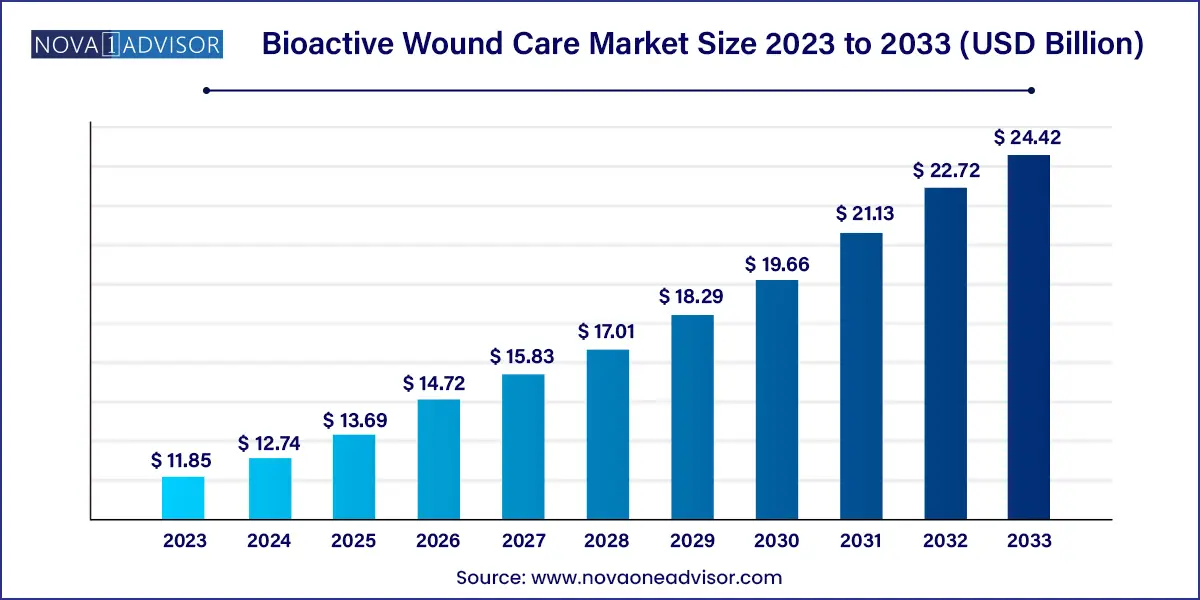
The global bioactive wound care market size was valued at USD 11.85 billion in 2023 and is anticipated to reach around USD 24.42 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 7.5% from 2024 to 2033.
The bioactive wound care market has emerged as a transformative domain in the field of advanced wound management. Unlike conventional dressings that merely protect a wound, bioactive wound care products actively interact with the wound bed to facilitate and accelerate the healing process. These products incorporate a wide array of biologically active materials—including silver ions, hydrogels, skin substitutes, and alginates—that aid in debridement, inflammation control, tissue regeneration, and infection prevention.
In 2024, the global bioactive wound care market was valued at over USD 10 billion and is expected to grow steadily through 2034. This growth is propelled by the increasing prevalence of chronic wounds, such as diabetic foot ulcers, venous leg ulcers, and pressure ulcers, as well as rising surgical volumes worldwide. Furthermore, aging populations, lifestyle disorders like obesity and diabetes, and a growing number of traumatic injuries (from burns to surgical complications) have made efficient wound care an urgent global healthcare priority.
Additionally, healthcare systems across the globe are focusing on reducing the length of hospital stays and preventing wound-related complications, leading to increased adoption of technologically advanced dressings that promote faster healing. The COVID-19 pandemic, while temporarily disrupting elective surgeries, underscored the importance of infection control and at-home wound management solutions, catalyzing innovation in self-applicable dressings and antimicrobial technologies.
Rise in Chronic Wounds and Diabetic Ulcers: The increasing prevalence of diabetes and vascular diseases is driving demand for advanced wound care solutions.
Shift Toward Outpatient and Home-Based Wound Management: Products designed for easy self-application are gaining popularity among patients and caregivers.
Increased Use of Antimicrobial Agents: Silver-based dressings, along with newer non-silver antimicrobials, are in high demand for infection prevention.
