The global geriatric medicine market size was valued at USD 158.90 billion in 2023 and is anticipated to reach around USD 333.64 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 7.7% from 2024 to 2033.
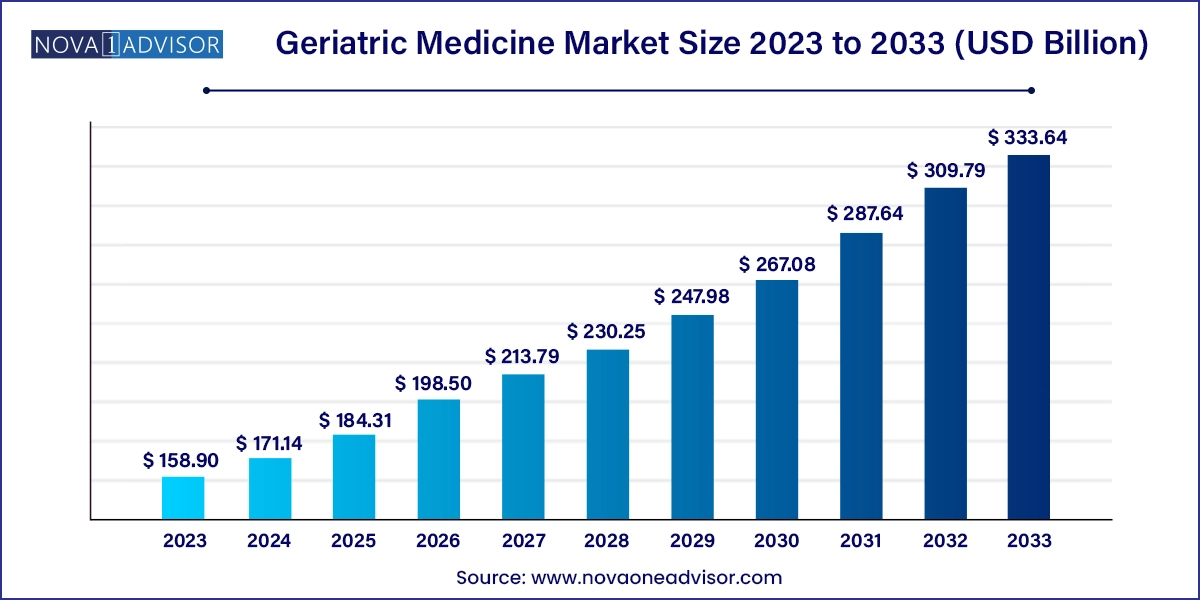
The U.S. geriatric medicine market size was exhibited at USD 43.12 billion in 2023 and is projected to hit around USD 93.76 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 8.1% during the forecast period 2024 to 2033.
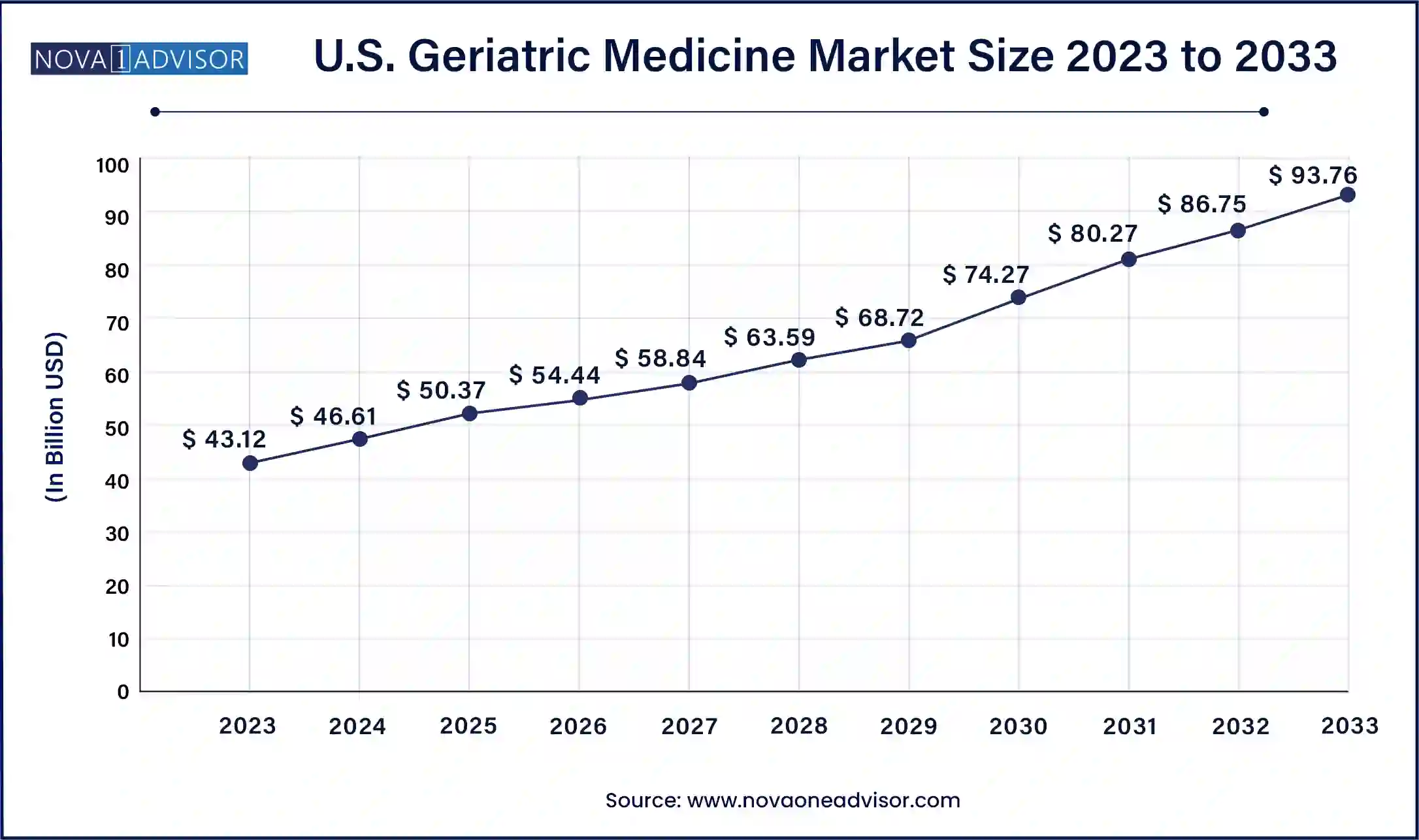
North America dominates the geriatric medicine market, accounting for the largest share due to its aging population, advanced healthcare infrastructure, and high healthcare expenditure. The United States, in particular, has over 54 million people aged 65 and older, a figure expected to exceed 80 million by 2040. This demographic shift is accompanied by rising incidences of obesity, cardiovascular disease, and neurodegenerative disorders. Medicare and Medicaid expansion has improved access to chronic disease treatments for older adults, while a thriving biopharmaceutical industry ensures the availability of cutting-edge medications.
Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing region, driven by the rapidly aging populations of China, Japan, South Korea, and India. China’s elderly population alone is expected to reach 400 million by 2050. Unlike the West, many Asia-Pacific countries are experiencing rapid aging alongside economic development, putting pressure on public health systems to adapt. Governments are increasingly funding geriatric hospitals, long-term care facilities, and domestic pharmaceutical production. Japan leads in innovation, particularly in dementia research, while India’s pharmaceutical sector is rapidly scaling up generic and biosimilar production to meet domestic and export demand.
The global geriatric medicine market is poised for sustained growth, driven by the rapid aging of the world’s population, the increasing prevalence of age-related chronic conditions, and the need for specialized therapeutic approaches tailored to older adults. Geriatric medicine also known as geriatric care refers to medical practices and drug therapies specifically designed for managing diseases, disabilities, and health conditions prevalent among the elderly. These include cardiovascular disorders, diabetes, arthritis, neurodegenerative diseases, and cancers.
As life expectancy continues to rise globally, especially in high- and middle-income countries, the population of individuals aged 65 and above is growing at an unprecedented pace. According to the United Nations, the number of people over the age of 65 is expected to more than double from 703 million in 2019 to 1.5 billion by 2050. This demographic shift has enormous implications for healthcare systems and pharmaceutical companies alike. The elderly population not only requires more frequent medical attention but also demands a broader range of medications that cater to multiple coexisting chronic diseases, commonly referred to as multimorbidity.
