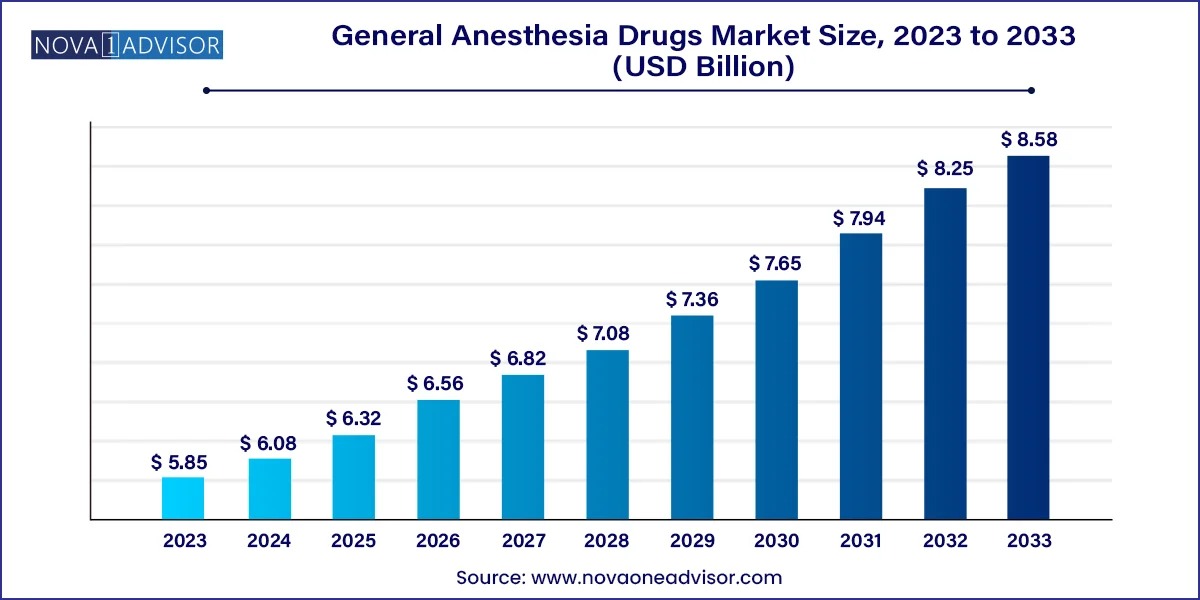
The global general anesthesia drugs Market size is expected to be worth around USD 8.58 Billion by 2033 from USD 5.85 Billion in 2023, growing at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 3.9% during the forecast period from 2024 to 2033.
The General Anesthesia Drugs Market plays a vital role in modern medicine, enabling millions of surgical procedures globally each year. General anesthesia involves the administration of drugs that induce a reversible loss of consciousness and sensation, allowing patients to undergo complex and often invasive surgeries without pain or psychological trauma. These anesthetic agents work on the central nervous system by either enhancing inhibitory pathways or suppressing excitatory responses, thereby facilitating unconsciousness, amnesia, muscle relaxation, and analgesia.
The increasing number of surgical procedures across hospitals and ambulatory surgical centers is one of the key forces driving demand for general anesthetics. With an aging global population, the incidence of age-associated health conditions such as cardiovascular disease, cancer, and degenerative joint disorders has significantly increased. These medical conditions often require surgical interventions under general anesthesia. Additionally, advancements in surgical techniques—particularly minimally invasive procedures—have expanded the scope of surgeries performed under general anesthesia, supporting market growth.
From an operational standpoint, the market is composed of several drug classes administered via different routes, primarily intravenous (IV) and inhalation. Intravenous agents such as propofol and dexmedetomidine are widely used for induction, while inhalation agents like sevoflurane and desflurane are preferred for maintenance of anesthesia. Drug choice often depends on patient physiology, procedure duration, comorbidities, and institutional preferences. Innovations in formulation, such as rapid-onset and short-acting agents, continue to optimize clinical outcomes while minimizing post-operative recovery time and adverse effects.
