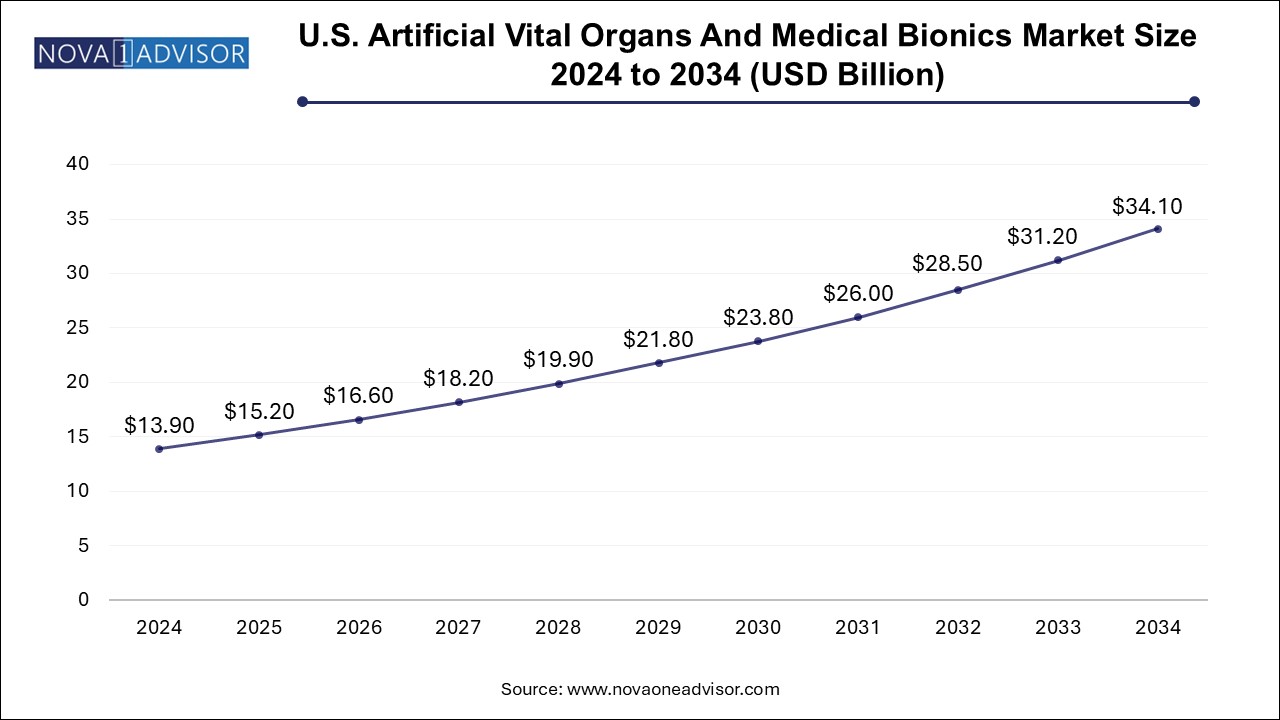
The artificial vital organs and medical bionics market size was exhibited at USD 41.13 billion in 2024 and is projected to hit around USD 101.01 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 9.4% during the forecast period 2025 to 2034.
