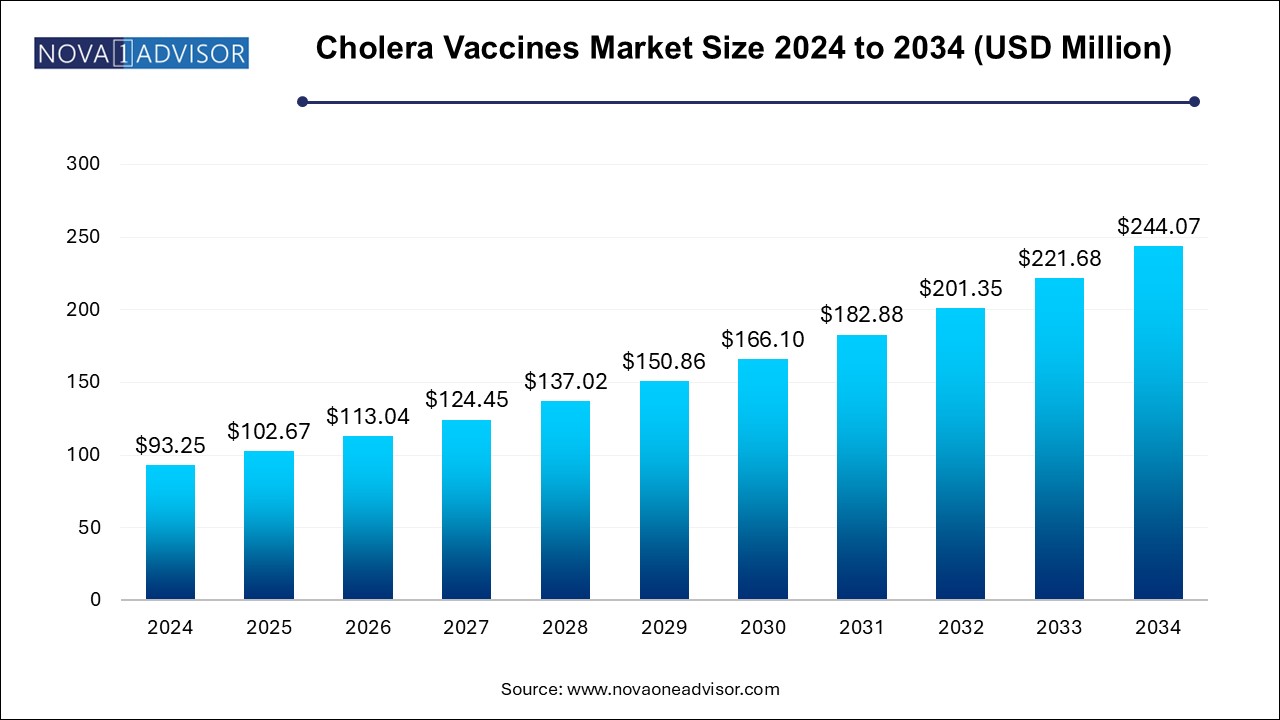
The cholera vaccine market size was exhibited at USD 93.25 million in 2024 and is projected to hit around USD 244.07 million by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 10.1% during the forecast period 2024 to 2034.
The cholera vaccines market plays a vital role in the global public health landscape, particularly in regions grappling with inadequate sanitation, contaminated water supplies, and recurring outbreaks of cholera—a waterborne bacterial infection caused by Vibrio cholerae. With approximately 1.3 to 4 million cholera cases reported globally each year, and 21,000 to 143,000 related deaths according to the World Health Organization (WHO), the importance of cholera vaccination as a preventive strategy cannot be overstated.
Cholera vaccines serve both proactive and reactive public health strategies. In endemic regions such as parts of Africa, Southeast Asia, and Latin America, oral cholera vaccines (OCVs) are administered routinely to mitigate long-term risks. During humanitarian crises, refugee displacement, and natural disasters, cholera vaccines act as rapid-response tools to curtail the spread of infection. The vaccine types range from inactivated/killed whole-cell preparations to live attenuated vaccines, offering short- to medium-term protection and forming an essential component of outbreak response kits maintained by international agencies.
