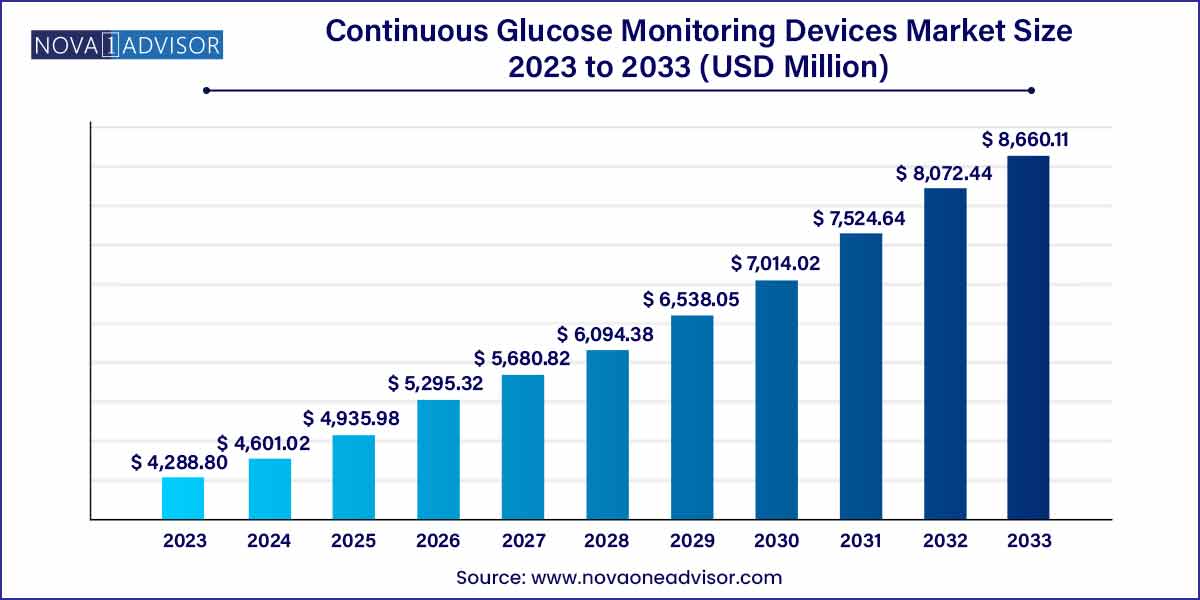
The global continuous glucose monitoring devices size was estimated at USD 4,288.80 million in 2023 and is expected to surpass around USD 8,660.11 million by 2033, and is poised to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.28% during the forecast period of 2024 to 2033.
The Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) Devices Market has witnessed a revolutionary trajectory over the past decade, transforming the management of diabetes from reactive to proactive. Continuous Glucose Monitoring systems provide real-time insights into blood glucose levels, enabling patients and clinicians to make timely and informed therapeutic decisions. Unlike traditional blood glucose meters that offer only snapshot readings, CGM devices offer a continuous stream of glucose data, typically updated every 5 minutes. This not only improves glycemic control but also significantly reduces the risk of long-term complications associated with diabetes, such as neuropathy, retinopathy, and cardiovascular disorders.
Global diabetes prevalence has soared, with over 537 million adults living with the condition in 2023, a number expected to surpass 640 million by 2030. This alarming trend has spurred both healthcare policy reforms and the adoption of innovative glucose management technologies like CGMs. Factors such as rising awareness, an aging population, and increasing adoption of wearable medical technologies have contributed to the robust growth of this market.
In recent years, the CGM market has transitioned from being niche and specialist-driven to mainstream and user-centric. Modern devices now feature smartphone connectivity, cloud-based data sharing, and algorithm-driven alerts. Companies are increasingly integrating artificial intelligence and predictive analytics into CGM ecosystems, moving toward a closed-loop diabetes management solution. With these advances, CGMs are not just tools they are becoming digital health platforms.
Integration of CGMs with Insulin Delivery Systems (Closed-Loop Systems): Development of artificial pancreas solutions using CGM and insulin pumps.
Miniaturization and Wearable Innovation: Newer CGMs are smaller, less intrusive, and more comfortable for long-term use.
App-Based Real-Time Monitoring: Bluetooth and 4G-enabled CGMs sync with mobile apps, enabling real-time glucose tracking and trend analysis.
