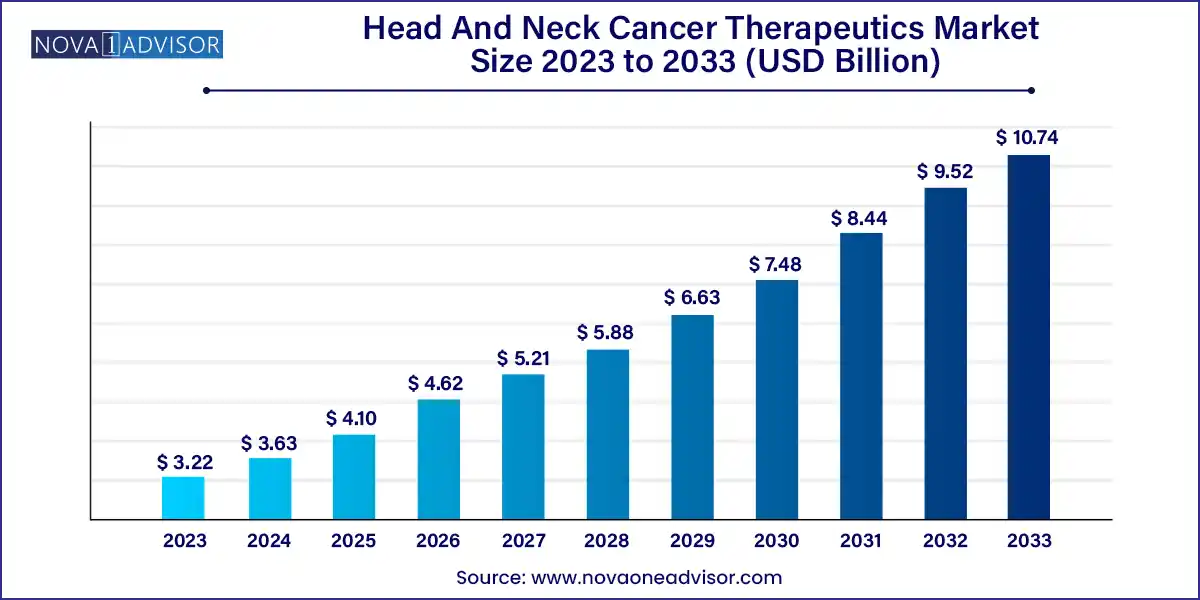
The global head and neck cancer therapeutics market size was exhibited at USD 3.22 billion in 2023 and is projected to hit around USD 10.74 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 12.8% during the forecast period of 2024 to 2033.
The Head and Neck Cancer Therapeutics Market represents a critical segment within the oncology space, focusing on the treatment of malignancies that originate in the oral cavity, larynx, pharynx, nasal cavity, and salivary glands. Head and neck cancers (HNC) account for approximately 4% of all cancers globally and are frequently associated with tobacco use, alcohol consumption, and human papillomavirus (HPV) infections.
Advancements in diagnostic imaging, early detection, and precision therapeutics have significantly improved survival outcomes in recent years. However, due to the anatomical complexity of the head and neck region, treatment can be particularly challenging, often requiring a multidisciplinary approach involving surgery, radiation, chemotherapy, targeted therapies, and increasingly, immunotherapy.
As the global incidence of these cancers rises particularly in low- and middle-income regions there is a heightened focus on expanding access to effective treatment modalities. The market is also witnessing a shift toward more patient-centric, less toxic therapeutic options, driving demand for targeted therapies and immune checkpoint inhibitors.
The head and neck cancer therapeutics market is expected to experience robust growth over the next decade, propelled by a growing patient population, expanding reimbursement frameworks, and a pipeline rich with innovative drug candidates, especially in immuno-oncology.
Growing Adoption of Immunotherapy: Checkpoint inhibitors like pembrolizumab and nivolumab are becoming first- or second-line standards in recurrent/metastatic HNC.
Increased Use of Molecular Biomarkers: Precision medicine is enabling stratified therapy based on HPV status, EGFR expression, and PD-L1 levels.
Combination Therapy Development: Trials are exploring combinations of immunotherapy with radiation or chemotherapy to enhance outcomes.
Rise in Oral Formulations: To improve quality of life and reduce hospital visits, oral chemotherapy and targeted therapy agents are gaining popularity.