Governments and non-governmental organizations (NGOs) including Gavi, the Vaccine Alliance, UNICEF, and Médecins Sans Frontières, collaborate with vaccine manufacturers to ensure widespread access to cholera vaccines through subsidized procurement and deployment in high-risk populations. Innovations in cold chain logistics, formulation, and oral dosing convenience have improved vaccine reach, especially in resource-constrained settings. The growing threat of climate change and urban overcrowding continues to amplify the demand for scalable and affordable cholera vaccination strategies.
While cholera is largely preventable, vaccine coverage remains inadequate in several high-burden areas due to supply bottlenecks, funding limitations, and geopolitical instability. However, increased R&D investments, improved manufacturing capacity, and strategic partnerships among global health bodies are expected to boost market performance significantly through 2034.
Rising global stockpile demands coordinated by WHO and Gavi to respond to cholera outbreaks and humanitarian emergencies.
Increased funding for vaccine development and local manufacturing capacity in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs).
Surge in R&D for thermostable and single-dose formulations, improving vaccine logistics and administration efficiency.
Integration of cholera vaccination into national immunization programs in endemic countries.
Growing use of public-private partnerships to accelerate vaccine access and market penetration.
Development of combination vaccines (e.g., cholera-typhoid) to streamline immunization in endemic regions.
Emphasis on oral vaccines for ease of administration and rapid deployment during outbreaks.
Adoption of digital tools and GIS mapping to track vaccination coverage and outbreak risk zones.
Increased traveler vaccination uptake amid growing global mobility and travel to endemic zones.
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 102.67 Million |
| Market Size by 2034 | USD 244.07 Million |
| Growth Rate From 2024 to 2034 | CAGR of 10.1% |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2024-2034 |
| Segments Covered | Type, Product, Distribution Channel, Region |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) | Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Regional Covered | North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, MEA |
| Key Companies Profiled | Valneva SE; Sanofi S.A.; Astellas Pharma, Inc.; Emergent BioSolutions Inc.; PavVax Inc.; EuBiologics Co., Ltd.; Shantha Biotechnics Limited; Hilleman Laboratories; Astellas Pharma Inc.; Incepta Vaccine Ltd.; Vabiotech |
A critical driver of the cholera vaccines market is the increasing frequency and geographic spread of cholera outbreaks, especially in low-income countries with limited access to clean water and sanitation infrastructure. The recurrence of cholera epidemics in parts of Africa, the Indian subcontinent, and Haiti underscores the persistent vulnerability of millions of people to this preventable disease.
In 2023 alone, several countries such as Malawi, Mozambique, and Syria reported severe cholera outbreaks, prompting emergency vaccination campaigns funded by WHO and Gavi. These rapid deployment efforts rely heavily on the global cholera vaccine stockpile—a reserve of millions of vaccine doses used during humanitarian crises. As climate change exacerbates flooding and droughts, the risk of water contamination and subsequent disease transmission grows, reinforcing the importance of preemptive and reactive vaccination efforts. The rise in conflict-induced displacement also fuels outbreak potential, particularly in refugee camps where basic hygiene and healthcare infrastructure is lacking. These conditions are contributing to consistent and growing demand for cholera vaccines worldwide.
Despite rising demand, a prominent restraint in the cholera vaccines market is supply chain bottlenecks and limited global manufacturing capacity, which restrict timely access during emergencies. Cholera vaccines, primarily produced by a handful of manufacturers, require stringent quality control and cold chain logistics, both of which pose challenges in LMICs.
For example, the global stockpile of cholera vaccines, managed by the International Coordinating Group (ICG), faced critical shortages in 2022 and 2023, leading to temporary shifts from two-dose to single-dose strategies to maximize reach. While efforts are underway to scale up production, delays in facility expansions, regulatory approvals, and raw material sourcing can create supply gaps, particularly during sudden surges in demand. Without a diversified manufacturing base and robust logistics networks, the market remains vulnerable to disruptions, ultimately impacting vaccination coverage and disease control efforts.
One of the most promising opportunities in the cholera vaccines market lies in the development of next-generation oral cholera vaccines (OCVs) with improved thermal stability and single-dose effectiveness. These innovations are critical for deployment in hot, humid, and infrastructure-limited settings where traditional cold chain requirements may be difficult to maintain.