In recent years, the general anesthesia drugs market has been influenced by developments in pharmacology, shifting healthcare infrastructure, and regulatory reforms. Moreover, increasing focus on patient safety, pain management, and cost-effective surgical care has prompted hospitals and anesthesiologists to adopt advanced anesthetic protocols. With demand growing across both developed and emerging economies, the global general anesthesia drugs market is poised for stable and sustained growth through the forecast period.
Shift Toward Outpatient and Day Surgeries: Rising preference for ambulatory surgical centers due to cost efficiency and shorter recovery times is increasing the use of fast-acting anesthetics.
Increasing Use of Total Intravenous Anesthesia (TIVA): Growing interest in TIVA techniques, particularly for neurosurgery and cardiac procedures, is propelling demand for intravenous agents like propofol.
Aging Population Driving Surgical Demand: The global rise in elderly populations, especially in countries like Japan, Germany, and the U.S., is increasing surgical volumes and the use of general anesthetics.
Improved Safety Profiles of Modern Anesthetics: New formulations with lower side-effect profiles, rapid induction, and better hemodynamic control are gaining favor among anesthesiologists.
Integration of Smart Infusion Systems: Advancements in drug delivery systems and monitoring equipment are enabling precision dosing and real-time patient monitoring during anesthesia.
Rising Incidence of Cancer and Orthopedic Conditions: Increased prevalence of surgeries for cancer resections and joint replacements is expanding the market scope.
Post-Pandemic Recovery in Surgical Volumes: Elective surgeries, previously postponed during the COVID-19 pandemic, are resuming, reviving the demand for general anesthetic drugs.
Expansion in Emerging Markets: Infrastructure development and improved surgical access in Asia-Pacific and Latin America are fostering market penetration for anesthesia drugs.
| Report Attribute | Details |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 6.08 Billion |
| Market Size by 2033 | USD 8.58 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2024 to 2033 | CAGR of 3.9% |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Forecast Period | 2024 to 2033 |
| Segments Covered | Drug, route of administration, end-use, application, region |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) | Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Report Coverage | Revenue forecast, company ranking, competitive landscape, growth factors, and trends |
| Key Companies Profiled | Baxter International Inc.; AstraZeneca; AbbVie Inc.; B. Braun Melsungen AG; Fresenius SE & Co. KgaA; Pfizer; Hospira Inc.; Aspen Pharmacare Holdings Limited; Hikama Pharmaceuticals plc; Abbott Laboratories |
One of the most significant drivers of the general anesthesia drugs market is the consistently increasing volume of surgical interventions globally. The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that over 300 million surgical procedures are performed each year, with the number expected to grow due to population aging, expanded access to healthcare, and rising incidence of non-communicable diseases.
The expansion of elective and life-saving surgeries such as cardiovascular bypass procedures, cancer resections, organ transplants, and orthopedic joint replacements directly contributes to the demand for reliable and fast-acting general anesthetics. Propofol, sevoflurane, and remifentanil are among the most commonly used agents to support such surgeries. Furthermore, improvements in anesthesia safety have reduced perioperative complications, making general anesthesia suitable even for high-risk patients. As surgical procedures become more sophisticated and widely accessible across developing nations, the corresponding increase in anesthesia drug consumption is expected to drive market growth over the coming decade.
While the general anesthesia drugs market shows promising growth potential, it faces notable restraints stemming from regulatory complexities and drug safety concerns. Anesthetic agents are classified as controlled substances in many jurisdictions and require strict compliance with manufacturing, labeling, storage, and dispensing standards. Regulatory agencies such as the U.S. FDA, the European Medicines Agency (EMA), and regional equivalents frequently review clinical efficacy and post-marketing safety data, occasionally issuing black-box warnings or mandating recalls.
For instance, contamination concerns, formulation instability, or adverse drug reactions (ADRs) can lead to product withdrawals, causing supply disruptions and impacting manufacturer reputation. Additionally, the time-consuming and costly approval processes for new anesthesia drugs limit market entry and innovation. Smaller firms often struggle to meet stringent pharmacovigilance and Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) requirements, which hampers product pipeline expansion. This regulatory burden, while necessary for patient safety, may limit the speed of innovation and market competitiveness.
