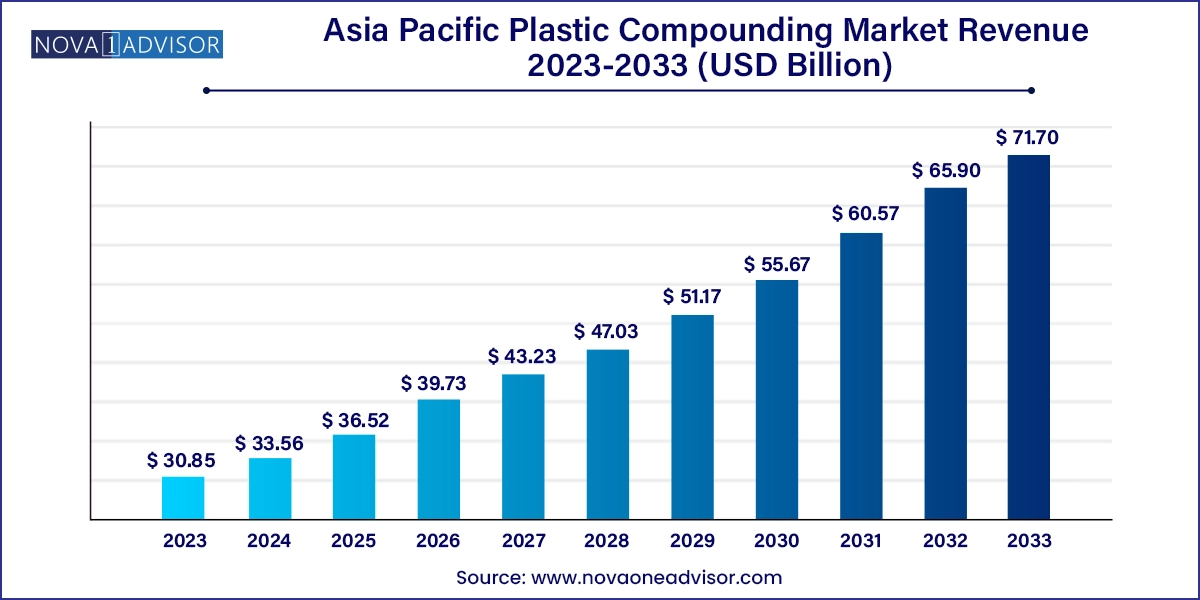
The Asia Pacific plastic compounding market size was exhibited at USD 30.85 billion in 2023 and is projected to hit around USD 71.70 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 8.8% during the forecast period 2024 to 2033.
The Asia Pacific plastic compounding market is rapidly emerging as a cornerstone of the region’s industrial and manufacturing boom. Plastic compounding, the process of blending polymers with additives, reinforcements, or fillers to improve material performance, is critical in tailoring plastics for specific applications across sectors like automotive, construction, electronics, and healthcare. In Asia Pacific, this market is fueled by strong industrial infrastructure, abundant raw materials, and increasing demand for lightweight, cost-effective, and durable materials.
Asia Pacific, led by manufacturing giants such as China, India, Japan, and South Korea, is seeing explosive growth in end-user industries that rely heavily on compounded plastics. From the proliferation of electric vehicles and consumer electronics to massive infrastructure development, the region's need for specialty polymers and advanced composites is escalating. Moreover, local governments’ push for “Make in Asia” initiatives, investments in petrochemicals, and adoption of circular economy principles are transforming both the scale and sophistication of the plastic compounding industry.
As regulatory scrutiny on environmental impact intensifies, players are also exploring bio-based and recycled alternatives, driving innovation. The competitive landscape is evolving quickly, with global and regional companies investing in R&D, plant expansions, and sustainable solutions to cater to diversified demand. With a dynamic blend of mature markets and fast-growing economies, Asia Pacific is not just a production hub but increasingly a center for innovation in plastic compounding.
Surging Demand from the Electric Vehicle (EV) Sector: Lightweight, heat-resistant compounded plastics are replacing metals in battery components, interiors, and structural parts.
Rising Focus on Bio-based and Recycled Compounds: Driven by government mandates and consumer sustainability preferences, companies are increasing the use of biodegradable or recycled plastics.
Advancements in Flame-retardant Compounds: With growing safety standards in construction and electronics, there’s rising demand for halogen-free and high-performance flame-retardant materials.
Miniaturization in Electronics: As devices shrink, there's a need for high-strength, thermally stable, and insulating compounded plastics.
Smart Manufacturing Integration: Industry 4.0 is enabling real-time monitoring and process control in compounding plants, enhancing quality and reducing waste.
