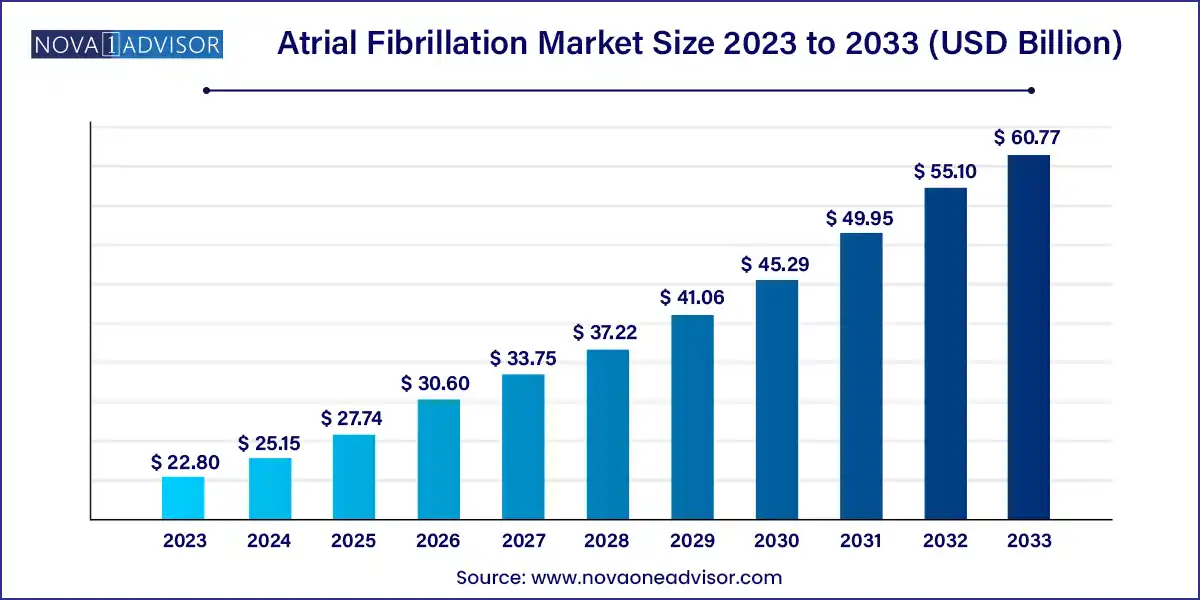
The global atrial fibrillation market size was exhibited at USD 22.80 billion in 2023 and is projected to hit around USD 60.77 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 10.3% during the forecast period of 2024 to 2033.
Atrial fibrillation (AF) is a common cardiac arrhythmia characterized by irregular and often rapid heart rhythm originating from abnormal electrical activity in the atria. AF is associated with increased risks of stroke, heart failure, cognitive decline, and overall mortality. The condition affects millions globally, and its incidence is rising due to aging populations, increasing prevalence of hypertension, obesity, and cardiovascular diseases.
The atrial fibrillation market comprises various treatment modalities, including pharmacological therapies (anti-arrhythmic and anticoagulant drugs) and non-pharmacological interventions such as catheter ablation, electrical cardioversion, and surgical procedures like maze surgery. These options aim to restore and maintain sinus rhythm, prevent thromboembolism, and reduce symptom burden.
Market growth is supported by advances in catheter ablation technology, increasing awareness about the long-term consequences of untreated AF, and a growing preference for minimally invasive procedures. Pharmaceutical companies continue to invest in the development of next-generation anticoagulants and rhythm-control drugs with better efficacy and safety profiles. The convergence of digital health and electrophysiology is also leading to remote monitoring tools that enhance post-treatment management and AF recurrence prediction.
Rising Adoption of Catheter Ablation as First-Line Therapy: Minimally invasive ablation procedures are increasingly preferred over chronic pharmacotherapy for symptomatic AF.