An exciting opportunity lies in the development of novel anesthetic formulations and delivery systems that enhance clinical precision and reduce systemic toxicity. Advances in nanotechnology, sustained-release mechanisms, and brain-targeted drug delivery are paving the way for next-generation anesthetic drugs. These innovations can help optimize the therapeutic window, improve onset/recovery times, and minimize adverse effects such as hypotension, nausea, and cognitive impairment.
Furthermore, the integration of anesthesia delivery systems with real-time patient monitoring and automated infusion pumps allows clinicians to titrate dosages with greater accuracy, reducing the margin of error and improving outcomes. Innovations like closed-loop anesthesia control (CLAC) systems, pharmacogenomics-guided anesthesia, and digital health analytics are contributing to personalized anesthesia strategies. Companies that invest in such R&D are likely to gain significant competitive advantage, especially in high-value hospital networks and academic surgical centers.
In 2023, the propofol segment dominated the market with a substantial revenue share of 25.41%, owing to its widespread use as the standard intravenous induction agent for general anesthesia. Known for its rapid onset, short duration of action, and favorable safety profile, propofol is extensively used across diverse surgical specialties. It facilitates smooth induction and recovery, making it ideal for outpatient and ambulatory procedures. Additionally, propofol is commonly employed in intensive care units (ICUs) for sedation during mechanical ventilation. Its versatility, availability in generic formulations, and relatively low cost further contribute to its market leadership.
Dexmedetomidine is the fastest-growing sub-segment, attributed to its increasing adoption in surgeries requiring light to moderate sedation without respiratory depression. As a selective alpha-2 agonist, dexmedetomidine is preferred in cardiac and neurosurgical procedures, as well as for ICU sedation. Its hemodynamic stability and analgesic-sparing effects make it particularly valuable in patients with comorbidities. With growing interest in opioid-sparing anesthesia and multi-modal analgesia protocols, the demand for dexmedetomidine is expected to rise significantly.
Intravenous route of administration dominated the market, driven by the popularity of drugs like propofol, midazolam, and dexmedetomidine for rapid induction and sedation. IV administration ensures precise dosing, quick onset, and smoother transitions between anesthesia stages. It is especially favored in emergency and outpatient settings where immediate drug effect is essential. The use of IV anesthetics also supports TIVA protocols, which eliminate the need for gas-based equipment and provide better hemodynamic control.
Inhaled anesthetics are witnessing steady growth, particularly in maintenance phases of prolonged surgeries. Agents such as sevoflurane and desflurane offer predictable depth of anesthesia and rapid washout, leading to shorter recovery times. Pediatric and bariatric surgeries often rely on inhalational anesthetics due to their efficacy and ease of titration. Technological enhancements in vaporizers and anesthesia workstations are further supporting the adoption of inhalation-based anesthesia.
General Surgery held the leading share, reflecting the broad scope of procedures it encompasses—from appendectomies and cholecystectomies to abdominal explorations and hernia repairs. These surgeries often require full-body anesthesia for effective pain control and patient immobilization. General anesthetics like sevoflurane and propofol are standard components of anesthesia protocols for such interventions. The routine and high-frequency nature of these procedures contributes to steady demand for anesthesia drugs.
Knee and hip replacements are emerging as the fastest-growing application segment, due to the rising prevalence of osteoarthritis and aging populations in developed countries. While some of these surgeries can be conducted under spinal anesthesia, general anesthesia is frequently used, particularly in bilateral or revision surgeries. The need for precise anesthetic management to avoid post-operative complications and facilitate early mobilization supports the growing utilization of both intravenous and inhaled anesthetics in orthopedic surgeries.
