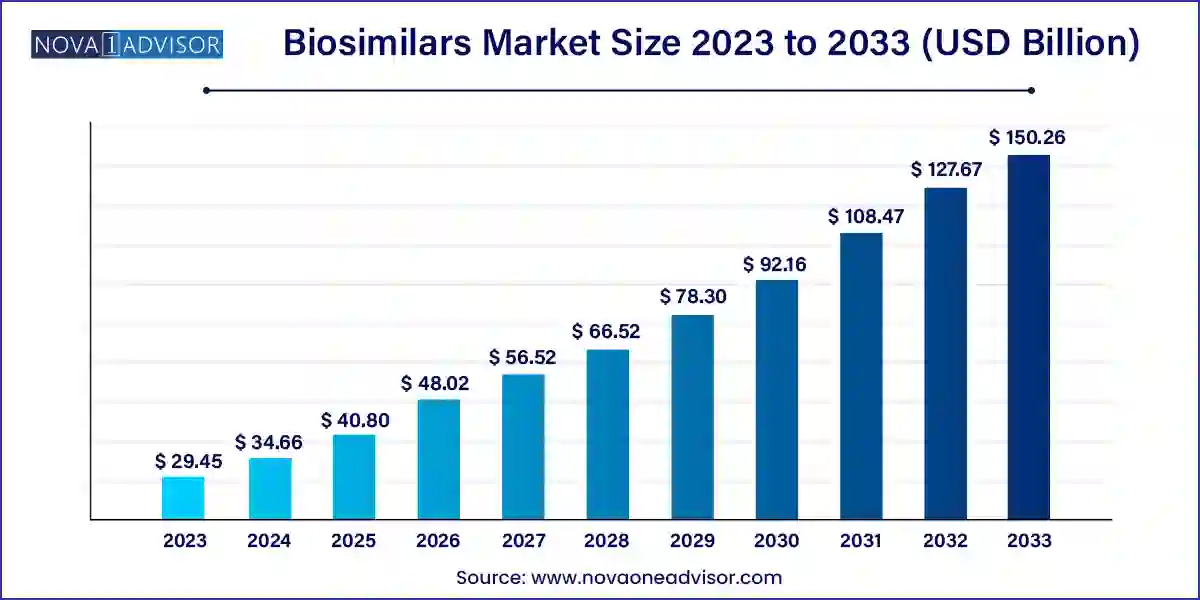
The global biosimilars market size was valued at USD 29.45 billion in 2023 and is anticipated to reach around USD 150.26 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 17.7% from 2024 to 2033.
Biosimilars Market Key Takeaways
The cost-effectiveness of biosimilar drugs and the high prevalence of chronic disorders globally are some major factors contributing to market growth. In addition, these drugs are comparatively easy to produce since they require less investment in research and development while providing similar results. This can help in cutting down expenditure on health. Moreover, the reduction in production cost and increasing demand can encourage producers to shift tobiosimilars due to increased profits, which can give a further boost to this market. Biosimilars may contain a bit different substances and combinations of medical ingredients but are considered alike to their reference biologics when it comes to effectiveness and safety.
Several regulations are in place to assess the compatibility and safety of biosimilar drugs. For instance, FDA’s Abbreviated New Drug Application Process requires applicants to scientifically prove that the performance of their product is similar to the reference biologics. It can be demonstrated by proving that their product takes a similar time to reach the bloodstream as the original product. Such regulations can help in building trust in these drugs and expand their market share.Moreover, the increasing prevalence of chronic or non-communicable diseases across the globe is also expected to drive the market. According to a statistic released by the World Health Organization in September 2022, non-communicable diseases, such as cancer, diabetes, and heart diseases, cause 41 million deaths every year out of which 77% of deaths belong to low- and middle-income countries.
However, due to the lack of awareness and high costs, many patients from these countries cannot afford the necessary treatments. Since biosimilars offer similar results and are cheaper than reference biologics, they can be used to increase access to life-saving treatments for patients in these countries and lead to an increase in its customer segment.The regulations with respect to producing biosimilars require about 8 years of exclusivity and the patent expiration of several products further creates an opportunity for the players in the market. An article released in February 2020 by MJH life sciences, The Center for Biosimilars suggests 20 oncology biologics are expected to expire by 2023, which can give a further boost to the market growth during the forecast period.
