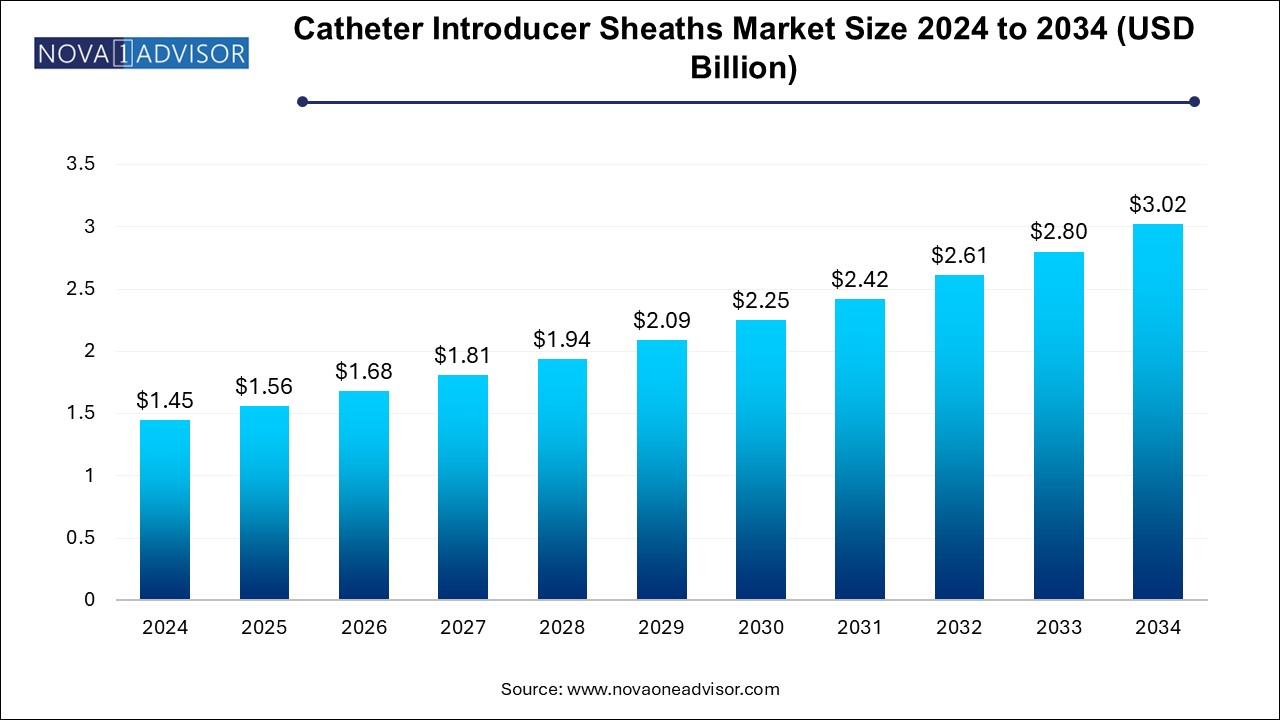
The catheter introducer sheaths market size was exhibited at USD 1.45 billion in 2024 and is projected to hit around USD 3.02 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 7.6% during the forecast period 2024 to 2034.
The catheter introducer sheaths market is an essential component within the interventional and vascular access medical devices space. Introducer sheaths are specialized delivery systems designed to facilitate the safe and efficient insertion of catheters, guidewires, and other interventional tools into the vasculature, primarily during diagnostic and therapeutic procedures. These sheaths are used across a variety of specialties, including interventional cardiology, neurology, radiology, and electrophysiology, and are critical in ensuring procedural success and patient safety.
Introducer sheaths provide a conduit that minimizes vascular trauma, prevents bleeding, and reduces procedural time. They are especially vital in complex catheterization procedures, including coronary angioplasty, transcatheter valve repair, pacemaker implantation, and electrophysiological ablation, where repeated instrument exchanges occur. The market consists of two primary product types: integrated introducer sheaths, which come with embedded valves and dilators, and separable introducer sheaths, designed for modularity and specific anatomical challenges.
The global demand for catheter introducer sheaths is propelled by the increasing prevalence of cardiovascular diseases (CVDs), chronic kidney disease (CKD), peripheral arterial disease (PAD), and neurovascular disorders. The growth of minimally invasive procedures, supported by technological advances in sheath design—such as hydrophilic coatings, kink resistance, and smaller outer diameters with larger inner lumens—are also boosting market adoption.
As healthcare systems continue to emphasize reduced procedure times, improved patient outcomes, and cost-efficiency, introducer sheaths are becoming indispensable tools in both routine and complex interventional settings. Furthermore, a surge in catheter-based interventions across outpatient and ambulatory surgical centers (ASCs) is creating a robust and expanding market opportunity for sheath manufacturers globally.
Rising adoption of minimally invasive interventions, increasing the demand for catheter introducer sheaths in cardiology, neurology, and vascular surgery.