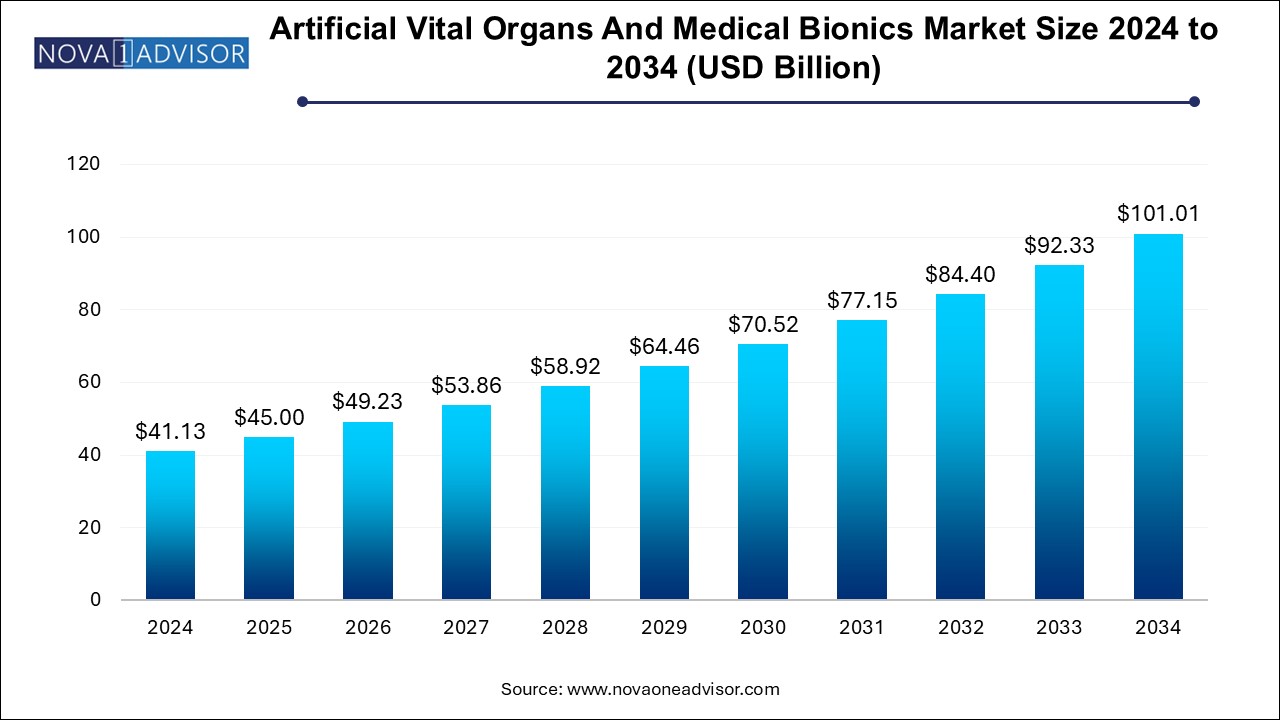
The U.S. artificial vital organs and medical bionics market size is evaluated at USD 13.9 billion in 2024 and is projected to be worth around USD 34.1 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 8.5% from 2025 to 2034.
North America dominated the artificial vital organs and medical bionics market in 2024. The region’s dominance can be attributed to its advanced healthcare infrastructure, high healthcare expenditure, and favorable regulatory frameworks. The U.S. leads the charge with significant investments in R&D and a strong presence of key players like Medtronic, Boston Scientific, and Zimmer Biomet. Government support through programs such as Medicare, coupled with private insurance, enables wider adoption of high-cost devices. Additionally, the region hosts leading universities and hospitals conducting pioneering research in artificial organ transplantation and bionic integration.
Asia Pacific is the fastest-growing region in this market. Factors such as a large aging population, rising incidence of chronic diseases, and healthcare reforms are driving growth. Countries like China, India, and Japan are focusing on manufacturing and innovation hubs. For instance, Japan has a robust rehabilitation technology sector, and India is seeing a surge in medical startups offering affordable bionic limbs. Government initiatives like "Make in India" and China’s "Healthy China 2030" are facilitating market expansion through incentives, infrastructure development, and skill training. Additionally, partnerships with global firms are bringing advanced technologies to these regions at lower costs.
The global Artificial Vital Organs and Medical Bionics Market represents a transformative intersection of bioengineering, regenerative medicine, and medical device innovation. This market is poised to revolutionize the healthcare sector by offering life-sustaining or function-restoring devices for patients suffering from organ failure, traumatic injuries, or congenital disabilities. Artificial organs such as hearts, kidneys, and lungs mimic the biological functions of their natural counterparts, while bionic systems—including exoskeletons, bionic limbs, and auditory implants—restore mobility, hearing, and vision.
