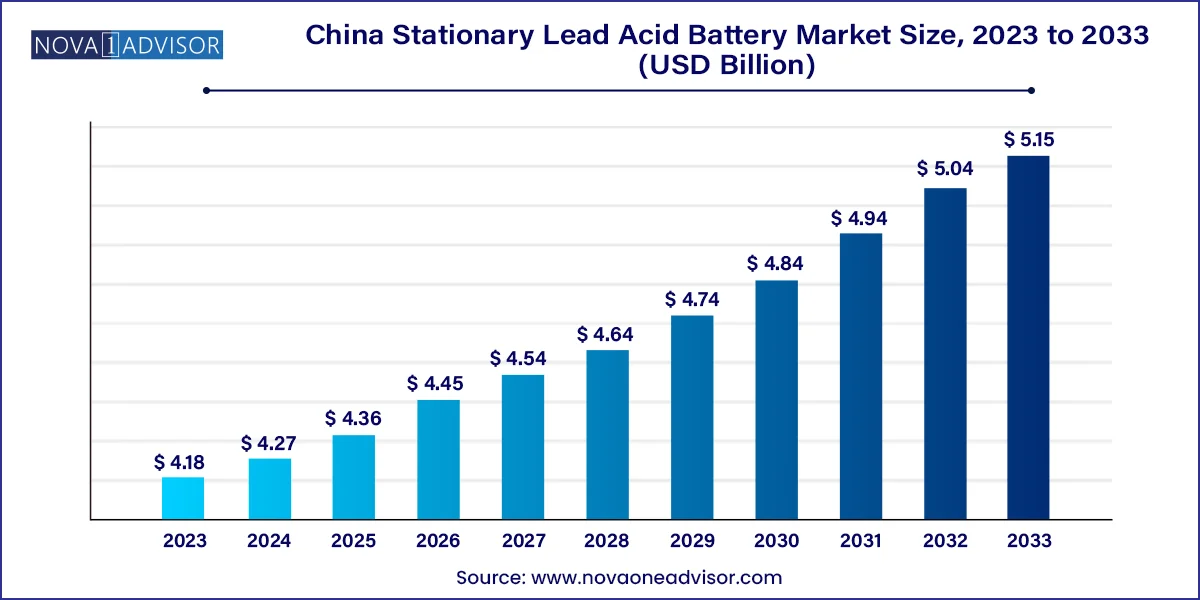
The China stationary lead acid battery market size was valued at USD 4.18 billion in 2023 and is anticipated to reach around USD 5.15 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 2.11% from 2024 to 2033.
The China Stationary Lead Acid Battery Market is a cornerstone of the nation’s robust energy infrastructure, supporting a wide array of critical sectors including telecommunications, utility grid stabilization, transportation, construction, and off-grid renewable energy systems. While the global battery industry is experiencing a transformative shift towards lithium-ion and advanced chemistries, lead acid batteries remain highly relevant in stationary applications due to their proven reliability, cost-effectiveness, and maturity in technology.
In China, the stationary lead acid battery market is primarily driven by the need for uninterrupted power supply, grid stability, and backup energy solutions for mission-critical operations. These batteries are widely deployed in telecom base stations, railway signaling systems, commercial and residential buildings, and in backup power systems for oil & gas installations. The surge in data centers and ongoing investments in smart grid infrastructure have further expanded the addressable market for lead acid battery storage systems.
Additionally, China's focus on ensuring power reliability in remote and underserved regions has encouraged the deployment of off-grid renewable energy systems, where lead acid batteries serve as the primary energy storage solution. Despite growing competition from newer technologies, lead acid batteries retain a strong foothold due to their robustness, scalability, and domestic manufacturing dominance.
China is not only the world’s largest producer of lead acid batteries but also a leading consumer, with several major domestic players accounting for a significant share of global exports. As the country continues to industrialize and digitalize, the market for stationary lead acid batteries remains poised for sustained growth, albeit with evolving use cases and increasing emphasis on environmental regulation and recycling.
Steady demand from telecom and grid backup applications: The telecom and utility sectors continue to rely on lead acid batteries for cost-effective energy backup solutions.