Technological advancements in sheath design, including anti-kinking properties, hydrophilic coatings, and biocompatible materials.
Growth in outpatient and ambulatory care driving preference for easy-to-use, disposable sheath systems.
Increased use of large-bore sheaths in structural heart procedures such as TAVR (Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement).
Integration of hemostatic valves and anti-backflow systems into introducer sheaths to reduce bleeding and contamination risks.
Expansion of training simulators using introducer sheaths for interventional radiology and cardiology education.
Surge in electrophysiology procedures fueling demand for long sheaths with torque control for precise catheter navigation.
Development of radiation-reducing sheath materials, especially relevant in high-exposure interventional procedures.
Growing investment in emerging markets, particularly in Asia Pacific and Latin America, expanding access to interventional therapies.
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 1.56 Billion |
| Market Size by 2034 | USD 3.02 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2024 to 2034 | CAGR of 7.6% |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2024-2034 |
| Segments Covered | Product, End-use, Region |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) | Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Regional Covered | North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, MEA |
| Key Companies Profiled | Terumo Corporation; Merit Medical; Medtronic; Galt Medical Corporation; Cordis Corporation; Oscor Inc; Abbott; Stryker; BD; B. Braun Interventional Systems Inc. |
One of the most significant drivers of the catheter introducer sheaths market is the escalating burden of cardiovascular disease (CVD), which remains the leading cause of death globally. Conditions such as coronary artery disease (CAD), heart failure, atrial fibrillation, and congenital heart defects are increasingly treated through minimally invasive catheter-based interventions rather than open surgery.
Procedures such as angioplasty, stenting, cardiac rhythm management (CRM), and transcatheter valve therapies all depend on vascular access systems, including introducer sheaths. These devices streamline catheter insertion, improve navigation efficiency, and maintain hemostasis, thereby reducing complications and procedure time. According to estimates from the World Heart Federation and WHO, CVD cases are expected to rise sharply due to aging populations, lifestyle diseases, and improved diagnostic capabilities—making catheter-based treatments more common and reinforcing sustained market demand.
Despite their utility, catheter introducer sheaths are not without risk. A key restraint is the potential for vascular access complications, including arterial dissection, hematoma formation, thromboembolism, and infection at the access site. Particularly in high-risk patient populations or during long procedures, the use of larger or rigid sheaths may contribute to vessel trauma or bleeding complications.
Moreover, sheath-related infections, though relatively rare, can have serious clinical consequences, including systemic sepsis. The challenge is heightened in patients with immunosuppression or chronic illness. As a result, clinicians may be cautious in adopting newer sheath products without robust data on safety, biocompatibility, and infection prevention features. Addressing these concerns through innovation in coatings, antimicrobial materials, and sheath design remains critical for continued growth.
An emerging opportunity for the catheter introducer sheaths market is the rapid growth of ambulatory surgical centers (ASCs) and office-based interventional suites, particularly in developed healthcare systems focused on cost containment and efficiency. ASCs are increasingly performing same-day interventions such as diagnostic angiography, vascular stenting, and electrophysiology studies, all of which rely on introducer sheaths.
These facilities require disposable, easy-to-use, low-profile introducer systems that can minimize patient downtime, reduce complexity, and ensure sterility. Manufacturers who can develop sheath kits tailored for outpatient procedures—featuring simplified setup, integrated valves, and compact packaging—are likely to gain a competitive edge. The global movement toward decentralizing healthcare delivery, supported by regulatory approvals and payer incentives, makes this a lucrative segment for growth.
The integrated introducer sheaths segment held the largest share of over 60.2% in 2024, Riven by their all-in-one design which includes dilators, hemostatic valves, and radiopaque markers. These systems streamline procedural workflows, enhance vascular access precision, and reduce the need for multiple product exchanges. Their popularity is particularly high in high-throughput hospital cath labs and structural heart intervention programs where ease and safety are paramount.
The seamless insertion process and minimal assembly requirements make integrated sheaths ideal for rapid deployment during critical procedures like coronary angiography or neurovascular catheterization. Leading devices often feature kink-resistant construction, color-coded sizing, and biocompatible coatings, enhancing both safety and user experience.
Separable introducer sheaths are the fastest growing product category, gaining traction for their modularity and ability to accommodate varying anatomical needs. These sheaths are particularly useful in pediatric interventions, complex aortic access, or electrophysiology, where procedural customization is often required. Their ability to be peeled or removed in stages without disrupting the catheter's position provides clinical flexibility.
As interventional procedures become more tailored and anatomically diverse, separable sheath systems offer a valuable tool for precision and adaptability—making them attractive to niche specialists and training institutions alike.
The hospitals segment held the largest share at 60.0% in 2024. Accounting for the largest share of catheter introducer sheath usage. These facilities perform the majority of complex cardiovascular, neurovascular, and oncological catheter-based procedures, often requiring multiple sheath insertions across disciplines. Hospitals also possess the infrastructure for large-volume procurement, device sterilization, and procedure standardization.
