) with antidiabetic therapies.
Surging demand for combination drugs, especially SGLT2 inhibitors and DPP-4 inhibitors in fixed-dose combinations.
Personalized medicine and pharmacogenomics applications in diabetes treatment planning.
Growing focus on weight management as part of diabetes care, promoting the use of dual-purpose drugs.
Strategic mergers and acquisitions among pharmaceutical companies to enhance product pipelines.
Emergence of plant-based and natural antidiabetic formulations, driven by consumer preference.
Increased regulatory approvals of novel drug molecules and fast-tracked clinical trials.
| Report Attribute | Details |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 93.00 Billion |
| Market Size by 2033 | USD 263.12 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2024 to 2033 | CAGR of 12.25% |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Forecast Period | 2024 to 2033 |
| Segments Covered | Drug class, diabetics type, route of administration, distribution channel, region |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) | Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Report Coverage | Revenue forecast, company ranking, competitive landscape, growth factors, and trends |
| Key Companies Profiled | AstraZeneca plc; Bayer AG; Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited; Eli Lilly and Company; Boehringer Ingelheim; Bristol-Myers Squibb; Pfizer, Inc.; Johnson & Johnson Services Inc.; Merck & Co. Inc ; Novartis AG |
One of the most significant drivers of the antidiabetics market is the escalating prevalence of type 2 diabetes, largely attributed to sedentary lifestyles, obesity, and dietary imbalances. As urbanization spreads and physical inactivity rises, more individuals—especially in low- and middle-income countries—are being diagnosed with diabetes at an earlier age. According to the World Health Organization, more than 90% of global diabetes cases are type 2. This form of diabetes, while initially manageable through lifestyle changes, often progresses to require pharmacological intervention. The expanding patient pool presents a consistent and growing demand for antidiabetic medications, particularly oral agents and insulin therapies.
Despite therapeutic advancements, the high cost of insulin remains a significant market restraint, particularly in developing nations where healthcare resources are limited. Insulin affordability is a global issue; in the United States, for instance, patients have faced price increases of over 100% in the last decade. Although biosimilars offer a partial solution, barriers such as patent protection, limited local production, and regulatory hurdles delay their widespread adoption. This price sensitivity impacts treatment adherence and leads to long-term complications, creating a critical health equity concern. Governments and health organizations continue to pressure manufacturers to address these pricing discrepancies.
An exciting growth opportunity in the antidiabetics market lies in the development of oral insulin and other non-invasive delivery systems. The conventional subcutaneous administration of insulin presents challenges in terms of patient compliance, especially among needle-phobic individuals. Recent innovations in drug delivery technologies are making oral, buccal, and transdermal routes viable for insulin and peptide-based therapies. Companies like Oramed Pharmaceuticals are pioneering oral insulin capsules, currently undergoing late-stage clinical trials. If successful, these novel modalities could revolutionize insulin therapy, enhance patient quality of life, and tap into a previously underserved segment of the diabetic population.
Insulin dominated the antidiabetics market, accounting for the highest share due to its critical role in managing both type 1 and advanced type 2 diabetes. Within insulin, long-acting variants like insulin glargine are extensively used to maintain basal insulin levels, ensuring steady glycemic control. Fast-acting insulin, such as insulin lispro and aspart, is also gaining popularity, especially among patients requiring tight postprandial glucose regulation. Innovations in insulin analogs and the introduction of smart insulin pens are further contributing to the segment's growth. Moreover, the uptake of premix insulin, particularly in countries like India and China, reflects rising demand for simplified treatment regimens.
GLP-1 receptor agonists are the fastest-growing segment in the antidiabetics drug class, driven by their dual benefit of glycemic control and weight reduction. Drugs like semaglutide (Ozempic and Rybelsus) have seen meteoric growth due to their once-weekly administration and proven cardiovascular benefits. These agents are increasingly favored in type 2 diabetes patients with obesity and heart conditions. Similarly, SGLT2 inhibitors such as dapagliflozin and empagliflozin are expanding their footprint beyond diabetes management into heart failure and chronic kidney disease, thanks to favorable outcomes from large-scale clinical trials.