The market is rapidly expanding due to rising chronic disease prevalence, increasing geriatric populations, and growing demand for organ transplantation. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), cardiovascular diseases are the leading cause of death globally, while end-stage renal disease continues to grow, escalating the need for both artificial and bionic organ systems. Traditional organ transplant waiting lists are often plagued by long delays and donor shortages. In this context, artificial organs and medical bionics offer a lifeline, providing patients with timely and often less invasive solutions.
Innovations such as 3D-printed organs, brain-computer interfaces (BCIs), and AI-powered exoskeletons are setting new standards. Public and private investments in biotech startups, academic research collaborations, and rising FDA approvals are fueling the market. As accessibility improves and prices gradually decline, emerging economies are also beginning to benefit from these technological marvels.
Rise of Personalized and 3D-Printed Organs: Technological breakthroughs in 3D bioprinting are enabling the creation of personalized artificial organs, particularly in kidney and liver segments.
Integration of AI and IoT in Bionics: Smart bionics powered by AI are now capable of real-time feedback and adaptive motion, dramatically improving patient quality of life.
Miniaturization and Portability: Devices like portable dialysis machines and compact artificial hearts are improving mobility and usability for patients.
Brain-Machine Interfaces (BMIs): Brain bionics are seeing significant progress, enabling paralyzed individuals to control devices using neural signals.
Increased Regulatory Approvals: Government bodies such as the FDA and EMA are accelerating the approval pathways for life-saving devices in light of urgent clinical needs.
Focus on Pediatric Applications: Companies are designing smaller, adaptable bionic limbs and heart devices suitable for children, widening the consumer base.
Global Shortage of Organ Donors: The ever-widening gap between demand and availability of donor organs is pushing healthcare systems to adopt artificial alternatives.
Military and Rehabilitation Use: Exoskeletons and bionic limbs are increasingly being used in defense sectors and for post-trauma rehabilitation of soldiers and accident victims.
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 45.0 Billion |
| Market Size by 2034 | USD 101.01 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2025 to 2034 | CAGR of 9.4% |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025-2034 |
| Segments Covered | Artificial Organs, Bionics, Region |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) | Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Regional scope | North America; Europe; Asia Pacific; Latin America; MEA |
| Key Companies Profiled | Medtronic, Inc.; LifeNet Health; Terumo Corporation; Ekso Bionics Holdings, Inc.; Nano Retina Ltd.; Edwards Lifesciences Corporation; InnoScot Health Ltd.; Ottobock SE & Co. KGaA; Orthofix Medical Inc. |
One of the strongest drivers propelling the artificial organs and medical bionics market is the rising global burden of chronic diseases leading to organ failure. Conditions like diabetes, hypertension, chronic kidney disease (CKD), and cardiovascular disorders are growing at an alarming rate. The International Diabetes Federation estimates that over 530 million people were living with diabetes in 2023, with projections reaching over 640 million by 2030. This rise is directly linked to increased cases of kidney failure, necessitating dialysis or artificial kidneys.
Furthermore, the number of individuals requiring organ transplants far exceeds the number of available donors. In the U.S. alone, more than 100,000 people await organ transplants, but only around 40,000 procedures are performed annually. Artificial organs such as total artificial hearts or implantable kidney systems are filling this void by offering temporary or long-term solutions. This driver, backed by global healthcare initiatives and rising investments, continues to stimulate R&D and commercialization.
Despite technological advances, the market faces a significant restraint in the form of high cost and limited accessibility, especially in low- and middle-income countries. Artificial organs and advanced bionics are priced in tens or hundreds of thousands of dollars. For instance, a total artificial heart can cost upwards of $125,000, excluding surgery and hospitalization charges. Similarly, high-end robotic bionic limbs can cost between $20,000 to $100,000 depending on the complexity.
These costs often make such solutions unaffordable to vast segments of the global population. Reimbursement policies are either limited or non-existent in many countries. Additionally, the technical expertise required to implant and manage these systems may not be available outside tertiary care hospitals. This combination of cost and infrastructure limitations hinders broader adoption, creating disparities in healthcare access.