Several research initiatives are focused on formulating freeze-dried or heat-stable OCVs that can be stored and transported without refrigeration, significantly enhancing logistical feasibility. Furthermore, single-dose vaccines could reduce programmatic costs, increase patient compliance, and facilitate faster outbreak control. These features are particularly attractive for emergency response teams operating in remote areas or during natural disasters. Continued investment in R&D, supported by global health agencies and philanthropic foundations, is likely to yield new entrants that address both efficacy and accessibility concerns, unlocking significant market growth potential.
The killed oral o1 and o139 segment dominated the market and accounted for the largest revenue share of 60.0% in 2024 and is expected to grow at the fastest CAGR of 11.5% over the forecast period. driven by their safety profile, ease of oral administration, and cost-effectiveness. These vaccines, such as Shanchol, are prequalified by WHO and widely deployed in both preventive and reactive contexts. Their use is expanding rapidly across Africa and Asia, as governments incorporate them into national immunization strategies. Their dual-serogroup formulation improves coverage against emerging strains, making them increasingly relevant in global cholera control efforts.
Whole cell Vibrio cholerae O1 vaccines with recombinant B-subunit dominate the market, primarily due to their proven efficacy, regulatory approvals, and inclusion in international vaccination programs. These vaccines stimulate robust immune responses and have been widely used in mass campaigns in cholera-endemic regions. They also offer partial cross-protection against other serogroups, enhancing their utility in outbreak containment.
Dukoral dominated the market and accounted for the largest revenue share of 32.5% in 2024 with extensive use in WHO-backed immunization programs across Asia and Africa. Manufactured by Shantha Biotechnics (a Sanofi company), Shanchol is a bivalent, inactivated oral vaccine effective against O1 and O139 strains. Its low cost, WHO prequalification, and suitability for large-scale campaigns have cemented its role as the go-to vaccine for humanitarian and public health agencies.
Vaxchora is expected to grow at the fastest rate CAGR of 14.1% over the forecast period, particularly in North America and Europe, where it is marketed for travelers visiting cholera-endemic regions. Developed by Emergent BioSolutions and approved by the U.S. FDA and European regulators, Vaxchora is a live attenuated single-dose oral vaccine. It offers rapid protection and is convenient for last-minute travelers. As global travel rebounds post-COVID and awareness increases, Vaxchora's adoption is
Hospital pharmacies in the distribution channel segment dominated the market and accounted for the largest revenue share of 46.0% in 2024, particularly in cholera-endemic countries and during organized immunization campaigns. Mass vaccination efforts managed by ministries of health, WHO, and NGOs rely heavily on centralized hospital-based systems for storage and distribution. These settings also facilitate medical supervision and patient record tracking, which are essential in high-risk populations.