Type 2 diabetes held the majority market share, fueled by its higher prevalence and the chronic nature of disease progression. Unlike type 1 diabetes, which typically manifests in childhood and requires immediate insulin therapy, type 2 diabetes offers a broader therapeutic landscape that includes oral antidiabetics, injectables, and lifestyle management. The variety of treatment options has led to a robust market presence for multiple drug classes. The rise of combination therapies and early pharmacological intervention has also broadened market opportunities.
Type 1 diabetes is a relatively smaller but steadily growing segment, owing to advancements in insulin pump technologies, continuous glucose monitoring (CGM), and artificial pancreas systems. Innovations such as ultra-rapid insulin formulations and closed-loop insulin delivery have improved disease management and quality of life for type 1 diabetics. Furthermore, ongoing research into pancreatic islet transplantation and immunotherapy-based cures continues to attract investor interest in this segment.
Subcutaneous administration dominated the market, primarily due to its long-standing role in insulin therapy. Subcutaneous injections are used for both basal and bolus insulin regimens and have been optimized through pen devices and pumps. The development of ultra-thin needles and automated injectors has also made this route more acceptable to patients. Furthermore, most GLP-1 receptor agonists are administered subcutaneously, contributing to the segment's continued dominance.
Oral administration is the fastest-growing segment, particularly with the rise of SGLT2 inhibitors and DPP-4 inhibitors that offer ease of use and high patient compliance. The success of oral semaglutide is indicative of a larger shift toward oral biologics. With the convenience and non-invasive nature of oral therapy, this route is projected to see exponential growth, especially in markets with aging populations and limited healthcare infrastructure.
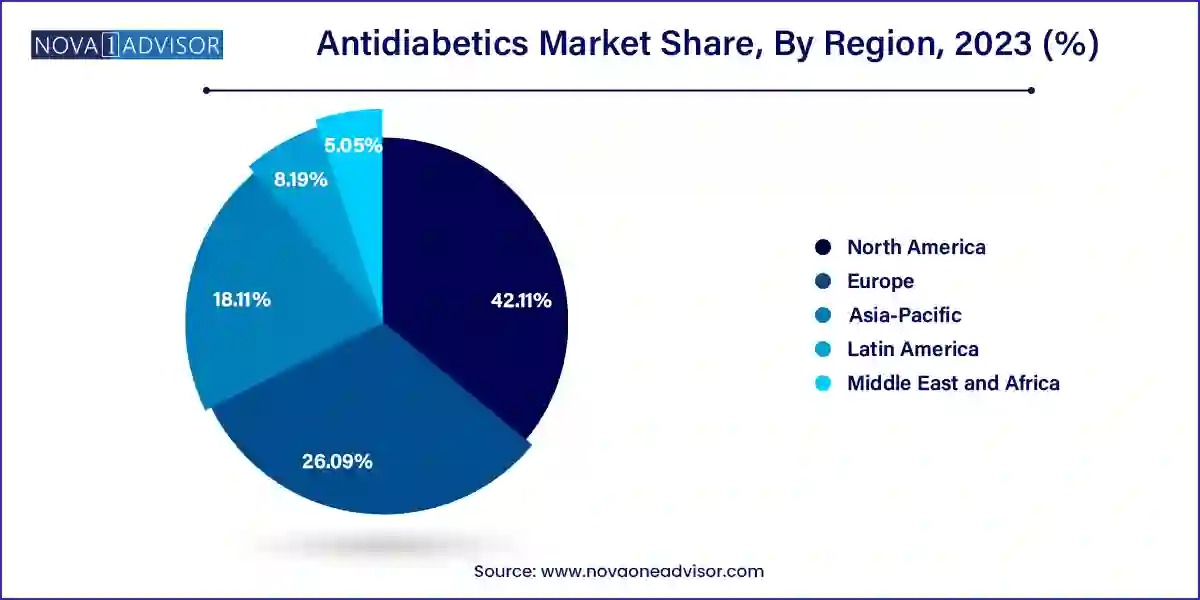
Retail pharmacies led the distribution channel segment, thanks to their extensive reach, convenience, and ability to fulfill recurring prescriptions. In many developing countries, retail outlets serve as the primary access point for diabetes medications, especially oral agents. Additionally, retail chains are increasingly partnering with pharmaceutical companies for better inventory management and patient education programs.
