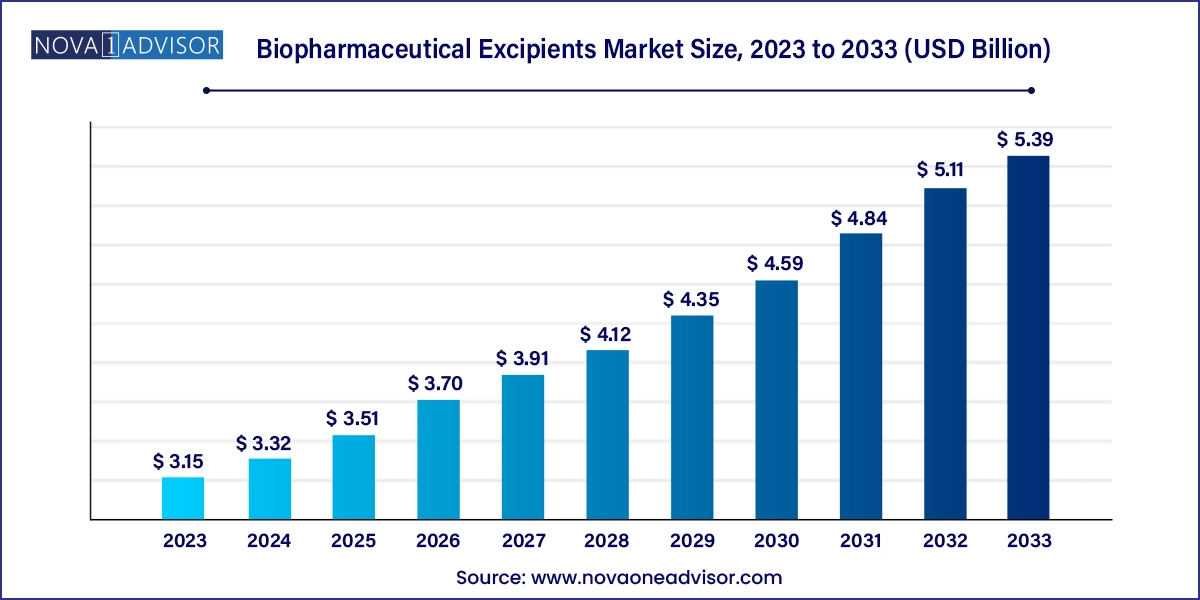
The biopharmaceutical excipients market size was exhibited at USD 3.15 billion in 2023 and is projected to hit around USD 5.39 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 5.52% during the forecast period 2024 to 2033.
The biopharmaceutical excipients market plays a pivotal role in the development and delivery of modern biologic drugs. Unlike traditional small-molecule drugs, biologics such as monoclonal antibodies, peptides, and nucleic acid-based therapeutics are complex and often sensitive to environmental conditions. Excipients, though pharmacologically inactive, are indispensable in stabilizing these products, enhancing bioavailability, facilitating targeted delivery, and extending shelf life.
Biopharmaceutical excipients are used in a range of formulations including injectables, lyophilized powders, and advanced delivery systems such as lipid nanoparticles (LNPs). As biopharmaceuticals increasingly dominate pipelines globally driven by innovation in immunotherapy, gene therapy, and mRNA vaccines the demand for specialized, high-purity excipients has surged. These excipients must meet rigorous regulatory standards and be manufactured under GMP conditions to ensure consistency, safety, and compatibility with sensitive biological molecules.
Key players in the pharmaceutical and biotechnology sectors are forging strategic partnerships with excipient manufacturers to co-develop excipients tailored to novel therapeutics. Moreover, the COVID-19 pandemic spotlighted the role of excipients, particularly in mRNA vaccine formulations where components like lipids, carbohydrates, and polyols were crucial for delivery and stability.
Increasing use of multifunctional excipients in biologics and vaccine formulations
Rising demand for GMP-grade and high-purity excipients tailored for injectable biopharmaceuticals
Expansion of lipid-based excipients for mRNA and gene therapy delivery systems
Strategic partnerships between biopharma companies and excipient suppliers
Growth of polyol and carbohydrate-based excipients in lyophilized and freeze-dried formulations
Innovation in surfactant chemistry to minimize protein aggregation and denaturation
Shift towards animal-free and plant-based excipient sources for safety and regulatory compliance
Regulatory agencies placing emphasis on excipient functionality and safety profiles in combination products
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 3.32 Billion |
| Market Size by 2033 | USD 5.39 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2024 to 2033 | CAGR of 5.52% |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Forecast Period | 2024-2033 |
| Segments Covered | Product, Region |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) | Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Country scope | North America; Europe; Asia Pacific; Latin America; Middle East & Africa |
| Key Companies Profiled | U.S.; Canada; Germany; U.K.; France; Italy; Spain; Denmark; Sweden; Norway; China; Japan; India; South Korea; Australia; Thailand; Brazil; Mexico; Argentina; South Africa; Saudi Arabia; UAE; Kuwait |
A primary driver of the biopharmaceutical excipients market is the expanding pipeline of biologic drugs that require excipients tailored for injectable and parenteral administration. Unlike oral solid dosage forms, injectable biologics need excipients that ensure solubility, stability, and protection against oxidation and aggregation. Common applications include stabilizers, solubilizers, bulking agents, surfactants, and cryoprotectants.