Proliferation of data centers and cloud infrastructure: The rapid expansion of China's digital economy is boosting the demand for uninterruptible power systems (UPS) powered by stationary lead acid batteries.
Ongoing rural electrification projects: Lead acid batteries are being deployed in off-grid and hybrid solar systems across western and central China.
Adoption of advanced VRLA (Valve Regulated Lead Acid) technologies: Sealed lead acid variants like AGM and Gel batteries are seeing increasing adoption due to safety and maintenance benefits.
Tightening environmental regulations and recycling mandates: The Chinese government is enforcing strict rules for lead acid battery disposal, driving innovation in sustainable battery designs.
Coexistence with lithium-ion in hybrid systems: Some utility and telecom setups are adopting hybrid configurations combining lead acid and lithium-ion batteries for optimized performance.
| Report Attribute | Details |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 4.27 Billion |
| Market Size by 2033 | USD 5.15 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2024 to 2033 | CAGR of 2.11% |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Forecast Period |
2024 to 2033 |
| Segments Covered | Application |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) | Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Report Coverage | Revenue forecast, company ranking, competitive landscape, growth factors, and trends |
| Key Companies Profiled | Tianneng Group; Chaowei Power Holdings Limited; China Shipbuilding Industry Corporation; Desay Battery Co.; Chilwee; Camel group; GS Battery; Shuangdeng; Narada; Leoch battery; Xiongtao vision |
One of the most prominent drivers sustaining the China stationary lead acid battery market is the ongoing and expanding demand from critical infrastructure segments—particularly telecommunications and utility grids. In a country where the telecom user base exceeds 1.7 billion mobile subscriptions and 1.3 million 5G base stations (as of 2024), the requirement for reliable backup power has become non-negotiable.
Lead acid batteries offer a cost-efficient and dependable solution for telecom tower installations across both urban and rural landscapes. These systems often operate in extreme weather conditions, where the mature and rugged performance characteristics of lead acid technology prove beneficial. Additionally, telecom operators like China Mobile and China Telecom continue to maintain legacy infrastructure where lead acid is fully integrated into their power management systems.
Moreover, China's aging electricity grid infrastructure frequently requires supplemental support in the form of battery energy storage systems to stabilize voltage and prevent outages. In such scenarios, lead acid batteries—especially VRLA types—remain a preferred choice due to their high surge capacity and maintenance-free operation. This entrenched demand from backbone sectors reinforces the lead acid battery’s position in the stationary storage market.
Despite its advantages, the stationary lead acid battery market in China faces mounting pressure from both technological advancement and evolving environmental regulations. Lithium-ion batteries, known for their higher energy density, lighter weight, and longer cycle life, are increasingly encroaching on traditional lead acid use cases—particularly in UPS and renewable energy storage.
Many commercial buildings and data centers are beginning to transition to lithium-ion for space efficiency and enhanced monitoring capabilities. Additionally, as prices for lithium-based systems continue to decline due to economies of scale and domestic cell production, the cost gap between lead acid and lithium-ion has begun to narrow, challenging the economic rationale for lead acid solutions in some applications.
Environmental regulations are also becoming more stringent. The Chinese Ministry of Ecology and Environment has tightened restrictions on lead processing and battery recycling to curb pollution and prevent lead contamination. While this is a welcome step from a sustainability standpoint, it places additional compliance costs on battery manufacturers and recyclers. Smaller players may struggle to meet these standards, leading to consolidation or market exit.
A notable opportunity lies in the use of lead acid batteries in off-grid renewable energy systems and microgrid applications, particularly in remote and underdeveloped areas of western and central China. The government’s push for rural electrification, combined with initiatives such as the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), has catalyzed the need for reliable, affordable, and easy-to-maintain energy storage solutions.
Solar photovoltaic (PV) systems installed in villages, agricultural regions, and border zones are often paired with lead acid batteries for storing excess generation. In such environments, where accessibility, cost, and simplicity take precedence over energy density or cycle life, lead acid offers a distinct advantage. The modularity and rugged nature of these batteries allow for easy installation and servicing without high-end infrastructure or skilled labor.