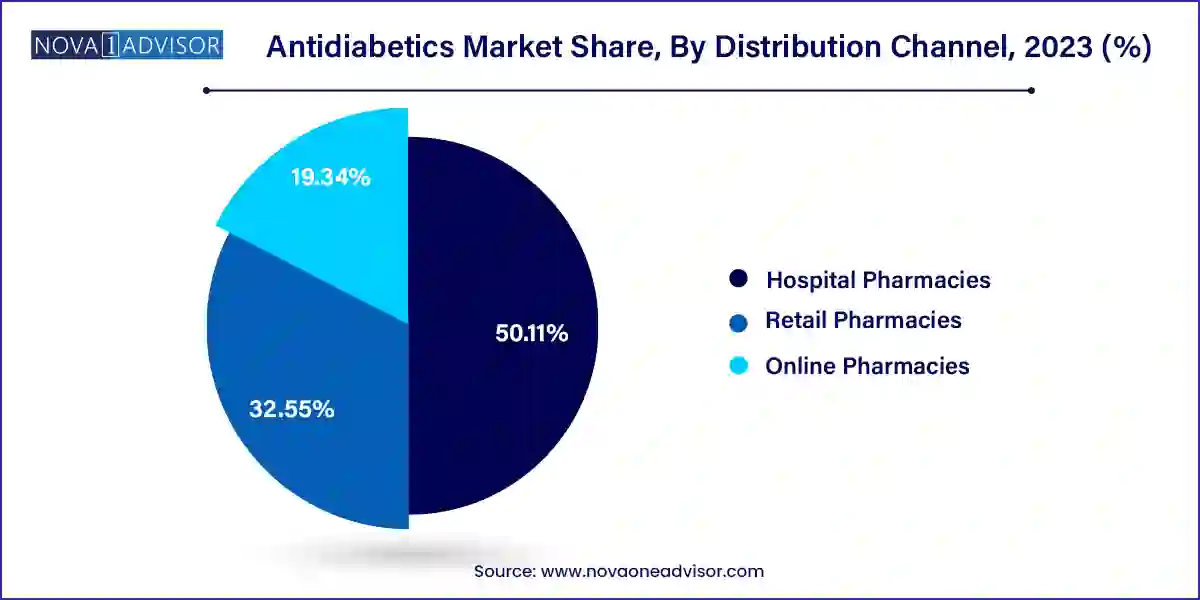
Online pharmacies are emerging as the fastest-growing channel, spurred by the digital transformation of healthcare and the COVID-19 pandemic. Platforms such as Amazon Pharmacy and local e-commerce portals now offer doorstep delivery of prescription drugs, digital consultations, and refill reminders. Their popularity is especially high among younger, tech-savvy populations and in urban areas with dense internet penetration.
March 2025: Novo Nordisk announced regulatory approval in the EU for its once-weekly basal insulin icodec, marking a significant advancement in long-acting insulin therapy.
February 2025: Eli Lilly completed the acquisition of Versanis Bio, a biotech firm focusing on obesity-linked metabolic disorders, reinforcing Lilly's dual-focus approach in diabetes and weight management.
January 2025: Sanofi launched an AI-based platform for personalized diabetes treatment planning in partnership with digital health startup Glooko, integrating wearable data with medication recommendations.
December 2024: Pfizer initiated Phase III trials for a novel oral GLP-1 receptor agonist targeting type 2 diabetes patients with concurrent cardiovascular conditions.
October 2024: AstraZeneca’s SGLT2 inhibitor, Forxiga (dapagliflozin), received FDA approval for expanded use in chronic kidney disease patients, highlighting the therapeutic versatility of the drug class.
The following are the leading companies in the antidiabetics market. These companies collectively hold the largest market share and dictate industry trends.
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2033. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the Antidiabetics market.
By Drug Class
By Diabetes Type
By Route of administration
By Distribution Channel
By Region