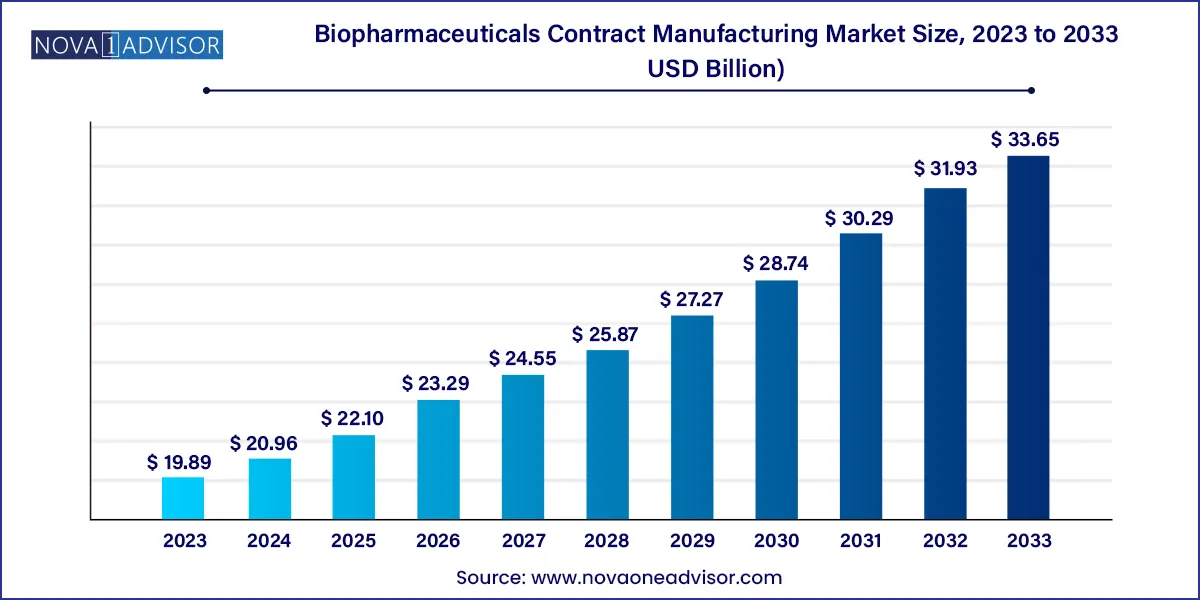
The global biopharmaceuticals contract manufacturing market size was estimated at USD 19.89 billion in 2023 and is projected to hit around USD 33.65 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 5.4% during the forecast period from 2024 to 2033.
The Biopharmaceuticals Contract Manufacturing Market often referred to as the biopharma CDMO (Contract Development and Manufacturing Organization) market has emerged as a critical backbone of the global life sciences industry. This market encompasses third-party manufacturing of biologics and biosimilars, offering biopharma companies flexibility, scalability, and access to specialized capabilities without building in-house infrastructure. Contract manufacturers provide services that span the entire product lifecycle, from early process development through scale-up, commercial manufacturing, and packaging.
Driven by an explosion of biopharmaceutical innovation including monoclonal antibodies (mAbs), recombinant proteins, gene therapies, and RNA-based therapeutics demand for reliable, high-capacity, and compliant manufacturing partners has soared. Smaller biotech firms, lacking internal capacity, are particularly reliant on outsourcing, while even large pharmaceutical companies are increasingly using CDMOs to manage cost pressures and navigate capacity constraints.
This market continues to grow in tandem with the pipeline of complex biologics. Advances in cell line engineering, bioprocessing technologies, and regulatory harmonization have further strengthened the business case for outsourcing. The competitive advantage lies not only in operational efficiency but in accelerating speed-to-market in a sector where timelines are crucial.
Rise in Demand for Mammalian Cell Culture Systems: Mammalian systems remain dominant due to their suitability for complex biologics like antibodies.
Shift Toward Single-Use Bioreactors: Disposable systems reduce contamination risks, shorten turnaround times, and lower upfront investment.
Increased Focus on Biosimilar Manufacturing: Patent expiries of blockbuster biologics are creating demand for biosimilar CDMO partnerships.
