The Asia Pacific pea protein market size was exhibited at USD 588.75 million in 2023 and is projected to hit around USD 2,070.43 million by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 13.4% during the forecast period 2024 to 2033.
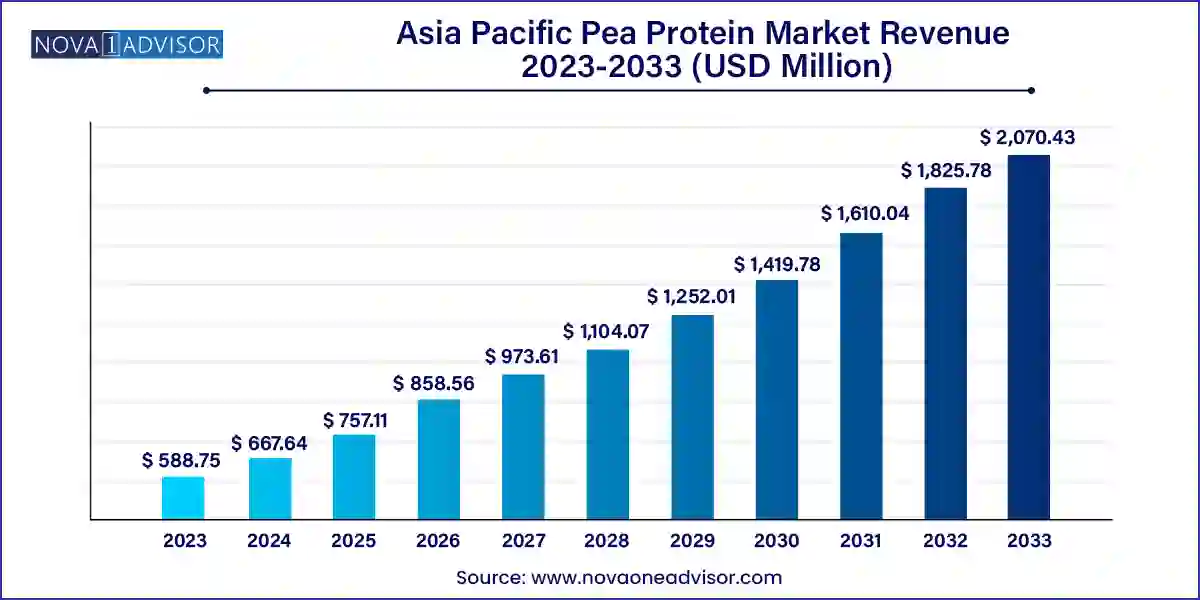
The Asia Pacific pea protein market is experiencing a significant upward trajectory, driven by shifting dietary patterns, rising plant-based awareness, and rapid urbanization across the region. Pea protein—recognized for its high digestibility, allergen-free profile, and sustainability—is being embraced as a clean-label ingredient across multiple sectors including food and beverages, nutraceuticals, animal nutrition, and cosmetics.
As the demand for alternative proteins surges, driven by both health-conscious consumers and environmentally aware younger demographics, pea protein has carved out a unique position. Unlike soy, which often carries allergen and GMO concerns, or animal proteins that face ethical and environmental scrutiny, pea protein presents a nutritionally rich, versatile, and increasingly available option. It is derived primarily from yellow split peas and can be processed into different formats such as isolates, concentrates, textured, and hydrolysates.
In countries like China and India, the traditional plant-based dietary base is being supplemented with high-protein, functional, and convenient food products to meet modern nutritional needs. Meanwhile, markets such as Japan, Australia, and South Korea are leading with innovation in protein-fortified drinks, meat analogs, and clean beauty products. The pea protein industry is quickly evolving into a strategic segment of the broader functional protein economy, attracting attention from global ingredient suppliers and regional startups alike.
Rising Popularity of Vegan and Flexitarian Diets: Driven by environmental awareness and health trends, consumers across Asia are shifting toward plant-centric diets.
Expansion in Functional Beverages and RTD Products: Pea protein is being used in shakes, fortified waters, and meal replacement drinks targeting millennials and fitness-conscious consumers.
Integration in Traditional Asian Foods: Local adaptations of noodles, dumplings, and soy-free sauces with pea protein content are emerging across Asia.
Allergen-Free and Clean Label Movement: As consumers reject artificial additives and allergens like soy, demand for neutral-tasting and allergen-free protein is rising.
Cosmetic Industry Adoption: Pea protein is being included in hair conditioners, serums, and facial creams for its strengthening and hydrating properties.
Increased Local Cultivation of Yellow Peas: Governments and agribusinesses are exploring localized sourcing to reduce dependency on imports.
Proliferation of DTC Brands: Direct-to-consumer pea protein brands are growing in India and China, leveraging influencer marketing and digital wellness platforms.