Adoption Beyond Type 1 Diabetes: Increasing usage in Type 2 diabetes patients, gestational diabetes, and even non-diabetic hypoglycemia.
Subscription-Based CGM Models: Companies are offering hardware-as-a-service with recurring revenue models, making CGM more affordable.
Pediatric and Geriatric Expansion: Specific designs and protocols for children and elderly patients are becoming more common.
AI-Powered Predictive Alerts: Advanced algorithms provide early warnings for hypo/hyperglycemia based on real-time trends.
Reimbursement Policy Improvements: Expanded insurance coverage and government subsidy programs are making CGMs more accessible.
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 4,288.80 Million |
| Market Size by 2033 | USD 8,660.11 Million |
| Growth Rate From 2024 to 2033 | CAGR of 7.28% |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Forecast Period | 2024-2033 |
| Segments Covered | Component, End-use, Connectivity, Region |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) | Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Regional Scope | North America; Europe; Asia Pacific; Central and South America; the Middle East and Africa |
| Key Companies Profiled | F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd.; Dexcom Inc.; Abbott Laboratories; Medtronic Inc.; Ypsomed AG; GlySens Incorporated; Ascensia Diabetes Care. |
The most influential driver in the CGM market is the rising prevalence of diabetes globally, especially Type 2 diabetes, which accounts for over 90% of all cases. Lifestyle shifts sedentary behavior, poor diet, urbanization have contributed to this surge. In developed markets like the U.S., one in three adults is estimated to have prediabetes, making them prime candidates for early intervention technologies like CGM.
The growing clinical evidence supporting CGM efficacy in improving HbA1c levels and reducing hypoglycemic episodes has prompted national health systems to adopt CGMs as part of standard diabetes care. For example, the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) in the UK updated its 2023 guidelines to recommend CGM for all patients using insulin therapy. Such endorsements not only boost clinical confidence but also increase device reimbursement, further driving market penetration.
While technological advancements have made CGMs more user-friendly, cost remains a critical barrier, especially in developing economies. The price of sensors which must be replaced every 7–14 days can be prohibitive for many patients, particularly where insurance coverage is limited. A full monthly CGM setup, including sensors, transmitters, and receivers, can range from $250 to $500 or more, depending on the brand and region.
Even in developed countries, reimbursement disparities exist. Some private insurers may only cover CGMs for Type 1 diabetes, excluding large segments of patients with Type 2 diabetes who would benefit from the technology. Additionally, rural populations often face accessibility issues due to the limited availability of trained healthcare providers to prescribe and manage CGM systems. These economic and infrastructural challenges hinder widespread adoption.
One of the most promising opportunities in the CGM market lies in the integration of CGMs with broader digital health platforms. Companies are increasingly bundling CGMs with mobile apps, fitness trackers, telemedicine services, and cloud-based data management tools. This creates a holistic patient monitoring system that not only tracks glucose levels but also monitors physical activity, diet, heart rate, and sleep patterns.
For example, in March 2024, Dexcom announced a collaboration with Fitbit to synchronize glucose readings with fitness data, allowing users to understand how exercise impacts their glucose trends. Such integrations open up vast commercial opportunities beyond traditional diabetic care, tapping into wellness and preventive health markets. Furthermore, remote patient monitoring (RPM) programs, fueled by government funding and insurance reimbursement, are adopting CGMs to manage high-risk patients outside clinical settings.
Sensors dominated the market, primarily because they are the central and most frequently replaced part of CGM systems. A sensor is inserted under the skin and continuously measures glucose levels in the interstitial fluid. As most sensors need replacement every 7–14 days, they represent a recurring revenue stream for manufacturers. Sensors have also seen the most innovation, with newer models offering longer wear times, better accuracy, and pain-free insertion. For instance, Abbott’s FreeStyle Libre 3 sensor offers 14-day wear and one-second data transmission, showcasing sensor innovation.
Meanwhile, transmitters are the fastest-growing component, particularly due to technological upgrades and demand for real-time data synchronization. Transmitters are responsible for relaying data from the sensor to the receiver or smartphone app. Some systems now use rechargeable, waterproof, and miniaturized transmitters that can be used for multiple sensor cycles. As patients demand uninterrupted, seamless glucose monitoring with better mobile connectivity, the transmitter segment continues to see impressive growth in terms of design and features.