The U.S. FDA had already approved three cancer-related biosimilars in 2022, which are expected to hit the market in 2023.These growing opportunities in this market are also encouraging key players to increase their investment in the research and development of biosimilars. For instance, according to an article published in Business Today in April 2022, Biocon Biologics had been planning to increase their R&D expenses by 10% to 15% to advance their pipeline of biosimilar molecules. The step is expected to help it strengthen its future position in the market. Currently, there is a boom in the pharmaceutical industry to develop biosimilar medications.
Over 700 clinical trials for biosimilars are being conducted worldwide for different indications including genitourinary, endocrinology, immunology, oncology, and other chronic diseases. The main objective of these trials is to determine the efficacy, similarity, and immunogenicity of a biosimilar drug. For instance, in April 2022, Amgen reported positive outcomes from the phase III study of its biosimilar candidate (abp 654) to Stelara (ustekinumab). Several leading companies, such as Hospira, Celltrion, Pfizer, Inc., Samsung Bioepis, and Biocon, have announced positive outcomes from the clinical trials of their biosimilar candidates. These results have a positive outreach in the market and are expected to boost market growth during the forecast period.
The COVID-19 pandemic had adversely affected the market. The pandemic led to disruptions of supply chains across the world, which restricted the supply of essential ingredients including Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient (API) needed to produce drugs. Many countries including the U.S. depended on China for the supply of these ingredients and it being the center of origin for COVID-19, the country was adversely impacted, which compelled it to block its supply to other countries. According to an article by Lazuline Bio, 70% of pharmaceutical production in India is dependent on China, and India supplies 18% of its total volume of APIs to the U.S. However, the supply chain was highly disrupted owing to the restrictions imposed by the governments of various nations.
Biosimilars Market Report Scope
| Report Attribute | Details |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 34.66 Billion |
| Market Size by 2033 | USD 150.26 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2024 to 2033 | CAGR of 17.7% |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Forecast Period | 2024 to 2033 |
| Segments Covered | Product, Application, Manufacturer Region |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) | Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Report Coverage | Revenue forecast, company ranking, competitive landscape, growth factors, and trends |
| Key Companies Profiled | Synthon Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Novartis, TevaPharmaceutical Industries Ltd., LG Life Sciences, Celltrion, Biocon, GenentechHospira, Merck Serono, Biogen idec, Inc. |
Biosimilars Market Dynamics
DRIVER: Launch of novel biosimilars
Various key market players operating in the market have a strong emphasis on the development of biosimilars. As of December 2022, FDA has approved 40 biosimilars, and 25 have launched in the US. During the COVID-19 pandemic, FDA approvals slowed significantly; however, approvals rebounded in 2022, with seven new biosimilar approvals. All seven biosimilars approved in 2022 referenced products with previously approved biosimilars; no biosimilars were approved in 2022 referencing new reference products. 2022 also registered four new product launches, including the first two Lucentis (ranibizumab) biosimilars. Additionally, in 2022, FDA designated two new interchangeable biosimilars: Rezvoglar (referencing Lantus (insulin glargine)) and Cimerli (referencing Lucentis (ranibizumab)). Although there was an overall decline in approvals during the 2020 to 2021 timeframe, the number of development programs participating in the FDA’s Biosimilar Development Program has continued to rise. As of April 2023, there are around 60–70 biosimilars under pipeline studies. (Clinical.gov); half of them will be launched in three to four years. Growing approvals of biosimilars will ensure access to a greater pool of therapeutics and drive market growth.
RESTRAINT: Complexities in Manufacturing
Developing biosimilars is a highly complex and costly process that requires significant investments, technical capabilities, clinical trial expertise, scientific standards, and quality systems. Unlike the development of generic medicines, biosimilar manufacturers must invest in clinical trials and post-approval safety monitoring programs similar to that of the original innovator companies. Developing a biosimilar is a complex process. Biosimilars, like all biologics, are produced through an intricate, multistep process using living cells. However, the cell line and manufacturing process of the reference product are proprietary and belong to the original manufacturer.