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 667.64 Million |
| Market Size by 2033 | USD 2,070.43 Million |
| Growth Rate From 2024 to 2033 | CAGR of 13.4% |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Forecast Period | 2024-2033 |
| Segments Covered | Product, Form, Source, Application, Country |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) | Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Country scope | India; China; Japan; Australia & New Zealand; South Korea |
| Key Companies Profiled | Shandong Jianyuan Foods Co., Ltd.; Yantai Oriental Protein Tech, Co., Ltd.; FENCHEM; Martin & Pleasance; Cargill, Inc.; Archer Daniels Midland Company; Ingredion Inc.; International Flavors & Fragrances Inc.; Foodchem International Corp.; Kerry Group PLC; Roquette Frères |
One of the most significant drivers of the Asia Pacific pea protein market is the dual trend of health consciousness and sustainability awareness among consumers. As lifestyle diseases such as obesity, diabetes, and cardiovascular disorders become more prevalent across Asian countries, consumers are shifting towards nutrient-dense, plant-based food options. Pea protein, being high in lysine and rich in iron, offers a healthy source of protein without the saturated fat content associated with animal-based sources.
In tandem with health, the growing awareness of climate change and environmental degradation has prompted consumers and companies alike to seek more sustainable alternatives. Pea cultivation has a smaller carbon footprint compared to traditional animal farming and does not require nitrogen fertilizers due to its nitrogen-fixing ability. The dual benefit of health and ecological sustainability makes pea protein a highly attractive proposition in the regional market.
Despite its many advantages, pea protein suffers from certain functional limitations that may restrain its adoption across a wider spectrum of applications. Notably, pea protein can exhibit a beany or earthy flavor profile, which is not always desirable in food and beverage formulations. Its solubility and texture, while suitable for meat analogs and shakes, may not be optimal for some bakery or dairy applications without extensive formulation or blending with other proteins.
Additionally, the texture of pea protein is not as versatile as animal-derived proteins, requiring technological intervention for use in high-end food applications. This increases production costs and may limit its use among price-sensitive consumers in some developing parts of the Asia Pacific region.
A key opportunity for the Asia Pacific pea protein market lies in the rapid expansion of the sports nutrition segment, driven by increasing gym memberships, a growing number of fitness influencers, and the widespread use of social media to promote healthy lifestyles. Countries like Australia, Japan, and India are witnessing an upsurge in the consumption of protein shakes, energy bars, and recovery drinks.
Pea protein offers an excellent alternative to whey protein for consumers who are lactose intolerant or seeking vegan alternatives. Its high branched-chain amino acid (BCAA) content supports muscle recovery and endurance. Brands are beginning to tap into this segment with customized formulations of pea protein powders enriched with vitamins and minerals, specifically targeting athletes, fitness enthusiasts, and health-conscious youth.
Isolates dominated the product segment owing to their superior purity and higher protein concentration, making them ideal for dietary supplements, medical nutrition, and protein powders. Pea protein isolates typically contain over 80% protein and minimal fat and starch, making them a popular choice in fitness and sports nutrition products across Australia, China, and South Korea. Companies are leveraging isolates for clean-label product lines, catering to consumers who demand transparency in food content.
However, textured pea protein is emerging as the fastest-growing segment due to its pivotal role in mimicking meat texture in plant-based meat products. Textured variants have excellent water retention, chewability, and elasticity—key attributes in meat substitutes. With companies like Green Rebel Foods (Indonesia) and Unlimeat (South Korea) rapidly developing pea-protein-based meats, this segment is set to witness exponential growth. Its popularity is especially evident in China and India, where meat analogs are gaining market traction.
The yellow split peas segment dominates the market as they are the most widely cultivated and processed variety for pea protein production. Their balanced amino acid profile and light color make them ideal for both food and nutraceutical applications. In India, where pulse cultivation is abundant, and in Australia, which exports significant volumes of peas, this segment remains key to the market’s supply chain.
Conversely, the ‘Others’ source category—including green peas and garden peas—is gradually carving a niche, especially among artisanal food producers seeking differentiators. These sources offer unique flavor notes and nutrient compositions, which appeal to premium and specialized product developers, particularly in Japan and South Korea.
Food and beverages represent the largest application segment, with sub-segments like meat substitutes and dietary supplements driving the majority of demand. Meat substitutes have gained immense popularity in urban India, where vegetarian populations are increasingly seeking protein-rich alternatives. Meanwhile, dietary supplements based on pea protein are gaining a foothold among Japanese and Australian consumers interested in muscle health, weight management, and wellness.