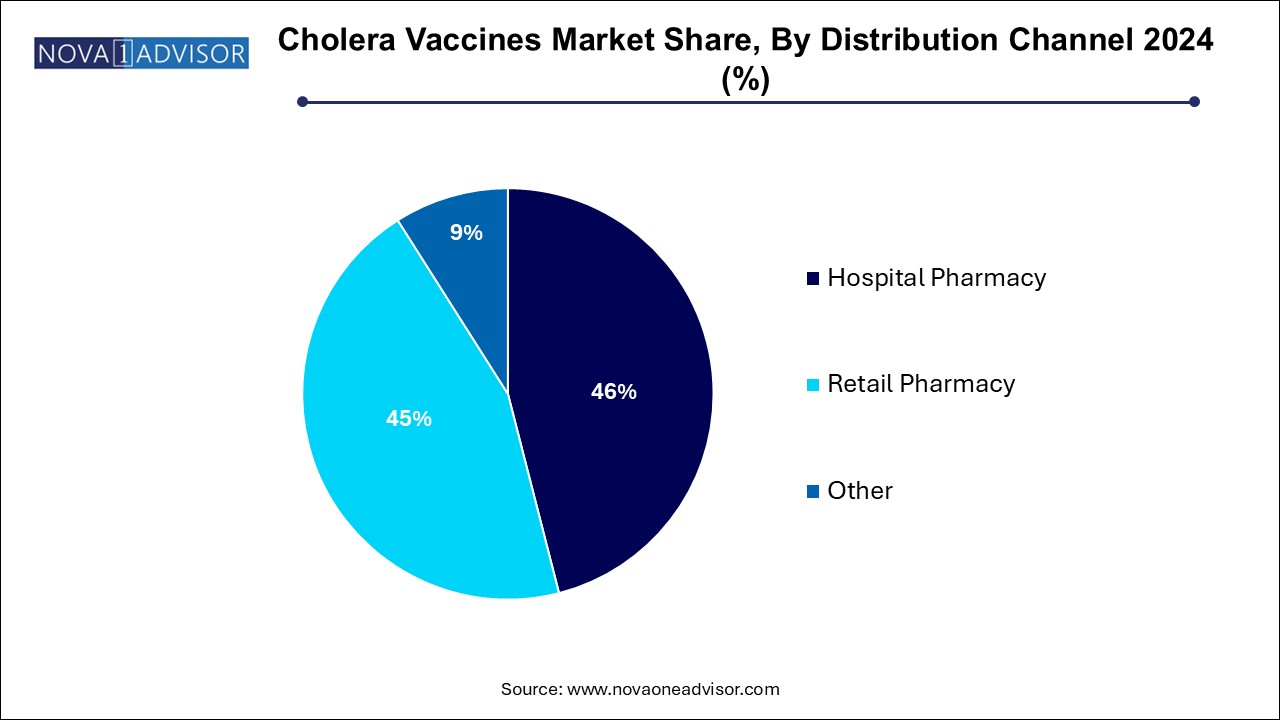
Retail pharmacies are the fastest growing distribution channel, especially in developed countries where individual travelers and expatriates seek preventive vaccination before visiting high-risk areas. Retail channels, including community pharmacies and online vaccine booking platforms, enhance accessibility and offer convenient immunization options. As travel health becomes a growing niche, retail pharmacies are expected to play a larger role in cholera vaccine distribution in urban and suburban areas globally.
The MEA region leads the cholera vaccines market, driven by high disease burden, recurring outbreaks, and large-scale humanitarian emergencies. Countries such as Yemen, Sudan, Ethiopia, Somalia, and Nigeria report frequent cholera cases due to poor water infrastructure, conflict, and population displacement. These nations are major recipients of cholera vaccine stockpile doses coordinated by WHO and Gavi.
In 2023, over 10 million doses of cholera vaccines were distributed across African countries as part of emergency response and preemptive campaigns. MEA's dominance is reinforced by partnerships between national health ministries and global health organizations to improve vaccine access and outbreak response capacity.
Asia Pacific is the fastest growing region, attributed to improved surveillance, expanded immunization programs, and increasing production capabilities. Countries like India, Bangladesh, and Nepal have witnessed historical cholera outbreaks but are now making significant progress through vaccination and infrastructure investment.
India, in particular, plays a dual role as a high-burden country and a manufacturing hub for cholera vaccines such as Shanchol. The rising domestic adoption of vaccines, growing middle-class health awareness, and participation in global health initiatives contribute to robust regional growth. Additionally, the region's manufacturing capacity and regulatory momentum are drawing attention from international partners looking to diversify supply chains.
March 2025 – Sanofi’s Shantha Biotechnics announced plans to triple its production capacity of Shanchol to meet rising global demand, supported by WHO and Gavi funding.
January 2025 – Emergent BioSolutions expanded Vaxchora distribution across European Union countries, citing a surge in travel vaccine prescriptions post-COVID.
November 2024 – International Vaccine Institute (IVI) entered a partnership with Incepta Vaccine Ltd. in Bangladesh to develop next-generation thermostable oral cholera vaccines.
August 2024 – WHO authorized a new two-dose killed cholera vaccine from a South Korean manufacturer for emergency stockpile inclusion, improving response capabilities.
May 2024 – Gavi committed $100 million in funding to replenish the global cholera vaccine stockpile and scale distribution in Africa and Southeast Asia.
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2034. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the cholera vaccine market
By Type
By Product
By Distribution Channel
By Regional