A promising opportunity lies in cross-industry collaborations and the expansion into emerging markets. Tech giants such as Google and Tesla have shown interest in neural interfaces and wearable bionics, respectively. Partnerships between medical device manufacturers and AI software developers are enabling smart bionic limbs that learn user movement patterns and improve over time. For instance, companies like Össur and Coapt are integrating machine learning into prosthetics to personalize motor control.
Simultaneously, emerging economies such as India, Brazil, and Southeast Asian nations are investing heavily in healthcare infrastructure and innovation hubs. Government support, such as India’s National Health Mission or Brazil’s Unified Health System (SUS), is opening doors for affordable bionic solutions and modular artificial organs. Manufacturers who localize production and adapt to regional needs are likely to experience rapid growth.
Kidney was the dominating artificial organ segment in 2024. This dominance is attributed to the soaring prevalence of end-stage renal disease (ESRD) and the limitations of dialysis treatment. According to the Global Burden of Disease Study, chronic kidney disease ranks as the 12th leading cause of death worldwide. The introduction of wearable and implantable artificial kidneys is reshaping the treatment paradigm. Companies like AWAK Technologies are pioneering portable dialysis machines that improve quality of life and reduce dependence on clinical settings. The high demand for long-term renal replacement therapy is expected to maintain this segment’s lead.
The liver segment is emerging as the fastest-growing artificial organ category. Acute liver failure and chronic liver diseases, such as cirrhosis and hepatitis C, are rising due to poor lifestyle habits, alcohol consumption, and viral infections. Current treatment options are limited to organ transplants, which are expensive and donor-dependent. Artificial liver support systems such as bio-artificial livers are being developed using hepatocytes and bioreactors. Companies like Vital Therapies and HepaStem are leading research in this domain. The potential for bridging therapy (keeping patients alive until a transplant is available) is a game-changer and a key factor in this segment's accelerated growth.
Bionic limbs were the dominant segment in 2024. These devices have gained traction due to increasing cases of limb amputations arising from trauma, vascular disease, or diabetes. Bionic limbs today incorporate sensors, actuators, and neural feedback systems to mimic natural motion. Companies like Ottobock and Open Bionics have introduced customizable and affordable prosthetic solutions. Veterans, accident victims, and congenital amputees are major users. User-centric design, smartphone connectivity, and 3D printing have made bionic limbs not only more functional but also accessible.
Exoskeletons are the fastest-growing segment in the medical bionics category. Initially used for military purposes, medical-grade exoskeletons are now widely applied in rehabilitation for stroke patients and individuals with spinal cord injuries. Firms like ReWalk Robotics and Ekso Bionics have developed FDA-approved robotic suits that aid in physical therapy and mobility. The rise of hospital-based rehab centers and demand for home-based wearable solutions are driving this growth. Future developments are likely to involve AI-powered exoskeletons that predict movement and adjust support accordingly.
Medtronic plc
Boston Scientific Corporation
Cochlear Ltd.
Zimmer Biomet Holdings Inc.
Edwards Lifesciences Corporation
Abiomed Inc.
SynCardia Systems LLC
BiVACOR Inc.
ReWalk Robotics
Ekso Bionics Holdings Inc.
Össur hf
Open Bionics
Ottobock SE & Co. KGaA
NeuroPace Inc.
Second Sight Medical Products Inc.
March 2025 – SynCardia Systems announced the development of a more compact version of its Total Artificial Heart, suitable for smaller-framed patients and women, with clinical trials commencing mid-2025.
February 2025 – Neuralink, a company founded by Elon Musk, received FDA approval to expand its clinical trials for brain-machine interfaces aimed at patients with spinal injuries.
January 2025 – BiVACOR, a company developing a total artificial heart based on rotary pump technology, secured $22 million in Series B funding to advance its first-in-human trials.
November 2024 – Össur introduced its next-generation bionic knee joint, featuring real-time adaptive gait recognition and AI-based fall detection.
October 2024 – Cochlear Ltd. launched its Smart Hearing Ecosystem in Europe, integrating mobile devices with cochlear implants to improve remote monitoring and tuning.
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2034. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the artificial vital organs and medical bionics market
By Artificial Organs
By Bionics
By Regional