Expansion of RNA and Gene Therapy CDMO Capabilities: mRNA vaccines and gene-modifying therapies are pushing the boundaries of contract manufacturing scope.
Adoption of Integrated CDMO Models: End-to-end service offerings—from development to fill/finish—are being favored for efficiency and risk mitigation.
Investment in Modular and Flexible Facilities: CDMOs are building agile infrastructures to cater to multiproduct and multiprocess manufacturing.
Growth in Strategic Collaborations and Long-term Contracts: Big pharma is entering multi-year alliances with CDMOs to lock in capacity and innovation.
| Report Attribute | Details |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 20.96 Billion |
| Market Size by 2033 | USD 33.65 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2024 to 2033 | CAGR of 5.4% |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Forecast Period | 2024 to 2033 |
| Segments Covered | Source, service, product, therapeutic area, region |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) | Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Report Coverage | Revenue forecast, company ranking, competitive landscape, growth factors, and trends |
| Key Companies Profiled | Boehringer Ingelheim GmbH; Lonza; Inno Biologics Sdn Bhd; Rentschler Biotechnologie GmbH; JRS Pharma; AGC Biologics; ProBioGen; Fujifilm Diosynth Biotechnologies U.S.A., Inc.; Toyobo Co., Ltd.; Samsung BioLogics; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.; Binex Co., Ltd.; WuXi Biologics; AbbVie, Inc; Novartis AG; ADMA Biologics, Inc.; Catalent, Inc; Cambrex Corporation; Pfizer Inc.; Siegfried Holding AG |
A fundamental driver of the biopharmaceutical contract manufacturing market is the rapid expansion of biologics pipelines, especially among small and mid-sized biotech firms. As of 2024, more than half of the molecules in clinical development globally are biologics. These include monoclonal antibodies, cytokines, and novel therapeutic platforms like RNA-based drugs.
Smaller biotech companies, which are often the primary developers of novel biologics, typically lack in-house manufacturing capabilities. They rely heavily on CDMOs for process development, scale-up, and regulatory-grade production. This outsourcing trend is intensified by the high capital costs, compliance requirements, and technical complexity associated with biomanufacturing. CDMOs with deep expertise and global regulatory alignment are therefore in high demand to fulfill these needs, reducing time-to-market and providing operational agility.
Furthermore, even big pharma firms are increasingly outsourcing secondary production steps or seeking CDMO partners for regional manufacturing strategies, particularly in Asia-Pacific and Europe.
A significant restraint in the market is the complexity of biopharmaceutical production and stringent regulatory oversight. Manufacturing biologics involves living cells and is highly sensitive to environmental conditions, requiring rigorous quality control, consistent process validation, and compliance with current Good Manufacturing Practices (cGMP).
This complexity increases the risk of batch failures, contamination, and delays especially for CDMOs that handle multiple clients and product types. The need to meet regulatory standards set by agencies like the FDA, EMA, and PMDA across global markets creates an added layer of cost, time, and documentation burden.
Smaller CDMOs may struggle to meet these high thresholds, particularly if they lack resources for continuous process monitoring, automation, and digital compliance infrastructure. As biopharma products become more complex, maintaining consistent product quality across multiple sites and regions remains a persistent challenge.
An exciting opportunity lies in the contract manufacturing of RNA-based drugs and gene therapies, which are transforming the therapeutic landscape. The success of mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccines has accelerated investment in RNA therapeutics for cancer, infectious diseases, and rare genetic disorders.
These advanced modalities require highly specialized manufacturing processes, including lipid nanoparticle (LNP) formulation, in vitro transcription (IVT), and vector production. Given the technical challenges and equipment costs, many biopharma companies are turning to CDMOs for RNA manufacturing capabilities.
Leading CDMOs are building dedicated facilities and acquiring technology platforms to accommodate this demand. As regulatory frameworks for gene and RNA therapies mature, and as pipeline candidates enter late-stage development, this niche is set to become a high-margin, long-term growth driver within the broader contract manufacturing ecosystem.
Mammalian cell-based production dominates the source segment, accounting for the majority of revenue share. This method is preferred for producing complex biologics such as monoclonal antibodies, fusion proteins, and hormones due to its ability to generate human-like glycosylation patterns. Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells are the most widely used mammalian systems, offering high productivity and scalability. Most FDA-approved biologics today are manufactured using mammalian systems, and demand continues to grow as pipeline complexity increases.