For new entrants, the cost of developing biosimilars ranges from USD 100–250 million, including the cost of constructing a plant capable of producing biosimilars on a large scale. Besides this, the estimated timeframe for setting up a biosimilar/biological production capacity is anywhere from five to seven years; the cost can vary based on the location. The requirement for such high investments extends the time for companies to break even or to get sufficient returns on investment. In addition, companies with manufacturing experience (especially in biologics), such as Amgen and Biogen Idec, will have a considerable advantage over new companies with no such manufacturing experience. Hence, large pharmaceutical companies are expected to dominate the market as they bring marketing, sales, R&D, and manufacturing expertise.
OPPORTUNITY: Emerging markets
Markets across the Asia Pacific, Latin America (LATAM), and the Middle East offer significant growth opportunities to biosimilar manufacturers primarily due to the presence of less-stringent regulatory guidelines in developing countries. They differ from established markets regarding regulatory pathways, payer perceptions, pricing, affordability, and competitive landscapes. China and India are considered attractive destinations for R&D outsourcing for global biosimilar development and manufacturing companies, mainly due to their low labor & laboratory setup costs and the availability of skilled resources. This has drawn significant attention from key market players.
The market in Asia Pacific is a dynamic and rapidly evolving industry, with several key players leading the way: Celltrion (South Korea), Samsung Bioepis (South Korea), Dr. Reddy’s Laboratories (India), Biocon, and Shanghai Henlius Biotech (China). These companies have been instrumental in developing and commercializing biosimilars in the region and are expected to continue driving innovation and growth in the coming years..
CHALLENGE: Excess competition and regulatory challenges
Competition in the market is among biosimilar manufacturers and from originator biologic manufacturers. Upon the entry of new biosimilar products in the market, the originator biologic manufacturer may defend using various means such as the launch of second-generation products, reformulations, dosing improvements, supporting devices, and competing on prices.
Product Insights
Based on product, the monoclonal antibodies segment accounted largest revenue share in 2023. Monoclonal antibodies are extensively used in the treatment of diseases such as cancer, rheumatoid arthritis, cardiovascular diseases, and multiple sclerosis. Monoclonal antibodies targets the specific infected cells in the treatment and hence is extensively used in the treatment of cancer, which led this segment to become the most dominant segment.
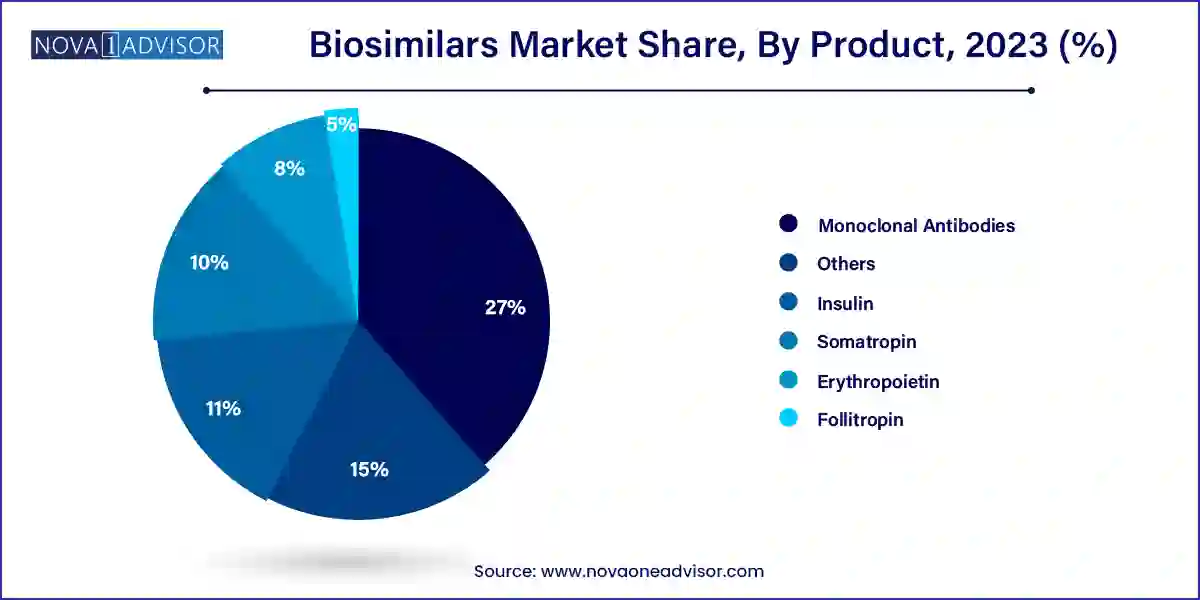
The erythropoietin segment is estimated to be the fastest-growing segment during the forecast period. The erythropoietin helps in the production of red blood cells in the bone marrow. Moreover it also treats the anemia effectively. The rising number of kidney related diseases are expected to propel the growth of this segment.