Biomaterial-Based Innovations: Collagen, hyaluronic acid, and other biomaterial-derived dressings are being developed to enhance regenerative capabilities.
Customized and 3D-Printed Dressings: Personalized wound care products, including bio-printed skin grafts, are gaining research and clinical interest.
Expansion of Reimbursement Policies in Developed Markets: Broader insurance coverage for bioactive wound care is improving accessibility and adoption rates.
Sustainability and Biodegradable Materials: Companies are investing in eco-friendly formulations and packaging to address environmental concerns.
Strategic Collaborations and M&A Activity: Key players are partnering with biotech firms to accelerate innovation and broaden their product portfolios.
| Report Attribute | Details |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 12.74 Billion |
| Market Size by 2033 | USD 24.42 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2024 to 2033 | CAGR of 7.5% |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Forecast Period | 2024 to 2033 |
| Segments Covered | Product, application, region |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) | Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Report Coverage | Revenue forecast, company ranking, competitive landscape, growth factors, and trends |
| Key Companies Profiled | B. Braun SE; Essity Health & Medical; 3M; Convatec Group PLC; Covalon Technologies Ltd; DermaRite Industries LLC; Hollister Incorporated; Integra LifeSciences Corporation; Johnson & Johnson Services, Inc.; Medtronic; Monlnlycke Health Care AB; Smith+Nephew |
One of the most powerful drivers in the bioactive wound care market is the global rise in chronic wounds, especially diabetic foot ulcers, pressure ulcers, and venous leg ulcers. According to recent clinical studies, nearly 6.7 million people in the U.S. alone suffer from chronic wounds. These wounds are not only painful and difficult to treat but also carry high risks of infection, hospitalization, and even limb amputation if not managed effectively.
Bioactive wound care products address this need by enhancing the healing environment, maintaining moisture balance, reducing microbial load, and supporting cellular repair. For example, alginate dressings derived from seaweed can absorb exudates while promoting a moist wound environment, while hydrocolloid dressings create a protective barrier and accelerate epithelialization. The ability of such dressings to reduce healing time and improve outcomes makes them indispensable for treating chronic wounds and has led to significant adoption in hospitals, outpatient clinics, and even home care settings.
Despite the evident benefits, the high cost of bioactive wound care products remains a significant barrier to widespread adoption, particularly in low- and middle-income countries. Compared to traditional dressings, bioactive products incorporate advanced technologies, proprietary formulations, and high-quality raw materials, making them considerably more expensive.
Hospitals and long-term care facilities in price-sensitive regions often hesitate to switch to bioactive alternatives unless fully reimbursed. Even in developed markets, the lack of awareness about cost-effectiveness in the long run—via reduced healing time and fewer complications—impacts decision-making. Smaller clinics and home care providers may opt for cheaper alternatives, thus limiting market penetration. Furthermore, frequent dressing changes in chronic wounds can accumulate substantial costs over time, underscoring the need for robust cost-benefit communication by manufacturers.
A compelling opportunity in this market lies in the continuous innovation of biomaterials and bioengineered skin substitutes. The development of next-generation dressings that combine anti-inflammatory agents, stem cells, growth factors, and matrix proteins is revolutionizing wound care. These products not only prevent infection but also accelerate tissue regeneration and reduce scarring.
Emerging research into hydrogel-based scaffolds, collagen-infused matrices, and hyaluronic acid-based delivery systems is enabling the launch of products that mimic the body’s natural healing processes. Furthermore, the introduction of 3D-printed skin grafts and active dressings embedded with drug-releasing nanofibers opens new horizons for treating complex wounds, including post-surgical incisions and burns. Companies that can effectively combine biotechnology with scalable production methods will be poised to lead the next wave of growth in this sector.
Moist wound care products dominated the bioactive wound care market in 2023, with foam and hydrocolloid dressings leading the segment. These products have proven efficacy in maintaining an optimal moist environment that facilitates autolytic debridement and accelerates healing. Foam dressings, known for their high absorbency and non-adherence to wound beds, are widely used in treating moderate to heavily exuding wounds. Hydrocolloids, on the other hand, offer both absorbency and barrier properties, making them ideal for pressure ulcers and superficial wounds. Their versatility, affordability, and ease of use have made them staples in both inpatient and outpatient settings.