In 2023, the hospitals segment dominated the market, capturing a substantial revenue share of 68.46%. As they perform the majority of complex and high-risk surgical procedures that require general anesthesia. Hospitals are equipped with multidisciplinary teams, advanced surgical infrastructure, and critical care units that enable continuous monitoring of anesthesia. Moreover, the presence of anesthesiology departments and intensive care services make hospitals the primary consumers of both induction and maintenance anesthetics. Institutional purchasing power and procurement policies also drive high-volume acquisitions of anesthesia drugs in this segment.
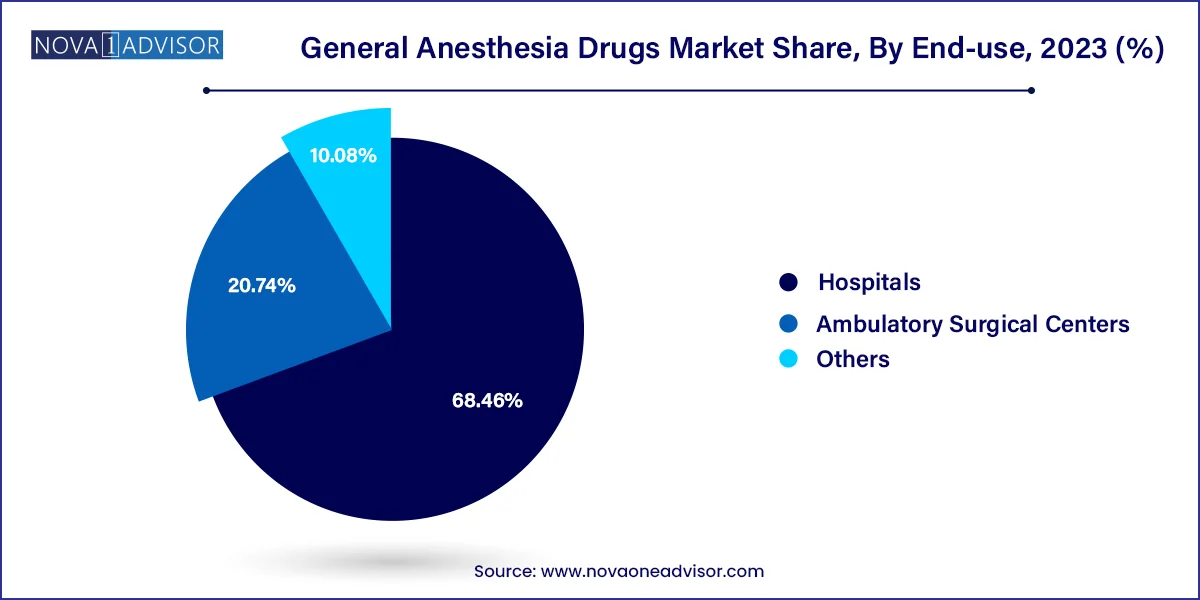
The Ambulatory Surgery Centers (ASC)s are anticipated to grow at the fastest CAGR of over 4.1% during the forecast period. Owing to the increasing shift toward day-care and minimally invasive procedures. ASCs demand anesthetics that offer fast onset and quick patient recovery, reducing post-operative care requirements. Drugs like propofol and desflurane are especially well-suited for this setting. The rising number of ASCs globally and patient preference for convenient, lower-cost surgical options are expected to propel anesthetic drug usage in this segment over the next decade.
February 2024: Fresenius Kabi launched a new formulation of propofol with extended shelf life for hospital use, aimed at reducing drug wastage and improving supply chain efficiency.
January 2024: Hikma Pharmaceuticals announced the U.S. FDA approval of its generic version of dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection, expanding its injectable anesthesia portfolio.
December 2023: AbbVie reported positive results from a Phase III trial comparing sevoflurane with newer inhalational agents for pediatric surgeries, positioning itself for regulatory expansion.
October 2023: Pfizer initiated a strategic collaboration with a Chinese distributor to expand the availability of remifentanil and midazolam in the Asia-Pacific region.
August 2023: Piramal Critical Care opened a new sterile injectable manufacturing unit in India to scale up production of propofol and fentanyl for global markets.
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2033. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the General Anesthesia Drugs market.
By Drug
By Route Of Administration
By End-use
By Application
By Region