Application Insights
Based on application, the oncology segment dominated the global biosimilars industry in 2023, in terms of revenue and is estimated to sustain its dominance during the forecast period. This is attributed to the availability of biosimilars at lower prices for the treatment of cancer and the rising prevalence of cancer among the global population. According to the International Agency for Research on Cancer, around 19.3 million new cancer cases and around 10 million cancer related deaths were reported in the year 2020, across the globe. Prevalence of breast cancer in the female population is surging, accounting for around 11.7% of the new cancer cases followed by the lungs cancer that accounted for 11.4% and colorectal cancer accounted for 10.0% in 2020. Hence, the growing demand for the biosimilar drugs for the treatment of cancer is boosting the segment growth.
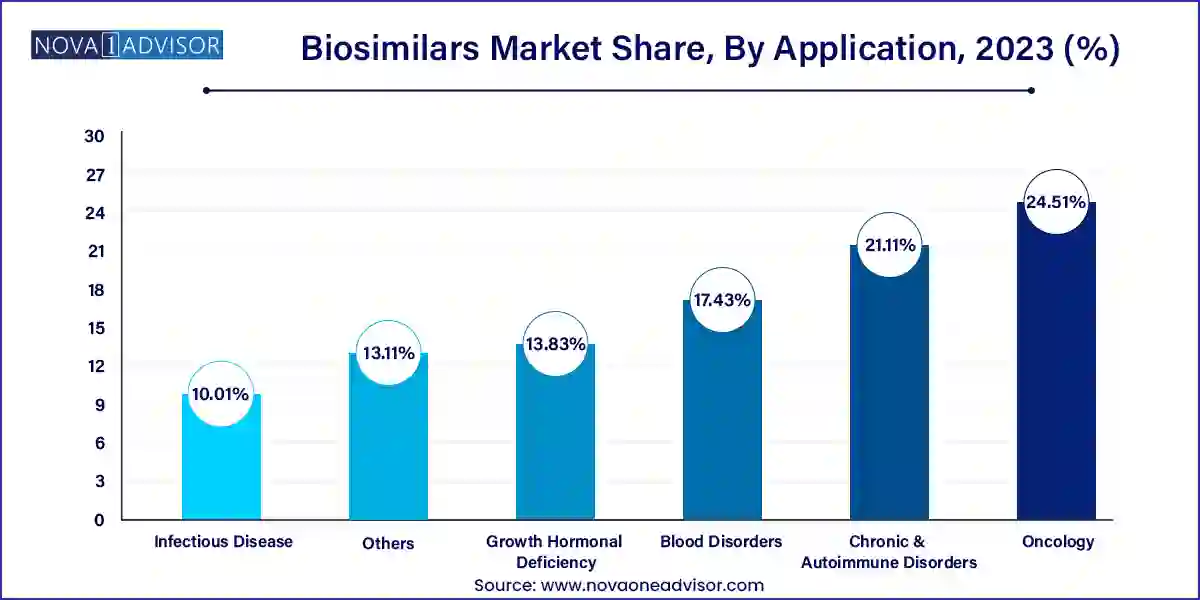
On the other hand, the growth hormonal deficiency segment is expected to be the fastest-growing segment during forecast period. The rising chances of kids getting affected with rare growth hormone deficiency during pregnancy is expected to drive the market. According to the National Organization for Rare Disorders, there are 50% chances of getting growth hormone deficiency to the child during pregnancy.