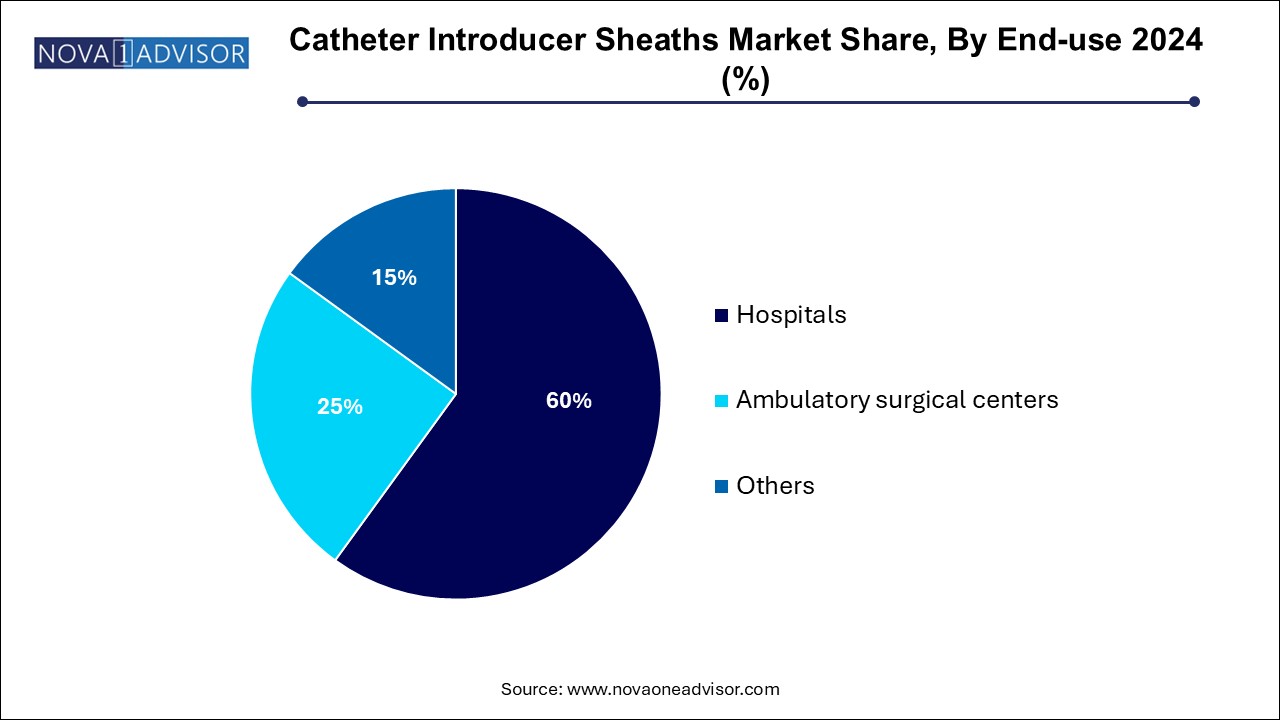
Moreover, tertiary care hospitals and academic medical centers are at the forefront of clinical trials, hybrid procedures, and next-gen device adoption, thereby driving early uptake of innovative sheath designs.
Ambulatory surgical centers (ASCs) represent the fastest growing segment, propelled by healthcare decentralization, reimbursement support for same-day procedures, and lower operating costs. ASCs are increasingly performing diagnostic angiograms, catheter ablations, and dialysis access procedures, which demand reliable, compact, and disposable sheath systems. Manufacturers catering to this segment are focusing on pre-packaged kits, intuitive labeling, and training aids, which align with the staffing models and workflow efficiency goals of outpatient settings.
North America currently dominates the global catheter introducer sheaths market, supported by a high prevalence of chronic cardiovascular diseases, robust interventional infrastructure, and strong regulatory support. The U.S. alone performs over 1 million cardiac catheterization procedures annually, with increasing adoption of catheter-based therapies in structural heart and electrophysiology fields.
The region also benefits from early commercialization of new sheath technologies, supported by companies like Boston Scientific, Medtronic, Terumo Medical, and Teleflex, who maintain advanced manufacturing, distribution, and training networks across the continent. Favorable reimbursement policies from Medicare and private insurers also encourage procedural growth and device utilization.
Asia Pacific is emerging as the fastest growing market, driven by rapidly developing healthcare infrastructure, increased access to minimally invasive care, and a large population base vulnerable to heart disease and stroke. Countries such as China, India, Japan, and South Korea are investing heavily in cath labs, interventional radiology suites, and cardiac care programs.
The growing pool of trained interventionalists, coupled with improved health insurance coverage and public health campaigns, is increasing the number of catheterization procedures. Additionally, local manufacturing and strategic partnerships are making introducer sheath products more affordable and regionally tailored. Asia Pacific’s focus on scaling both tertiary and primary interventional access presents major growth potential for both global and regional device manufacturers.
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2034. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the catheter introducer sheaths market
By Product
By End-use
By Regional