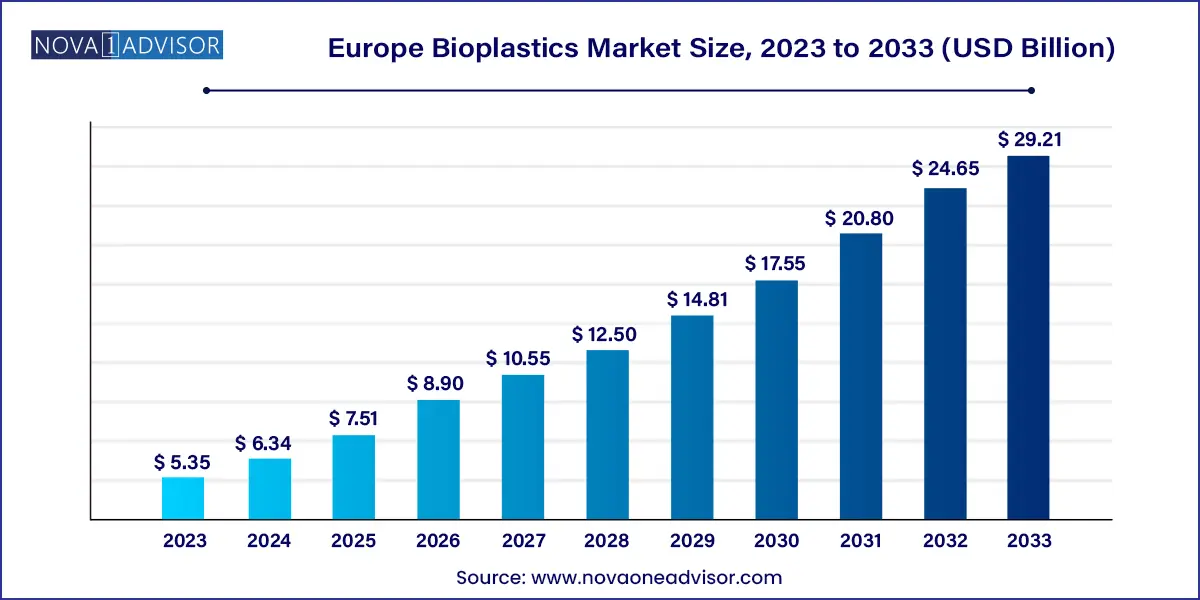
The Europe bioplastics market size was exhibited at USD 5.35 billion in 2023 and is projected to hit around USD 29.21 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 18.5% during the forecast period 2024 to 2033.
The Europe bioplastics market stands at the forefront of global sustainable material innovation, driven by regulatory push, corporate ESG commitments, and evolving consumer consciousness around plastic pollution. Bioplastics plastics derived from renewable biomass sources such as corn starch, sugarcane, cellulose, and other agricultural by-products are increasingly viewed as the viable alternative to fossil fuel-based polymers. Europe, known for its strong environmental stance, circular economy policies, and proactive waste legislation, has emerged as one of the most fertile grounds for bioplastics research, production, and commercialization.
Bioplastics can be broadly categorized as either biodegradable or non-biodegradable, depending on their chemical structure and environmental degradation behavior. While biodegradable plastics like PLA (Polylactic Acid) and PBAT (Polybutylene Adipate Terephthalate) are designed to decompose under specific conditions, non-biodegradable bioplastics such as bio-based polyethylene and bio-PET mimic the performance of traditional plastics while reducing carbon footprint.
Driven by packaging, agriculture, and automotive sectors, bioplastics are increasingly utilized in applications where environmental impact reduction and material innovation intersect. Major retailers across Europe from Carrefour in France to Tesco in the UK—are switching to compostable or bio-based packaging formats. Simultaneously, car manufacturers like BMW and Volkswagen are using biopolymers in interior components to reduce vehicle weight and boost sustainability metrics.
Government initiatives such as the EU’s Green Deal, single-use plastic bans, and plastic taxation are further catalyzing market growth. While challenges like production costs and industrial composting infrastructure persist, Europe's mature recycling ecosystem, innovation hubs, and policy alignment make it an attractive landscape for sustained investment in bioplastics.
Ban on single-use plastics driving bioplastic demand: EU-wide bans and national legislations are forcing a shift to compostable and recyclable bio-based materials.
Packaging industry leads bioplastic integration: Bioplastics are becoming standard in food service ware, films, carrier bags, and trays, especially in FMCG.
Investment in industrial composting and biodegradation infrastructure: To support PLA and PBAT usage, countries are scaling up municipal and industrial composting capacities.
R&D in high-performance non-biodegradable bioplastics: Companies are investing in bio-based PET and polyamides for durable, long-life applications like textiles and electronics.
Automotive sector innovating with bio-based composites: Lightweight bio-based polymers and blends are being integrated into interiors, panels, and wiring.
Emergence of hybrid bioplastics: Blending biodegradable and durable materials for specific use-cases like agriculture mulch films and medical packaging is gaining traction.
Public-private partnerships in bioplastic scale-up: Governments and manufacturers are co-funding pilot plants and innovation hubs to accelerate domestic production.
Shift toward second-generation feedstocks: Use of agricultural waste and non-food biomass is rising to reduce the food-versus-fuel debate.
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 6.34 Billion |
| Market Size by 2033 | USD 29.21 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2024 to 2033 | CAGR of 18.5% |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Forecast Period | 2024-2033 |
| Segments Covered | Product, Application, Country |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) | Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Country scope | Germany; UK; France; Rest of Europe |
| Key Companies Profiled | BASF SE; Biome Bioplastics; Carbois; Braskem S.A.; Novamont S.P.A.; Sabic; Teijin Limited; Toray Industries, Inc.; Total Corbion PLA; Avantium N.V. |
A defining growth driver of the Europe bioplastics market is the strong regulatory momentum built around the European Union’s commitment to climate neutrality and circular economy goals. The European Green Deal, alongside policies like the Circular Plastics Alliance and Packaging and Packaging Waste Regulation (PPWR), is accelerating the adoption of sustainable alternatives across all levels of production and consumption.