Regional Insights
North America dominated the market with the largest revenue share of 41.0% in 2023. driven by the expiration of patents for established biologic drugs. This region has the potential to become global suppliers of affordable, safe, and effective biosimilars. With more biosimilars in development across Asia-Pacific than anywhere else, emerging Asian economies are poised to enhance their domestic biologics and biotechnology capabilities. This positions domestic and regional manufacturers in these markets to potentially assume a global leadership role in the biosimilars industry in the near future.
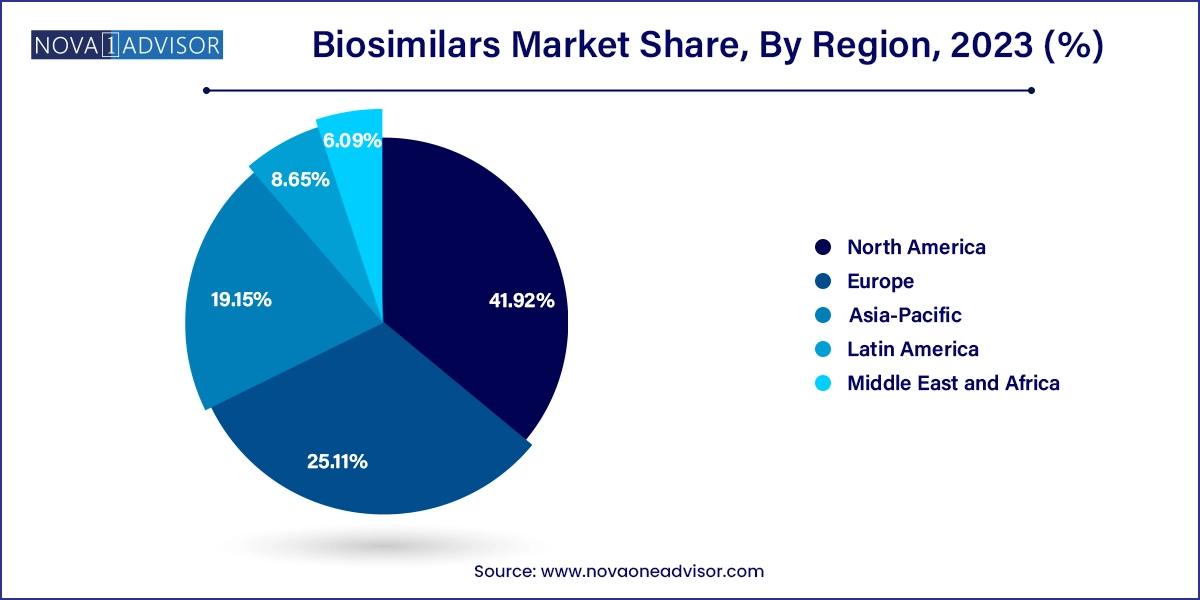
Europe is observed to grow at a notable rare in the biosimilars market, having pioneered regulatory frameworks for biosimilar approval and development. The European Medicines Agency (EMA) and the European Commission have created comprehensive information materials to enhance the understanding of biosimilars within the EU. With over 65 biosimilars approved, the EU holds the highest number of biosimilar approvals globally. While evaluation and approval occur at the EU centralized level, individual Member States are responsible for guidance on their use, including interchangeability, switching, and substitution practices. The EMA, a decentralized EU body, plays a critical role in maintaining high standards for biosimilar medicines, solidifying Europe's leadership in this sector.
Recent Developments of Biosimilars Industry:
Biosimilars Market Top Key Companies:
Biosimilars Market Report Segmentation
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2033. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the Biosimilars market.
By Product
By Application
By Manufacturer
By Region