Home care settings dominated the CGM market, a trend amplified by the COVID-19 pandemic, which encouraged remote patient monitoring. Many CGM systems are now designed for self-insertion, real-time alerts, and mobile access, empowering patients to manage their conditions independently. The push for patient-centered care, coupled with growing awareness of proactive health management, has cemented home use as the primary end-use segment. This shift also aligns with the broader movement toward telehealth and decentralized healthcare delivery.
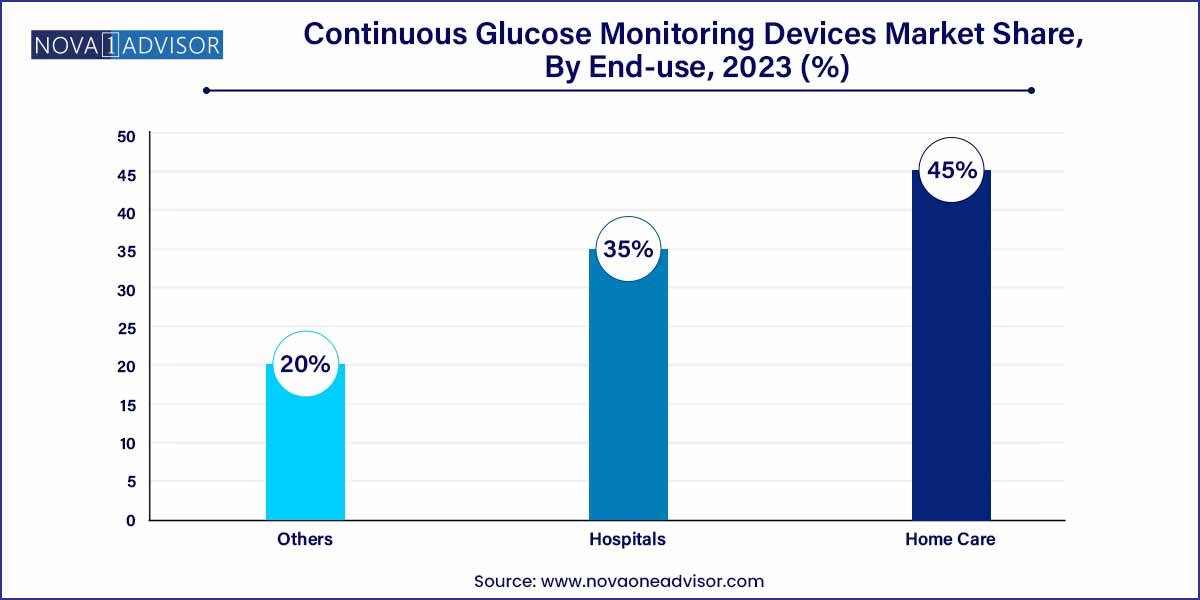
However, hospitals are the fastest-growing end-use segment, driven by CGM adoption in acute care settings, especially ICUs. Inpatient glucose management has been a topic of growing research interest. Hospitals are increasingly using CGMs for critically ill or post-surgical diabetic patients to reduce complications and mortality risks. Additionally, clinical studies evaluating CGMs in gestational diabetes and pediatric endocrinology are paving the way for wider use in hospital systems. Several pilot programs in the U.S. and EU have shown improved outcomes with inpatient CGM use.
Bluetooth-enabled CGMs dominate the market, offering seamless integration with smartphones, smartwatches, and cloud platforms. Bluetooth facilitates continuous data transfer with minimal battery consumption, supporting 24/7 tracking and instant alerts. Most next-generation CGMs now feature Bluetooth as a standard, reflecting the growing expectation for real-time, mobile-accessible health data. Devices like Dexcom G6 and G7 operate fully via Bluetooth, eliminating the need for dedicated receivers and expanding user convenience.
At the same time, 4G-based CGMs are the fastest-growing segment, particularly in professional or high-risk monitoring scenarios. 4G connectivity enables remote patient monitoring in real-time, especially useful for clinicians tracking elderly or ICU patients. It also supports faster uploads of glucose data for physician review, a critical requirement for AI-assisted decision support systems. The growing global 4G penetration, even in rural areas, is accelerating the viability and scalability of such systems.