Development of Novel Oral Anticoagulants (NOACs): Drugs such as apixaban and rivaroxaban are replacing warfarin due to improved safety and reduced monitoring.
Emergence of Pulsed Field Ablation (PFA): PFA is gaining traction as a non-thermal ablation technique offering reduced risk to surrounding tissues.
Integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI is being used for ECG interpretation, ablation target identification, and arrhythmia prediction.
Wearable ECG Monitors for Early Detection: Smartwatches and wearable patches are enabling early diagnosis and treatment initiation.
Increased Use of Hybrid Procedures: Combining pharmacologic and ablation strategies is becoming standard in refractory or persistent AF cases.
Focus on Stroke Prevention: Emphasis on effective anticoagulation strategies to reduce AF-associated stroke risks, especially in elderly patients.
Geographic Expansion of Specialized Electrophysiology Centers: New AF clinics and EP labs are opening in Asia-Pacific and Latin America.
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 25.15 Billion |
| Market Size by 2033 | USD 60.77 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2024 to 2033 | CAGR of 10.3% |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Forecast Period | 2024-2033 |
| Segments Covered | Treatment Type, End-use, Region |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) | Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Regional Scope | North America; Europe; Asia Pacific; Central and South America; the Middle East and Africa |
| Key Companies Profiled | AtriCure Inc.; Boehringer Ingelheim GmbH; Boston Scientific Corporation; Bristol-Myers Squibb Corporation; Cardio Focus Inc.; Sanofi Aventis; Biosense Webster Inc.; Endoscopic Technologies Inc.; Abbott (St. Jude Medical Inc.); Johnsons & Johnson. |
One of the primary drivers of the AF market is the rising global incidence and prevalence of atrial fibrillation, particularly among aging populations. According to recent estimates, over 33 million individuals globally live with AF, and this number is expected to more than double by 2050. AF often coexists with other chronic conditions such as hypertension, diabetes, sleep apnea, and obesity, all of which are on the rise due to lifestyle factors and demographic shifts.
The growing burden of AF places enormous strain on healthcare systems due to frequent hospitalizations, stroke-related complications, and long-term morbidity. Consequently, there is increasing clinical and policy focus on early diagnosis, efficient treatment, and prevention of thromboembolic events. Health authorities and clinical societies have updated treatment guidelines to include catheter ablation and NOACs, further fueling demand for innovative AF therapies.
Despite advances in treatment options, a major restraint for the AF market is the risk of procedural complications and the high cost of advanced therapies. Catheter ablation, though effective, carries inherent risks such as cardiac tamponade, pulmonary vein stenosis, and phrenic nerve injury. These concerns limit adoption, particularly in older or frail patients and in regions lacking experienced electrophysiologists.
Furthermore, NOACs and ablation procedures are expensive compared to traditional therapies like warfarin or rate-control drugs. In low-income regions, healthcare access and reimbursement challenges make these options unattainable for many patients. The requirement for repeated procedures in persistent or refractory AF cases further escalates healthcare costs, creating economic burden for both payers and patients.
An exciting opportunity in the AF market lies in the emergence of non-thermal ablation technologies, such as pulsed field ablation (PFA). Unlike conventional methods that use heat (radiofrequency) or cold (cryoablation), PFA employs high-voltage electric fields to ablate cardiac tissue with enhanced safety and precision. This technique minimizes collateral damage to esophageal, neural, and vascular structures critical in reducing adverse outcomes and procedural anxiety.
Additionally, AI-driven platforms are revolutionizing patient care by assisting in AF detection (via ECG analysis), treatment planning, and follow-up monitoring. AI-enhanced electroanatomic mapping and simulation tools are improving ablation success rates and reducing procedure time. These innovations are particularly beneficial for expanding access in resource-limited or rural settings through remote monitoring and tele-EP services.