Non-mammalian systems, including microbial and yeast expression systems, are the fastest-growing segment, particularly in the production of biosimilars, vaccines, and non-glycosylated proteins. These systems offer advantages like shorter production times, cost efficiency, and robustness. Companies are increasingly using engineered E. coli or yeast strains to produce next-gen biologics such as enzymes and growth factors.
Process development services currently dominate, especially in early-stage outsourcing. Biopharma companies rely heavily on CDMOs to optimize upstream and downstream parameters before committing to full-scale manufacturing. These services include cell line development, media optimization, purification protocols, and scale-up validation, forming the foundation of commercial manufacturing success.
Fill & finish operations are the fastest-growing service category, driven by rising demand for sterile packaging of biologics in prefilled syringes, vials, and cartridges. With the rise of self-injection biologics and parenteral administration routes, final formulation, aseptic filling, and packaging are increasingly outsourced to CDMOs with advanced isolator and lyophilization technologies.
Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) dominate the product segment, as they continue to be the most commercially successful class of biologics. CDMOs are heavily invested in developing infrastructure, bioreactors, and regulatory frameworks specifically for mAb production. Applications in oncology, autoimmune diseases, and infectious diseases ensure continued growth and high-volume production.
Antisense, RNAi, and molecular therapies represent the fastest-growing subsegment, reflecting the next wave of innovation. The approval of RNA-based therapies and growing clinical pipelines in rare diseases and oncology have created a surge in demand for niche CDMO expertise. These therapies require unique synthesis, encapsulation, and quality testing capabilities, pushing CDMOs to invest in specialized facilities.
Oncology remains the largest therapeutic area, accounting for a dominant share of contract manufacturing revenue. The biopharma industry’s focus on immuno-oncology, mAbs, and targeted therapies has driven demand for flexible, scalable manufacturing platforms. Many oncology biologics are produced using mammalian systems with rapid scale-up needs, making CDMO partnerships essential.
Neurology is the fastest-growing therapeutic area, due to increasing approvals and late-stage trials for biologics targeting diseases like Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and multiple sclerosis. The complexity of neurological disease biology requires advanced biologics such as antibody-drug conjugates, biosimilars, and gene therapies—all of which demand specialized production environments.
North America dominates the global biopharmaceutical contract manufacturing market, led by the United States. The region boasts a mature biopharma ecosystem, stringent regulatory frameworks, and a high concentration of CDMOs and biopharmaceutical companies. The U.S. is home to major players like Thermo Fisher Scientific, Catalent, and Lonza (U.S. operations), which continue to expand capacity and technology portfolios. The region also benefits from robust funding for biotech startups and public-private collaborations for pandemic preparedness and advanced therapeutics.
Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing region, driven by rising investment in biopharma manufacturing hubs in countries like China, India, and South Korea. Governments are incentivizing CDMO capacity building through tax benefits and infrastructure support, while domestic biotech companies increasingly turn to outsourcing for cost-effective scale-up. Additionally, global pharma firms are partnering with APAC-based CDMOs for regional supply chain optimization and regulatory approvals. China's “Made in China 2025” initiative and India’s “Pharma Vision 2020” further fuel regional momentum.
Samsung Biologics (April 2025): Announced the completion of its fifth plant in Incheon, South Korea, expanding its capacity to over 600,000 liters—making it the world’s largest single-site CDMO.
Catalent (March 2025): Signed a multi-year RNA drug manufacturing partnership with a top-10 global pharma company, focusing on personalized oncology therapeutics.
Lonza (February 2025): Launched a new mammalian manufacturing suite in Visp, Switzerland, aimed at rapid scale-up of monoclonal antibodies.
WuXi Biologics (January 2025): Expanded its U.S. and European footprint by acquiring manufacturing facilities in Pennsylvania and Germany to support global clients.
Thermo Fisher Scientific (December 2024): Invested $450 million in advanced fill-finish and packaging capabilities across three global sites to meet demand for complex biologics and vaccines.
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2033. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the Biopharmaceuticals Contract Manufacturing market.
By Source
By Service
By Product
By Therapeutic Area
By Region