In contrast, the personal care and cosmetics segment, while currently smaller, is one of the fastest-growing areas. Pea protein hydrolysates are increasingly being used in skincare and haircare formulations due to their ability to moisturize and restore damaged cells. South Korean beauty brands, for example, are introducing products with hydrolyzed pea protein for sensitive skin, capitalizing on the growing ‘clean beauty’ movement.
The dry form of pea protein holds the lion's share of the market due to its ease of storage, cost-effectiveness, and longer shelf life. It is widely used across multiple industries, from protein powders to pet food, offering a practical and scalable ingredient for manufacturers. Dry forms are especially prevalent in countries like Japan and Australia, where food processors seek cost-efficient, bulk ingredients that maintain consistency.
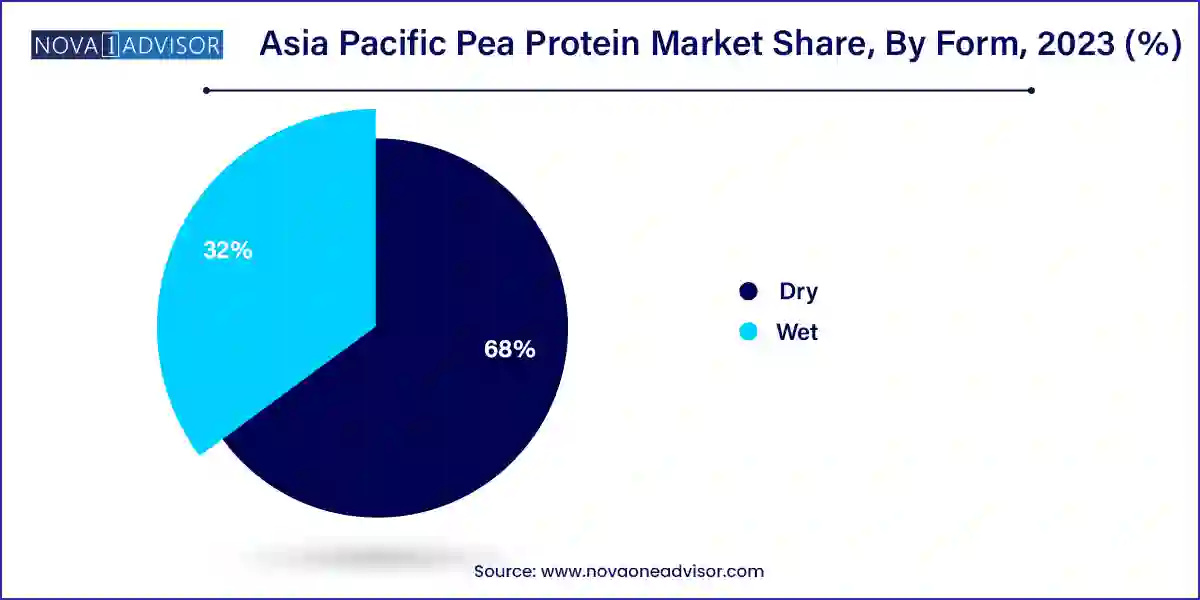
Nevertheless, the wet form of pea protein is witnessing increasing demand, particularly in beverage applications. Its better solubility and smoother mouthfeel make it ideal for ready-to-drink (RTD) formulations such as plant-based milk, smoothies, and energy drinks. Innovations in microfiltration and enzymatic processing are enhancing the functionality of wet-form pea proteins, making them more desirable in premium applications.
India represents one of the most promising markets for pea protein in Asia Pacific. With a large vegetarian population, rising urbanization, and a booming wellness industry, the country provides fertile ground for plant-based protein alternatives. The government’s push for nutritional fortification in foods and the rise of health-conscious millennial consumers are pushing demand across product categories, especially in the food and beverage sector.
Startups and legacy food companies alike are investing in pea protein for protein bars, meat analogs, and protein-enriched snacks. Brands like OZiva and MyProtein have already introduced pea protein isolates in their product lines. India’s growing nutraceutical and fitness market, combined with traditional culinary preferences for legumes, presents a unique landscape for sustained growth of pea protein-based solutions.
Roquette, a leading player in the global pea protein market, announced in March 2024 the expansion of its innovation center in Singapore, focusing on customizing plant-based protein solutions for Asian consumers.
In January 2024, Shandong Jianyuan Group based in China unveiled a strategic partnership with a Japanese food tech company to develop pea-based meat analogs for the Japanese and Korean markets.
Burcon NutraScience, a Canadian pea protein innovator, signed a collaborative agreement with an Indian plant-based nutrition company in February 2024 to launch tailored products for Indian consumers.
Ingredion inaugurated its new protein processing facility in April 2024 in Australia, aimed at serving Asia Pacific markets with a broader range of plant proteins, including textured pea protein.
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2033. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the Asia Pacific pea protein market
Product
Form
Source
Application
Country