The geriatric medicine market includes a range of pharmaceutical products used in the treatment of common conditions such as hypertension, osteoporosis, Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, diabetes, chronic pain, and mental health disorders. The complexity of managing geriatric health necessitates a multi-pronged pharmaceutical approach that emphasizes safety, efficacy, and patient-specific customization. Polypharmacy the use of multiple drugs by a single patient is a defining feature of geriatric care, prompting innovation in drug delivery mechanisms, drug interaction screening, and personalized medication management.
Furthermore, the shift toward home-based and long-term care settings has led to increased reliance on retail and online pharmacies. This shift is transforming the supply chain and distribution landscape of geriatric therapeutics, creating new opportunities for digital health and e-commerce integration. Companies are increasingly investing in wearable health technologies, remote diagnostics, and AI-powered platforms to manage chronic illnesses more efficiently in aging populations.
Rise in Multimorbidity Management: The increasing incidence of elderly patients with two or more chronic illnesses is driving demand for combination therapies and personalized medication regimens.
Expansion of Online Pharmacies: The growing use of e-commerce platforms among caregivers and older adults is reshaping drug distribution and accessibility.
Digital Therapeutics and Remote Monitoring: Integration of wearable devices, telehealth platforms, and mobile apps in chronic disease management is transforming geriatric care models.
Geriatric Oncology Development: With cancer prevalence rising in older populations, pharmaceutical companies are focusing on geriatric-specific oncology treatments with better tolerance profiles.
Neurodegenerative Disease Innovation: Significant R&D investments are being made in addressing Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and other cognitive disorders, often in collaboration with academic institutions.
Healthcare Infrastructure Expansion in Developing Nations: Emerging markets in Asia-Pacific and Latin America are investing in elderly care programs, opening new growth avenues for geriatric drugs.
Policy and Reimbursement Enhancements: Government reforms across Europe and North America are improving drug coverage for older adults, incentivizing companies to expand product lines.
| Report Attribute | Details |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 171.14 Billion |
| Market Size by 2033 | USD 333.64 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2024 to 2033 | CAGR of 7.7% |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Forecast Period | 2024 to 2033 |
| Segments Covered | Therapeutics, condition, distribution channel, region |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) | Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Report Coverage | Revenue forecast, company ranking, competitive landscape, growth factors, and trends |
| Key Companies Profiled | F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd.; AbbiVie, Inc; Amgen, Inc; Pfizer, Inc; UCB, Inc.; Novartis AG; Bristol-Myers Squibb Company; Johnson and Johnson Services, Inc; Merck and Co., Inc; Sanofi; GSK plc; Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Ltd. |
Antihypertensive medications dominated the geriatric therapeutics segment, driven by the high prevalence of cardiovascular diseases among the elderly. Hypertension is one of the most common age-related chronic conditions, often managed using ACE inhibitors, beta-blockers, and calcium channel blockers. These medications form the foundation of many elderly patients’ treatment regimens and are typically prescribed in conjunction with other drugs. As awareness of hypertension's link to stroke and kidney failure grows, proactive screening and treatment are increasing among older populations. Pharmaceutical companies continue to innovate with extended-release formulations and fixed-dose combinations to simplify dosing for aging individuals.
In contrast, antipsychotic drugs are emerging as the fastest-growing segment, particularly for managing conditions such as dementia-related psychosis, Parkinson’s disease-related hallucinations, and late-life depression. Aging populations are seeing an increase in cognitive disorders, often accompanied by behavioral and psychological symptoms. While the use of antipsychotics in geriatric care remains controversial due to side effects, advances in second-generation medications with improved safety profiles are fostering renewed adoption. Additionally, public awareness and caregiver education are reducing the stigma around mental health, contributing to higher diagnosis rates and demand for psychiatric treatments tailored to older adults.