Collaborative R&D Efforts: Companies are partnering with research institutes and OEMs to develop application-specific formulations, especially in healthcare and aerospace.
Expansion of Local Supply Chains: Regional players are investing in local production and sourcing to mitigate the risks of global supply chain disruptions.
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 33.56 Billion |
| Market Size by 2033 | USD 71.70 Million |
| Growth Rate From 2024 to 2033 | CAGR of 8.8% |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Forecast Period | 2024-2033 |
| Segments Covered | Source, Product, Application, Country |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) | Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Country scope | Japan, China, India, South Korea |
| Key Companies Profiled | BASF SE; SABIC; LyondellBasell Industries N.V.; Kraton Polymers Inc.; RTP Company; The 3M Company; Teijin Plastics; Polyplastics Asia Pacific Sdn Bhd; Melchers Malaysia; Helistrom Sdn Bhd; Sheng Foong Plastic Industries Sdn Bhd; The Inabata Group; CIPC Resin; Sin Yong Guan & Co.; Eveready Manufacturing Pte Ltd.; Compounding and Coloring Sdn Bhd |
A key driver of the Asia Pacific plastic compounding market is the exponential growth of industrialization and urban infrastructure development. Governments across the region, notably in China and India, are pouring investments into building smart cities, expanding transportation networks, and upgrading housing facilities. For instance, China’s Belt and Road Initiative and India’s “Smart Cities Mission” have significantly increased the demand for advanced construction materials.
Plastic compounds play a crucial role here by offering versatility, durability, and cost-efficiency for applications ranging from pipes and fittings to insulation, roofing membranes, and interior panels. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) and polypropylene (PP) compounds are particularly sought after for their mechanical strength and weather resistance. These compounded plastics are helping meet the evolving construction codes and environmental regulations while improving construction speed and cost control. As infrastructure initiatives scale up and diversify, the demand for high-performance compounded materials is expected to climb further.
Despite rapid growth, the plastic compounding market in Asia Pacific faces significant challenges related to environmental sustainability. As concerns over plastic waste pollution grow, regulatory authorities across the region are imposing stringent restrictions on the use of non-biodegradable and single-use plastics. Countries such as India have implemented bans on certain plastic products, and China has launched aggressive campaigns to cut down on plastic waste and improve recycling efficiency.
These regulations increase operational complexity for compounders, who must now ensure compliance with evolving standards while also managing supply chain disruptions for raw materials. Additionally, the negative public perception of plastics is pressuring manufacturers and end users to shift toward eco-friendly alternatives, which may come at higher costs or pose technical limitations. For companies heavily reliant on fossil-based compounds, adapting to this new sustainability landscape requires significant investment in R&D, retooling, and collaboration with downstream partners.
An exciting opportunity in the Asia Pacific plastic compounding market lies in the rising demand for recycled and bio-based polymers. Driven by the global shift toward sustainability, countries in the region are incentivizing green technologies and circular economy models. This is creating a fertile ground for developing plastic compounds that integrate post-consumer or post-industrial recycled materials and bio-based feedstocks.
For example, Thailand’s "Bio-Circular-Green (BCG) Economy Model" encourages innovations in renewable materials, while China’s recycling regulations are boosting demand for recycled polyethylene and polypropylene compounds. Local compounders are innovating with hybrid formulas that blend recycled content without compromising strength or aesthetics. Moreover, bio-based plastics such as polylactic acid (PLA) and bio-PET are gaining interest for use in packaging, agriculture, and medical applications. This trend is also attracting foreign investments and R&D collaborations, signaling a high-growth pathway for sustainable plastic compounding.
Polypropylene (PP) emerged as the leading product segment, thanks to its versatility, chemical resistance, and affordability. PP compounds are extensively used in automotive components, medical containers, electrical housings, and packaging films. Its ability to be reinforced with glass fibers or minerals makes it ideal for lightweight structural applications. In automotive manufacturing hubs like India, South Korea, and China, PP compounding is a critical part of localized component manufacturing, offering an optimal balance of performance and cost.
Polycarbonate (PC) compounds are growing the fastest, driven by increasing applications in electronics, optical media, and automotive lighting. PC offers high impact strength, clarity, and dimensional stability, making it suitable for advanced displays, LED covers, and medical device housings. Recent advancements in flame-retardant and UV-stabilized PC compounds are further expanding its use in outdoor and high-temperature environments. With the miniaturization of consumer electronics and shift to electric vehicles, PC compound demand is forecasted to rise significantly across the region.
