The global biopharmaceutical third-party logistics size was exhibited at USD 126.80 billion in 2023 and is projected to hit around USD 231.40 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 6.2% during the forecast period of 2024 to 2033.
.jpg)
The biopharmaceutical third-party logistics (3PL) market is an indispensable pillar of the global pharmaceutical supply chain, facilitating the seamless movement, storage, and distribution of biopharmaceutical products from manufacturing facilities to end-users, including hospitals, pharmacies, and research institutions. Unlike conventional pharmaceuticals, biopharmaceuticals—such as vaccines, monoclonal antibodies, recombinant proteins, and gene therapies are highly sensitive to temperature, humidity, and physical conditions. This makes their transportation and storage exceptionally complex, requiring specialized logistics services with advanced cold chain infrastructure, regulatory compliance, and real-time monitoring capabilities.
As the global demand for biologics surges due to the rise in chronic diseases, aging populations, and breakthroughs in precision medicine, the importance of reliable and compliant 3PL partners has never been greater. Furthermore, the expansion of clinical trials, the globalization of pharmaceutical manufacturing, and the decentralization of healthcare delivery systems have added new layers of complexity to biopharmaceutical logistics.
The COVID-19 pandemic underscored the critical role of biopharmaceutical logistics. The unprecedented distribution of mRNA vaccines—which required ultra-cold storage and efficient last-mile delivery put the spotlight on the logistical prowess of companies like DHL, UPS Healthcare, and FedEx. As we advance, the biopharmaceutical 3PL market is expected to become even more vital, with innovations in digital supply chain visibility, drone-based deliveries, and AI-driven route optimization.
Expansion of Cold Chain Capabilities: Increasing investments in refrigerated transport, ultra-low temperature freezers, and cryogenic containers are supporting the growing volume of temperature-sensitive biologics.
Integration of IoT and Real-Time Monitoring: Companies are deploying smart sensors and RFID tags to ensure visibility, traceability, and condition control throughout the supply chain.
Rise of Outsourced Logistics Models: Biopharma firms are increasingly outsourcing logistics functions to focus on R&D and commercialization, fostering long-term 3PL partnerships.
Emergence of Specialized Biopharma Logistics Providers: Niche players with GMP-compliant warehouses, specialized packaging, and regulatory expertise are gaining traction.
Sustainability Initiatives: Eco-friendly packaging, carbon offsetting in freight, and energy-efficient warehousing are being adopted to align with ESG commitments.
Regulatory Stringency and Global Harmonization: Compliance with FDA, EMA, WHO GDP (Good Distribution Practices), and ISO guidelines is driving the adoption of advanced quality control systems.
Last-mile Innovation: The rise of home-based therapies and direct-to-patient models is reshaping last-mile delivery strategies with an emphasis on flexibility and precision.
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 126.80 Billion |
| Market Size by 2033 | USD 231.40 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2024 to 2033 | CAGR of 6.2% |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Forecast Period | 2024-2033 |
| Segments Covered | Supply Chain, Service Type, Region |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) | Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Regional Scope | North America; Europe; Asia Pacific; Central and South America; the Middle East and Africa |
| Key Companies Profiled | DHL International GmbH.; SF Express; United Parcel Service of America, Inc.; AmerisourceBergen Corporation; DB Schenker; Kuehne and Nagel; Kerry Logistics Network Ltd.; Agility. |
One of the most influential drivers propelling the biopharmaceutical 3PL market is the rising demand for temperature-sensitive biologics. As of 2024, biologics represent over 40% of new drug approvals by the U.S. FDA, including monoclonal antibodies, cell therapies, vaccines, and gene-based treatments. These biologics are extremely sensitive to temperature fluctuations and often require cold chain or even ultra-cold chain logistics (e.g., -80°C for mRNA vaccines).
Take the example of Pfizer-BioNTech’s COVID-19 vaccine, which required specialized cold chain capabilities for storage at -70°C. This led to a global race to upgrade logistics infrastructure, with companies like UPS Healthcare launching "freezer farms" and FedEx expanding cold chain hubs. With more complex biologics like CAR-T cell therapies and RNA therapeutics entering the market, 3PL providers must be equipped to handle highly sensitive payloads under strict conditions, driving demand for robust cold chain solutions and specialized expertise.