Cardiovascular diseases were the dominant condition treated by geriatric medicines, reflecting the global burden of heart disease among seniors. Atherosclerosis, heart failure, atrial fibrillation, and ischemic heart disease are rampant in this demographic and require ongoing medication management. Treatments include statins, anticoagulants, antiplatelet agents, and vasodilators, forming a multi-modal therapeutic approach. Innovations in cardiac care, including home-based ECG monitoring and wearable defibrillators, have also increased patient adherence to cardiovascular medications in outpatient settings. This segment benefits from long-term prescriptions and widespread healthcare access, particularly in developed regions.
Meanwhile, neurological disorders are the fastest-growing condition segment, spurred by rising cases of Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s, and mild cognitive impairment. As life expectancy increases, so does the likelihood of experiencing degenerative neurological changes. The complexity of managing these conditions often involving multi-drug regimens, caregiver support, and behavioral therapy drives the need for specialized pharmaceuticals. Japan, which has the world's oldest population, has seen rapid development in neuroprotective therapies and early diagnostic markers, further fueling segment growth.
Hospital pharmacies currently dominate the distribution landscape, owing to the frequent hospitalization of elderly patients for acute exacerbations of chronic diseases. Hospitals serve as key access points for initiating complex drug regimens and managing transitions of care. Moreover, high-value medications such as biologics and specialty drugs for cancer and autoimmune conditions are often dispensed through hospital channels under close supervision.
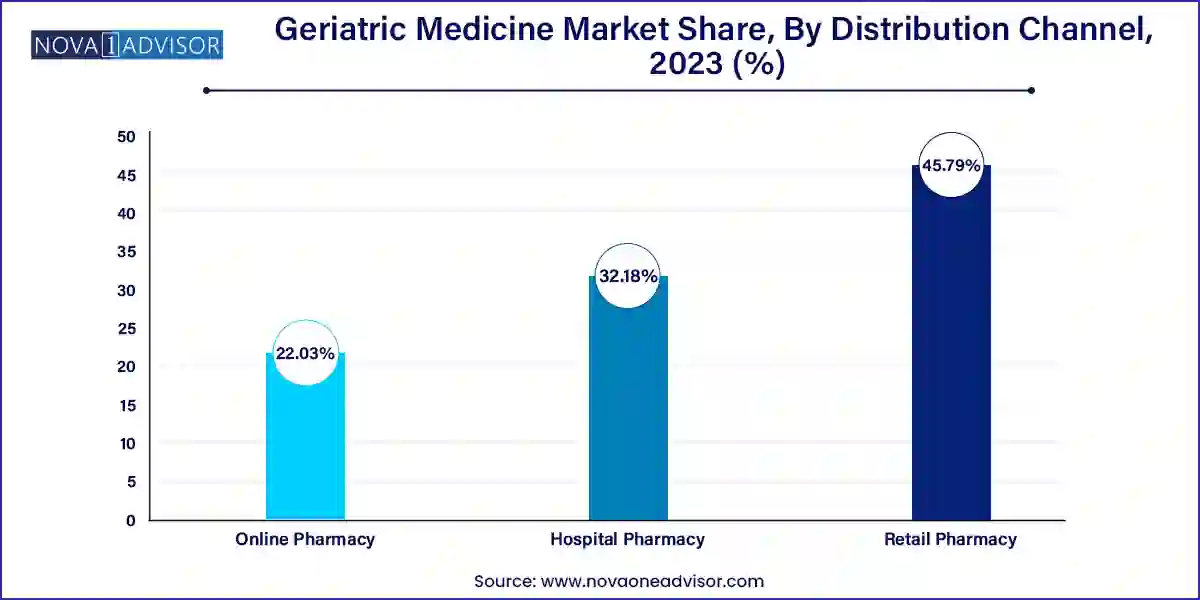
However, online pharmacies represent the fastest-growing channel, driven by increasing internet penetration, caregiver convenience, and home-based chronic care models. The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the adoption of online pharmaceutical services among seniors and their families. Features such as automatic refills, dosage reminders, and doorstep delivery have made e-pharmacy platforms popular, particularly in urban settings. E-commerce giants are also entering the healthcare space, offering subscription-based models for elderly care medication, thereby expanding access and affordability.
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2033. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the Geriatric Medicine market.
By Therapeutics
By Condition
By Distribution Channel
By Region