Moreover, localized microgrid projects supported by hybrid energy systems—solar, diesel, and battery—are beginning to proliferate as China expands access to electricity. In this context, lead acid batteries serve as the first level of backup due to their low acquisition cost and established supply chains. If properly managed with modern battery management systems (BMS), these storage units can deliver reliable performance with predictable degradation curves. This use case continues to create steady demand even as urban markets modernize.
The Telecommunication held the largest revenue share of 53.67% in 2023. largely due to the extensive coverage of telecom infrastructure across the country. As the world’s largest mobile network with extensive 4G and 5G footprints, China’s telecom base stations require highly reliable backup systems to ensure uninterrupted service. Lead acid batteries, especially Valve Regulated Lead Acid (VRLA) types, are the default energy storage solution for telecom towers due to their cost-effectiveness, thermal tolerance, and ease of replacement.
Major operators such as China Mobile, China Unicom, and China Telecom continue to install new towers in suburban and semi-urban areas to meet the growing demand for high-speed connectivity. Even in high-rise buildings, indoor telecom modules depend on lead acid backup batteries housed in secure, climate-controlled rooms. Given the long lifecycle requirements and the low cost per kWh, this application will likely retain its lead, particularly in regions where infrastructure upgrades are incremental rather than revolutionary.
Off-grid renewable energy is the fastest-growing application segment. China’s policy drive to promote clean energy access in remote and mountainous regions has led to a sharp increase in the deployment of solar and wind hybrid systems. These installations typically include lead acid batteries for energy storage, allowing communities and facilities to operate independently of the main grid. In Tibet, Xinjiang, and Inner Mongolia, hundreds of off-grid solar installations are currently operating with lead acid battery banks, providing electricity to schools, clinics, and irrigation pumps.
The government’s plan to expand the New Socialist Countryside program and deploy clean energy in agricultural zones is further enhancing this segment’s momentum. Additionally, several pilot projects funded by provincial governments are trialing microgrids with lead acid-lithium hybrid storage systems, signaling a new wave of flexible deployment models.
China is not only a major consumer but also a global leader in the production and export of lead acid batteries. The country's vast industrial base, state-backed infrastructure initiatives, and dominant telecom network make it an ideal environment for the deployment of stationary lead acid battery systems. According to recent industry data, China accounts for over 40% of global lead acid battery output, with a large share allocated to domestic stationary storage.
Regulatory support for legacy backup systems in critical sectors like railways, telecom, and government buildings continues to sustain market demand. Moreover, local governments provide incentives for rural energy projects that incorporate reliable and affordable technologies like lead acid batteries.
In cities like Shenzhen, Guangzhou, and Chengdu, major battery manufacturers such as Narada Power, Sacred Sun, and Tianneng are driving innovation in VRLA technology and integrated storage systems. These players are collaborating with real estate developers, government agencies, and data center operators to deploy intelligent UPS systems with enhanced thermal management and remote diagnostics.
At the same time, China’s strict environmental regulations, such as the “Green Lead” initiative, are driving battery producers toward more sustainable practices. Manufacturers are investing in closed-loop recycling, lead reclamation, and waste treatment technologies to align with national environmental goals. This dual emphasis on economic utility and ecological responsibility continues to shape the trajectory of the market.
February 2024 – Narada Power announced a strategic agreement with China Mobile to supply 500,000 VRLA battery units for new 5G base stations across rural China, with initial deployments in Sichuan and Yunnan provinces.
January 2024 – Tianneng Power launched a new smart battery management platform designed to monitor the performance and safety of lead acid batteries in building-integrated backup systems across commercial real estate hubs in Shanghai.
December 2023 – Sacred Sun secured a contract with the State Grid Corporation of China (SGCC) to provide stationary lead acid batteries for backup power at 120 substations in the northern and northeastern provinces.
November 2023 – Leoch International established a new recycling facility in Anhui province, focused on processing and recovering materials from retired lead acid battery systems in compliance with China’s updated e-waste laws.
October 2023 – Fengfan Co., Ltd. expanded its research division to focus on hybrid lead-lithium energy storage systems for microgrid and renewable integration projects in western China.
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2033. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the China Stationary Lead Acid Battery market.
By Application