With blockbuster biologics dominating therapeutic areas such as oncology, autoimmune disorders, and rare diseases, manufacturers rely on excipients that support large-molecule integrity during production, storage, and administration. For example, polysorbates are often used to prevent protein denaturation, while mannitol and sorbitol act as cryoprotectants in lyophilized products. The shift toward self-administered biologics and pre-filled syringes further accelerates the need for injectable-grade excipients that meet strict quality benchmarks.
A major restraint in the market is the complex and inconsistent regulatory framework surrounding the use of excipients in biopharmaceutical formulations. While excipients are classified as inactive ingredients, their interaction with biologics can impact efficacy and safety. As such, regulatory bodies like the FDA and EMA demand detailed documentation, toxicological data, and manufacturing controls.
However, global variations in excipient monographs, compendial standards, and registration requirements create compliance challenges for multinational companies. The lack of harmonization results in delays, increased testing burdens, and costly reformulation in some markets. Smaller players and emerging biopharma firms may find it difficult to navigate this fragmented regulatory landscape, especially when introducing new or innovative excipient technologies.
One of the most promising opportunities lies in the increasing use of excipients in mRNA vaccines and gene therapies, where novel delivery systems are key to therapeutic efficacy. mRNA-based therapies, which require lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) for intracellular delivery, rely heavily on excipients such as PEGylated lipids, phospholipids, and cholesterol derivatives. These excipients facilitate mRNA encapsulation, protect it from enzymatic degradation, and ensure targeted release.
The success of COVID-19 mRNA vaccines by Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna has validated this platform, leading to widespread R&D activity in cancer immunotherapy, infectious diseases, and rare genetic conditions. Excipients tailored for nucleic acid stability, immunogenicity modulation, and precise biodistribution are in high demand. This opens opportunities for innovation and expansion among excipient suppliers developing next-generation delivery systems.
By Product: Solubilizers & Surfactants/Emulsifiers
Solubilizers and surfactants/emulsifiers dominate the product segment, as they are essential for maintaining the physical and chemical stability of protein-based drugs. Within this segment, triglycerides and esters are commonly used for solubilizing hydrophobic compounds and reducing interfacial tension in emulsions. Surfactants such as polysorbates and poloxamers play a crucial role in preventing protein aggregation and maintaining solution clarity, particularly in monoclonal antibody and vaccine formulations.
Triglycerides are among the fastest-growing subsegments, especially medium-chain triglycerides (MCTs), which are increasingly used in lipid-based delivery systems for poorly water-soluble biologics. Their biocompatibility, stability, and ability to enhance absorption make them ideal for both parenteral and oral liquid biologics. As more biologics require solubilization strategies to enhance shelf life and therapeutic efficacy, the demand for tailored emulsifiers will continue to rise.
By Product: Polyols
Mannitol leads the polyols category, widely utilized as a bulking agent and cryoprotectant in lyophilized biopharmaceutical products. Its chemical inertness, compatibility with proteins, and ability to stabilize formulation pH make it a preferred excipient in vaccines, monoclonal antibodies, and hormone therapies. Mannitol also improves the cake structure and reconstitution time of freeze-dried biologics, which is critical for stability during transportation and storage.
Sorbitol is the fastest-growing polyol, benefiting from its dual role as a stabilizer and osmotic agent in injectable biologics and oral liquid drugs. It supports protein integrity during freeze-thaw cycles and provides a sweetening effect in oral pediatric biotherapeutics. As biopharma companies focus on patient-centric formulations and expand pediatric drug portfolios, sorbitol usage is expected to grow significantly.
By Product: Carbohydrates
Sucrose dominates the carbohydrate-based excipients segment, extensively used as a stabilizer in both solution-based and lyophilized biologics. It prevents protein aggregation and denaturation during freeze-drying and enhances stability in aqueous formulations. Sucrose is especially prevalent in monoclonal antibody products and in vaccines where cold chain stability is a critical factor.
Dextrose and starch-based derivatives are gaining traction, particularly in formulations for cell therapies and personalized vaccines. These carbohydrates act as metabolic substrates and energy sources during cell storage and infusion. Furthermore, starch-based excipients are being explored as biodegradable polymers for sustained-release biologics, expanding their applicability beyond conventional stabilizers.
North America dominates the global biopharmaceutical excipients market, primarily due to the presence of a mature biopharmaceutical industry, advanced research infrastructure, and strict regulatory standards. The United States leads in both biologics innovation and excipient manufacturing, supported by key players such as Pfizer, Merck, and Thermo Fisher Scientific. The region also benefits from government funding for mRNA and gene therapy development, which has increased demand for high-grade excipients.
Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing region, driven by rapid biopharmaceutical expansion in China, India, South Korea, and Japan. These countries are investing heavily in biologics manufacturing, contract research, and vaccine production. The emergence of regional biopharma players and CDMOs has increased local demand for quality excipients, especially in injectable and lyophilized formulations. Additionally, government incentives for biopharma manufacturing and collaborations with Western pharmaceutical firms are further accelerating regional growth.
March 2025: Roquette announced the launch of a new GMP-grade polyol excipient line tailored for injectable biologics and mRNA vaccines.
January 2025: BASF collaborated with a U.S.-based biotech firm to co-develop lipid-based excipients for next-generation gene therapy delivery.
December 2024: Cargill expanded its pharma-grade carbohydrate facility in Belgium to meet growing demand for injectable excipient-grade sucrose and dextrose.
October 2024: Croda International received EMA certification for its animal-free polysorbate 80 variant aimed at monoclonal antibody stabilization.
August 2024: Evonik launched a new lipid nanoparticle (LNP) platform under its Health Care division to support mRNA and oligonucleotide-based drug delivery.
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2033. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the biopharmaceutical excipients market
Product
Regional