Pharmacological treatment dominates the atrial fibrillation market, largely due to the widespread use of anticoagulants and anti-arrhythmic medications. Among these, anticoagulant drugs such as apixaban, dabigatran, and rivaroxaban have revolutionized stroke prevention in non-valvular AF. Their advantages over warfarin such as fewer dietary restrictions, reduced monitoring, and better safety profiles have made them the standard of care in many countries.
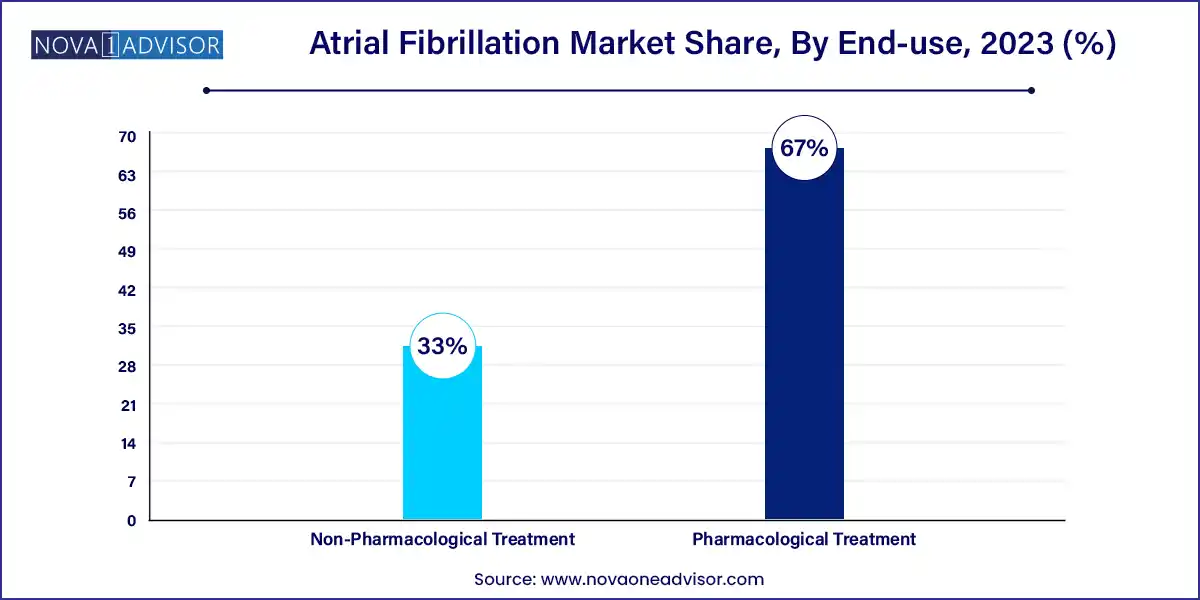
Non-pharmacological treatment, especially catheter ablation, is the fastest-growing segment. Within ablation, radiofrequency and cryoablation are the most established, used to isolate pulmonary veins and prevent erratic electrical impulses. High-Intensity Focused Ultrasound (HIFU) and pulsed field ablation are gaining attention for their ability to target tissues with minimal thermal injury. Maze surgery and electric cardioversion continue to play roles in select patient populations, particularly where catheter ablation is contraindicated or ineffective.
Hospitals dominate the end-use segment, as they offer comprehensive AF care including emergency treatment, diagnostics, pharmacologic initiation, and interventional electrophysiology. Tertiary care centers and university hospitals often serve as ablation hubs, with integrated cardiac surgery, imaging, and intensive care support. They also facilitate clinical trials and AI-based research projects for advanced AF care.
Specialty clinics are the fastest-growing end-use segment, driven by the global expansion of dedicated electrophysiology centers and outpatient catheter labs. These clinics enable streamlined, cost-effective AF management and follow-up, with shorter wait times and specialized care teams. Increasing adoption of ambulatory monitoring, same-day ablation procedures, and digital patient education tools is boosting the relevance of AF-focused specialty settings.