One of the major constraints faced by stakeholders in the biopharmaceutical 3PL market is the stringent and fragmented regulatory environment. Logistics providers must comply with a multitude of regulations across different jurisdictions, including the U.S. FDA’s 21 CFR Part 11, European Union’s GDP guidelines, WHO’s GDP standards, and regional transportation regulations. Ensuring compliance across all touchpoints transportation, warehousing, documentation, temperature control, and personnel training requires significant investment in quality systems and audits.
For instance, a single deviation in temperature during shipment could render an entire batch of biopharmaceuticals unusable, leading to financial losses and reputational damage. Moreover, for global shipments, challenges such as customs clearance delays, documentation errors, or misalignment between regulatory frameworks can disrupt the supply chain. These complexities can act as barriers for new entrants and limit scalability for smaller logistics firms.
A compelling opportunity in the biopharmaceutical 3PL market lies in the expansion of personalized medicine, particularly cell and gene therapies that demand individualized treatment and patient-specific logistics. Personalized therapies often require "vein-to-vein" tracking—where cells are extracted from a patient, modified in a lab, and then returned for infusion. This workflow necessitates highly specialized logistics involving chain of identity, chain of custody, real-time temperature monitoring, and precise scheduling.
In parallel, the trend toward home-based healthcare, accelerated by the pandemic, has triggered growth in direct-to-patient (DTP) delivery models. Patients now receive biologics and injectable treatments at home, requiring 3PL providers to manage last-mile delivery with cold chain precision. For instance, Marken (a UPS company) has expanded its DTP capabilities to support clinical trials and post-market distribution, helping patients access life-saving therapies without visiting hospitals. This shift is not only improving patient compliance but also creating a new revenue channel for 3PL providers.
Cold chain logistics dominated the biopharmaceutical 3PL market in 2024, owing to the growing need for temperature-controlled transportation and storage solutions. Biologics, blood components, vaccines, and advanced therapy medicinal products (ATMPs) require stringent environmental control during transit. Cold chain infrastructure includes refrigerated vehicles, cryogenic freezers, temperature-controlled containers, and real-time tracking systems. The increased launch of vaccines for seasonal diseases, as well as the ongoing distribution of COVID-19 and mRNA vaccines, has created long-term demand for cold chain services. Logistics companies are investing in infrastructure across urban and rural areas to ensure seamless cold chain continuity.
Non-cold chain logistics are expected to be the fastest-growing segment, particularly with the rising demand for traditional pharmaceutical products, over-the-counter (OTC) drugs, and non-temperature-sensitive APIs (active pharmaceutical ingredients). While biologics dominate in terms of complexity and cost, the global volume of non-cold pharmaceuticals remains significant. These include tablets, capsules, and topical products that do not require refrigeration but still need protection against moisture, light, and tampering. As e-pharmacies grow and last-mile delivery expands, efficient non-cold chain services—such as temperature-controlled packaging, automated inventory management, and scalable warehousing—are increasingly essential.
Transportation services held the largest share of the market, driven by the essential need to move biopharmaceutical products between manufacturing plants, distribution centers, clinical sites, and end-users. This segment is further categorized into air freight, sea freight, and overland transportation. Among these, air freight dominates, especially for high-value, time-critical biologics that require fast and secure movement. DHL Global Forwarding, for instance, has developed temperature-controlled air freight solutions like "DHL Thermonet" to support global pharmaceutical logistics with GDP compliance and visibility.
Warehousing and storage is projected to be the fastest-growing service segment, fueled by the increasing volume of clinical trials and commercialization of biologics requiring cold or ultra-cold storage. Modern warehousing goes beyond storage—it includes automated inventory systems, barcode tracking, climate monitoring, and order fulfillment services. 3PL companies are investing in strategic locations near airports, seaports, and urban healthcare hubs to provide on-demand warehousing. Temperature-controlled facilities designed to store sensitive vaccines and personalized treatments are becoming more prevalent, and strategic alliances between biopharma firms and 3PLs are being formed to co-develop dedicated warehouse hubs.
North America accounted for the largest market share in 2024, led by the United States, which hosts a significant concentration of biopharmaceutical manufacturing facilities, R&D hubs, and logistics providers. The U.S. also boasts a highly advanced cold chain infrastructure and benefits from favorable regulatory support for biologics and specialty drugs. The region’s mature healthcare ecosystem, coupled with the high adoption of personalized medicine, creates sustained demand for 3PL services. Major logistics players such as UPS Healthcare, FedEx, Cardinal Health, and McKesson have headquarters or large operations in North America, enabling fast, large-scale distribution of therapies. Government initiatives like Operation Warp Speed during the COVID-19 pandemic further demonstrated North America's leadership in biopharma logistics.