Fossil-based compounds dominated the Asia Pacific plastic compounding market, largely due to their mature supply chains, broad compatibility, and affordability. These compounds derived from petroleum-based polymers like PE, PP, and PVC are extensively used in automotive, consumer goods, construction, and electronics. Despite environmental concerns, fossil-based plastics offer unmatched mechanical and thermal performance for heavy-duty applications. In markets like China and India, government-backed petrochemical expansions are ensuring steady availability and cost competitiveness of fossil-derived polymers, maintaining their stronghold in the market.
Recycled plastics are expected to grow at the fastest rate, fueled by environmental mandates and corporate sustainability goals. Recycled polypropylene and polyethylene compounds are now widely used in automotive trims, furniture, and packaging films. Companies such as Toray and Lotte Chemical are investing in mechanical recycling technologies to improve the quality and consistency of recycled feedstocks. Meanwhile, startups are innovating in chemical recycling and upcycling, enabling the use of difficult-to-recycle materials in high-performance applications. As eco-labeling and green certifications gain traction in Asia, demand for recycled compound grades is poised for rapid acceleration.
The automotive segment dominated the application spectrum, as plastic compounding is central to weight reduction and fuel efficiency. Asia Pacific’s large automotive production base, particularly in Japan, India, and China, uses compounded plastics for bumpers, dashboards, under-the-hood components, and battery enclosures. OEMs are demanding high-performance plastics with enhanced flame resistance, impact strength, and durability, leading to a surge in custom compound formulations. Additionally, the region’s increasing focus on electric mobility is accelerating the use of thermally conductive and flame-retardant compounds.
Medical devices represent the fastest-growing application, spurred by healthcare infrastructure development, especially post-pandemic. Compounded plastics like TPU, PP, and PVC are used in syringes, IV bags, catheters, and surgical instruments. These polymers are preferred for their sterility, biocompatibility, and cost-effectiveness. Countries like China, India, and Indonesia are ramping up local medical device manufacturing, encouraging demand for specialized medical-grade compounds. As regulatory standards improve and exports grow, this segment is expected to maintain its growth trajectory.
China dominates the Asia Pacific plastic compounding market in terms of production, consumption, and innovation. The country’s vast industrial ecosystem, spanning automotive, electronics, and construction sectors, heavily relies on compounded plastics. Government policies like “Made in China 2025” and “Dual Circulation Strategy” support domestic production of advanced materials. Additionally, China is home to numerous compounding hubs, especially in provinces like Zhejiang, Guangdong, and Jiangsu. In recent years, Chinese firms have been investing in bio-compounds and recycled plastic formulations to align with the government’s carbon neutrality goals.
India is one of the fastest-growing markets, driven by its expanding manufacturing base and infrastructure boom. With a young population, rapid urbanization, and favorable government policies like “Make in India,” demand for plastic compounds in sectors such as construction, automotive, and FMCG is surging. Domestic compounders are increasingly forming joint ventures with global firms to introduce high-tech materials and broaden application areas. Moreover, India’s growing emphasis on sustainability is pushing for innovations in recycled plastic compounding, especially for packaging and consumer goods.
Japan maintains a significant share of the market due to its advanced R&D capabilities and high-end application requirements. Known for its precision-driven industries, Japan consumes large volumes of engineered plastic compounds in electronics, automotive, and medical devices. The country is also leading the innovation curve in bio-compounds, investing in PLA, PBS, and other biodegradable alternatives. Japanese firms are pioneering next-gen compounding technologies involving nanofillers, flame retardants, and antimicrobial additives for niche applications.
South Korea’s plastic compounding market is shaped by its dominance in electronics and automotive exports. Companies like LG Chem and Lotte Chemical are major players in developing advanced thermoplastics and elastomeric compounds. With growing investment in EV battery production and semiconductor packaging, demand for specialty compounds is rising. The government’s push for green technology and energy efficiency is also encouraging the development of sustainable compound alternatives.
January 2025: LG Chem announced the expansion of its plastic compounding facility in Yeosu, South Korea, focusing on flame-retardant and high-heat compounds for EV applications.
February 2025: Toray Industries launched a new line of recycled PP and PET compounds with enhanced mechanical properties aimed at consumer electronics manufacturers in Japan and Southeast Asia.
March 2025: Lotte Chemical unveiled a bio-based polycarbonate compound made from renewable feedstock at the India Plast Show, signaling its commitment to sustainable innovation.
April 2025: Mitsubishi Chemical Corporation partnered with an Indian startup to develop antimicrobial PVC compounds for medical tubing and surgical equipment production.
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2033. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the Asia Pacific plastic compounding market
Source
Product
Application
Country