The EU’s ban on single-use plastic items such as cutlery, plates, straws, and stirrers implemented under the Single-Use Plastics Directive (SUPD) has opened massive opportunities for compostable and bio-based solutions. Companies are being mandated to redesign packaging and increase recyclability, with Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) making manufacturers accountable for end-of-life waste. Such measures are incentivizing retailers and brands to switch to bioplastics to comply with regulations while enhancing brand perception.
Despite the policy support, a key restraint in the Europe bioplastics market lies in the limited availability of industrial composting infrastructure and public misconceptions around biodegradability. Many biodegradable plastics, especially PLA and PBAT blends, require specific conditions (temperature, humidity, microbial activity) to degrade effectively, which are often only met in controlled industrial composting facilities.
Unfortunately, such facilities are not yet evenly distributed across Europe. Countries like Germany and the Netherlands are well-equipped, but Eastern European nations lag behind. Moreover, many consumers assume biodegradable plastics can decompose naturally in marine or soil environments, leading to improper disposal and environmental persistence. These issues highlight the need for improved labeling, consumer education, and infrastructure harmonization to unlock the full sustainability potential of bioplastics.
An underutilized but rapidly expanding opportunity for the European bioplastics market lies in agriculture and automotive applications. In agriculture, biodegradable mulch films, plant clips, and seedling trays are replacing conventional polyethylene products, especially in organic farming. These bioplastics reduce labor (no removal needed post-harvest), prevent soil contamination, and improve crop yield by regulating microclimate and moisture retention.
In the automotive sector, bio-based polyamides, polyurethanes, and composites are being adopted in interior panels, cable housings, door trims, and underbody panels. Manufacturers like Audi and Mercedes-Benz are embedding biomaterials into next-gen electric vehicle platforms to improve LCA scores and meet EU end-of-life vehicle directives. As sustainability becomes integral to automotive branding and performance optimization, demand for high-performance bioplastics in this segment is expected to soar.
Packaging was the largest application segment in the Europe bioplastics market, reflecting its pervasive use in food service, retail, e-commerce, and consumer goods. Bioplastics are increasingly used in flexible and rigid packaging formats, including trays, pouches, films, and clamshells. Major European supermarket chains now offer bio-based bags, produce containers, and compostable meat packaging as alternatives to petroleum-based plastics. Legislative measures—such as France’s ban on plastic packaging for over 30 fruits and vegetables (enforced in January 2022)—have accelerated the shift toward bioplastic solutions.
Automotive & transportation is one of the fastest-growing application areas due to the growing emphasis on lightweighting and carbon reduction. Bio-based polymers are being used in dashboards, air ducts, floor mats, and noise insulation systems. Companies like Renault and Fiat have announced the use of castor-oil-based polyamides and PLA composites in newer models. These materials not only offer performance parity with traditional polymers but also reduce vehicle weight and emissions. EU policies promoting electric mobility and sustainability certification are further encouraging tier-one suppliers to integrate bioplastics into car design.
Biodegradable bioplastics dominated the European market, especially in applications like packaging, agriculture films, and food service products. Materials such as PLA, starch blends, and PBAT are favored for their compostability, aligning with stringent EU waste and landfill directives. Polylactic Acid (PLA), derived from fermented plant starch (often corn or sugarcane), is widely used for rigid containers, film wraps, and disposable utensils. Its compatibility with food contact regulations and heat resistance make it suitable for food packaging. Countries like Italy and France, where compostable waste collection is more advanced, are witnessing increased PLA uptake in supermarkets and restaurants.
.webp)
Non-biodegradable bioplastics such as bio-based polyethylene (bio-PE), bio-PET, and polytrimethylene terephthalate (PTT) are the fastest-growing segment, driven by their application in durable goods. These materials behave like traditional plastics but are derived from renewable resources, offering low carbon footprints without sacrificing performance. Bio-PET is gaining traction in beverage bottles, textile fibers, and electronics casings due to its clarity and tensile strength. Brands like Coca-Cola and Danone have launched bottles made from up to 30% bio-based PET as part of their circular packaging initiatives. As industries seek materials compatible with existing recycling infrastructure, this segment is poised for exponential growth.
Germany: The Dominant Market Force
Germany leads the Europe bioplastics market in terms of production capacity, consumption, and innovation. The country’s strong manufacturing base, well-developed waste management infrastructure, and proactive environmental policies make it a hotbed for bioplastic development. German companies like BASF, FKuR, and BIOTEC are pioneers in bioplastic formulations. Furthermore, research institutions such as Fraunhofer Institute are actively involved in biopolymer optimization and recycling innovation. Germany’s dual system for waste separation enables efficient composting and collection of biodegradable plastics, especially in urban areas.
France: Fastest Growing Market with Strong Regulatory Impulse
France is emerging as the fastest-growing market, bolstered by progressive legislation and a national commitment to banning petroleum-based plastics. The French Anti-Waste Law (Loi AGEC), which mandates compostable materials in place of plastics for certain packaging and food service items, is driving massive demand for bioplastics. Companies like Vegeplast and Lactips are gaining attention with novel starch- and protein-based materials. Retail chains are rapidly switching to bioplastic-based fruit bags, bakery packaging, and ready-meal containers. With robust public awareness campaigns and government-backed subsidies, France is poised to become a benchmark for bioplastic adoption.
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2033. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the Europe bioplastics market
Product
Application
Country