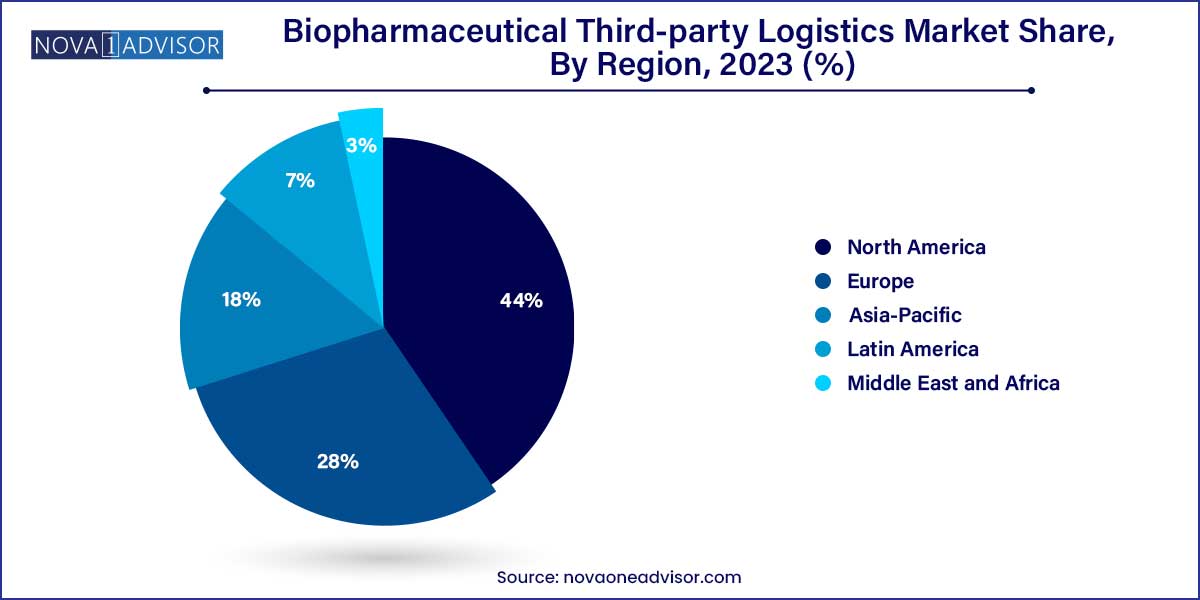
Asia-Pacific is projected to be the fastest-growing region, driven by increasing investments in healthcare infrastructure, rising demand for biologics, and government efforts to improve domestic pharmaceutical manufacturing. Countries like China, India, Japan, and South Korea are experiencing rapid growth in biologics R&D, with numerous biosimilar products under development. For example, India’s Serum Institute and China’s WuXi Biologics are expanding production capacities for vaccines and biologics. To support this growth, 3PL providers are establishing local warehousing, enhancing temperature-controlled trucking fleets, and introducing digital monitoring tools tailored to regional needs. The Asia-Pacific region is also experiencing a shift in clinical trials from the West to the East, necessitating localized yet globally coordinated 3PL services.
March 2025 – UPS Healthcare announced a $300 million expansion of its cold chain network across Europe and Asia-Pacific, adding new GDP-compliant facilities and air cargo infrastructure in Germany, India, and Singapore.
February 2025 – DHL Supply Chain introduced SmartSensor X5, an advanced temperature and humidity tracker for real-time monitoring of biopharmaceutical shipments, enhancing its digital cold chain capabilities.
January 2025 – FedEx Express launched its BioTrack analytics dashboard, allowing biopharma clients to track vaccine and biologic shipments with end-to-end visibility, including environmental deviations.
December 2024 – Kuehne+Nagel acquired a majority stake in QuickSTAT, a specialist in time-critical transportation for cell and gene therapies, strengthening its position in personalized medicine logistics.
November 2024 – Marken (a UPS company) expanded its direct-to-patient (DTP) services to 12 new countries in Latin America and Asia, supporting decentralized clinical trials and home-based treatments.
This report forecasts revenue growth at global, regional, and country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2033. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the global biopharmaceutical third-party logistics.
Supply Chain
Service Type
By Region