North America dominates the atrial fibrillation market, with the U.S. accounting for the largest share. This dominance is driven by a high prevalence of cardiovascular disease, robust reimbursement frameworks, availability of advanced ablation systems, and strong presence of key players such as Medtronic, Abbott, and Boston Scientific. The American College of Cardiology and Heart Rhythm Society’s guidelines promote early rhythm control and ablation, influencing provider practices.
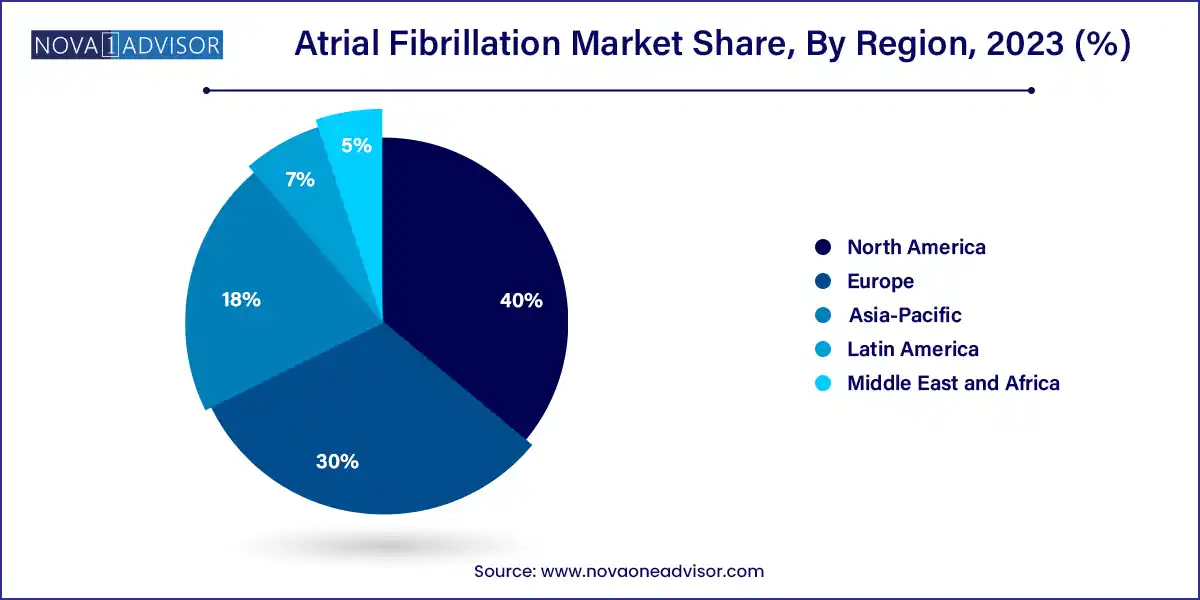
Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing region, led by countries such as China, India, Japan, and South Korea. Rising healthcare investments, large untreated AF populations, and government initiatives to improve cardiac care infrastructure are fueling growth. Japan has emerged as an early adopter of pulsed field ablation and AI-enhanced ECG diagnostics. In India, public-private partnerships and remote telecardiology initiatives are expanding access to specialized care.
Medtronic (April 2025): Received CE Mark for its Affera™ pulsed field ablation system, targeting rapid and safe treatment for paroxysmal AF.
Boston Scientific (March 2025): Announced successful completion of its FARAPULSE PFA global trial, showing promising results for non-thermal ablation efficacy.
Abbott Laboratories (February 2025): Launched a new AI-powered ECG monitoring patch for early AF detection and remote care in the U.S. and Europe.
Biosense Webster (January 2025): Expanded its Thermocool SmartTouch™ line with real-time lesion visualization and contact force technology for complex AF cases.
AliveCor (December 2024): Partnered with major insurers to deploy its KardiaMobile 6L ECG devices for home-based AF screening across chronic disease populations.
This report forecasts revenue growth at global, regional, and country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2033. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the global atrial fibrillation market.
Treatment type Scope
End-Use Scope
By Region