North America remains the dominant market for CGM devices, accounting for the largest revenue share globally. The U.S. leads in both CGM adoption and innovation, with companies like Dexcom, Abbott, and Medtronic headquartered there. Strong reimbursement structures, advanced healthcare infrastructure, and high awareness levels among diabetic patients fuel market leadership. For instance, Medicare has expanded its coverage to include CGMs for Type 2 diabetes patients on insulin therapy, marking a pivotal shift toward universal adoption.
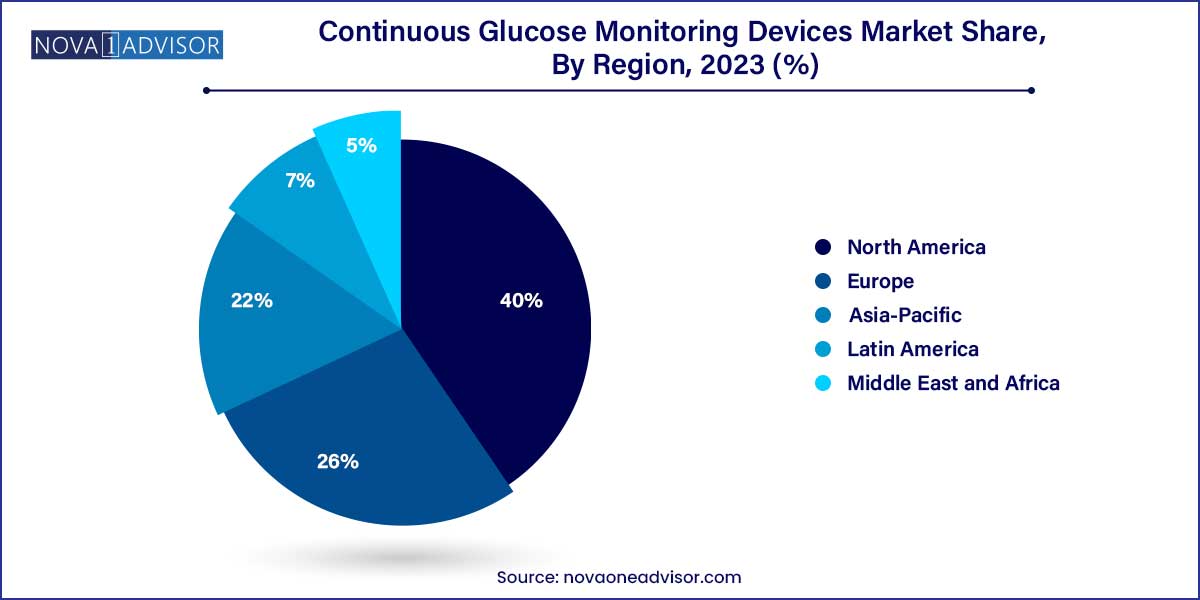
Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing region, driven by increasing diabetes prevalence, expanding healthcare access, and the entry of low-cost CGM devices. Countries like India and China are home to the world’s largest diabetic populations, yet CGM penetration remains under 5%, offering massive growth potential. In February 2025, India’s health ministry approved the inclusion of CGM devices in its public health insurance scheme for senior citizens. Simultaneously, local manufacturers are launching affordable devices tailored to price-sensitive markets, intensifying regional competition and adoption.
March 2025 – Dexcom launched its highly anticipated Dexcom G7 in Canada, featuring a 60% smaller sensor and 12-hour grace period for sensor replacement.
January 2025 – Abbott received FDA clearance for FreeStyle Libre 3, expanding its use to non-insulin-treated Type 2 diabetes patients.
December 2024 – Medtronic announced a strategic collaboration with Samsung Health to provide CGM insights directly on Samsung Galaxy smartwatches.
October 2024 – Indian company Tata Digital Health introduced a domestic CGM device, Tata SugarSense, priced 40% lower than imported competitors, aiming to target India’s middle-income diabetic population.
August 2024 – Eversense (Senseonics) announced extended wear-time trials for its implantable CGM sensor aiming for 365-day sensor durability.
June 2024 – Glooko partnered with Insulet Corporation to launch a unified CGM-pump-insulin data dashboard for healthcare providers.
This report forecasts revenue growth at global, regional, and country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2033. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the global continuous glucose monitoring devices.
Component
End-use
Connectivity
By Region