The fastest-growing product segment is active dressings, particularly biomaterial-based and skin substitute products. Biomaterials such as collagen and chitosan have emerged as regenerative agents that promote granulation tissue formation and cellular migration. Skin substitutes, both synthetic and bioengineered, are gaining traction in treating complex wounds such as diabetic ulcers and burns. Companies like Organogenesis and Integra LifeSciences are leading the charge in this space, offering advanced skin grafts that integrate with the wound bed and stimulate native tissue formation. As clinical evidence supporting these technologies accumulates, hospitals are increasingly integrating them into treatment protocols.
General surgery remains the largest application segment, especially in fields like plastic, dermatological, and pediatric surgery. Surgical site infections (SSIs) are a persistent concern in postoperative care, and bioactive wound dressings serve a crucial role in preventing infection and promoting tissue regeneration. Dermatological surgeries, in particular, benefit from hydrogel and film-based dressings that provide transparency, allowing visual inspection without removal. Pediatric applications also require gentler, hypoallergenic solutions, and bioactive dressings with soothing and hydrating properties offer a viable option.
Minimally invasive surgery (MIS) is the fastest-growing application, due to the increasing global adoption of laparoscopic and robotic procedures across specialties. While MIS results in smaller incisions and quicker recovery, it still demands effective wound closure and infection prevention. Bioactive wound care solutions like film dressings, antimicrobial hydrocolloids, and active matrix dressings are being used to prevent micro-infections and reduce post-op scarring. As outpatient surgeries become more common and same-day discharges increase, the demand for self-adherent, long-wearing bioactive dressings is expected to surge.
North America led the bioactive wound care market in 2024, supported by robust healthcare infrastructure, high healthcare spending, and strong reimbursement frameworks. The U.S., in particular, exhibits high awareness and adoption of advanced wound care protocols. The growing incidence of diabetes, obesity, and trauma-related injuries further fuels demand. Government initiatives aimed at reducing hospital-acquired infections and promoting chronic wound management best practices have also contributed to market maturity.
Major players like 3M, Smith & Nephew, and Mölnlycke maintain strong footprints in the region, supported by extensive distribution networks and ongoing innovation. The presence of prominent wound care conferences and academic collaborations accelerates product development and clinician education. With a favorable regulatory climate and an aging population, North America is expected to maintain its leadership position through the forecast period.
Asia-Pacific is poised to be the fastest-growing region, driven by expanding healthcare access, rising chronic disease prevalence, and greater investment in advanced medical technologies. Countries like China, India, and Japan are witnessing increasing cases of diabetic ulcers and surgical wounds, creating significant unmet needs. Governments across the region are allocating greater budgets to modernize healthcare systems, improve hospital infrastructure, and enhance access to quality wound care.
While cost sensitivity remains a challenge, the emergence of local players and joint ventures with global firms are helping to lower price barriers. Moreover, growing medical tourism in countries like Thailand, Malaysia, and South Korea is contributing to the demand for sophisticated postoperative wound care. As awareness increases and healthcare delivery systems improve, the Asia-Pacific market is expected to exhibit double-digit growth in the coming decade.
The following are the leading companies in the bioactive wound care market. These companies collectively hold the largest market share and dictate industry trends.
March 2025 – 3M Health Care Division introduced “Tegaderm Bio+,” a new foam dressing embedded with plant-derived anti-inflammatory agents aimed at reducing peri-wound irritation in post-operative patients.
February 2025 – Smith & Nephew announced a strategic collaboration with a South Korean biotech firm to co-develop hydrogel-based wound care solutions incorporating stem cell-derived growth factors.
January 2025 – Mölnlycke Health Care launched “Mepilex Active Silver,” an upgraded silver-based antimicrobial dressing with extended wear time, targeting diabetic foot ulcer management.
December 2024 – ConvaTec Group Plc completed its acquisition of a startup specializing in 3D-printed skin grafts, signaling its intent to lead the regenerative wound care market.
November 2024 – Organogenesis Inc. received FDA approval for its new skin substitute matrix “PuraDerm,” specifically designed for pediatric burn victims, featuring high elasticity and low immunogenicity.
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2033. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the Bioactive Wound Care market.
By Product
By Application
By Region