Digital Therapeutics and Remote Monitoring: Use of AI and mobile health platforms to track treatment adherence and manage side effects remotely.
Partnerships and Collaborations: Pharma-biotech partnerships are accelerating the development of next-gen HNC therapeutics.
Focus on Patient Quality of Life (QoL): Therapies are increasingly being evaluated for QoL outcomes such as speech and swallowing function.
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 3.63 Billion |
| Market Size by 2033 | USD 10.74 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2024 to 2033 | CAGR of 12.8% |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Forecast Period | 2024-2033 |
| Segments Covered | Therapy Type, Route Of Administration, Distribution Channel, Region |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) | Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Regional Scope | North America; Europe; Asia Pacific; Central and South America; the Middle East and Africa |
| Key Companies Profiled | Eli Lilly and Company; Sanofi; Merck & Co., Inc.; Clinigen Group plc.; Bristol-Myers Squibb Company; AstraZeneca; Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited; Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd; F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd. |
The surge in human papillomavirus (HPV)-related oropharyngeal cancers has become a defining factor in the expansion of the HNC therapeutics market. In countries like the U.S., HPV-positive cases now outnumber HPV-negative HNCs, which were traditionally linked to tobacco and alcohol.
This shift in etiology has significant therapeutic implications. HPV-positive HNCs respond better to treatment and have more favorable prognoses. Consequently, treatment paradigms are evolving to focus on less aggressive regimens that maintain high efficacy with reduced toxicity.
Pharmaceutical companies are investing in HPV-targeted vaccines, antibody therapies, and gene therapies. Furthermore, screening and vaccination campaigns are driving early detection and increasing the number of patients eligible for curative therapies.
While the emergence of targeted therapy and immunotherapy has revolutionized treatment, it also introduces substantial cost burdens. Drugs like cetuximab (targeted EGFR therapy) and pembrolizumab (anti-PD-1 immunotherapy) can cost tens of thousands of dollars per patient annually.
These costs limit accessibility, particularly in developing regions where healthcare systems may not support full reimbursement. Even in high-income countries, prior authorization requirements and insurance variability hinder widespread use. Hospitals and clinics often face challenges in maintaining drug inventory and managing patients who are underinsured or uninsured.
This cost-related barrier underscores the importance of biosimilar development and pricing reforms to ensure equitable access to life-saving therapies.
A promising opportunity lies in expanding therapeutic access in emerging economies, where the incidence of head and neck cancers especially due to chewing tobacco and alcohol use is high. Markets like India, Southeast Asia, Brazil, and sub-Saharan Africa have seen limited access to modern treatments, representing untapped growth potential.
Additionally, early detection programs using AI-based imaging, biomarker screening, and mobile diagnostics can significantly increase treatment success rates. Companies that invest in partnerships with public health systems and NGOs to promote early screening and subsidized care will likely see both commercial and humanitarian gains.
Chemotherapy remains the dominant therapy type, particularly cisplatin and 5-fluorouracil-based regimens, which are widely used in both definitive and palliative settings. Despite advancements in targeted options, chemotherapy is still the most accessible and cost-effective treatment, especially in low-resource settings.
Immunotherapy is the fastest-growing therapy type, with drugs like pembrolizumab (Keytruda) and nivolumab (Opdivo) demonstrating significant efficacy in recurrent/metastatic settings. These agents enhance the immune system's ability to detect and attack cancer cells and are being tested in earlier-stage disease through clinical trials. Their inclusion in first-line regimens marks a major shift in therapeutic strategy and opens the door for durable responses in otherwise poor-prognosis patients.
Injectable administration dominates the market, driven by the delivery format of chemotherapy and monoclonal antibodies. Intravenous administration is standard for drugs like cetuximab and platinum-based therapies, requiring specialized infusion centers and monitoring.
Oral therapies are gaining traction rapidly, particularly among targeted agents and certain chemotherapy drugs like capecitabine. Oral drugs enhance patient convenience, reduce the burden on healthcare infrastructure, and allow for home-based care in certain settings. This trend is especially relevant for palliative care and maintenance therapy, where quality of life is paramount.
Hospital pharmacies lead in terms of distribution, as most treatments are delivered in an inpatient or outpatient infusion setting under close clinical supervision. Complex therapies, adverse event monitoring, and intravenous administration necessitate hospital-based dispensing.
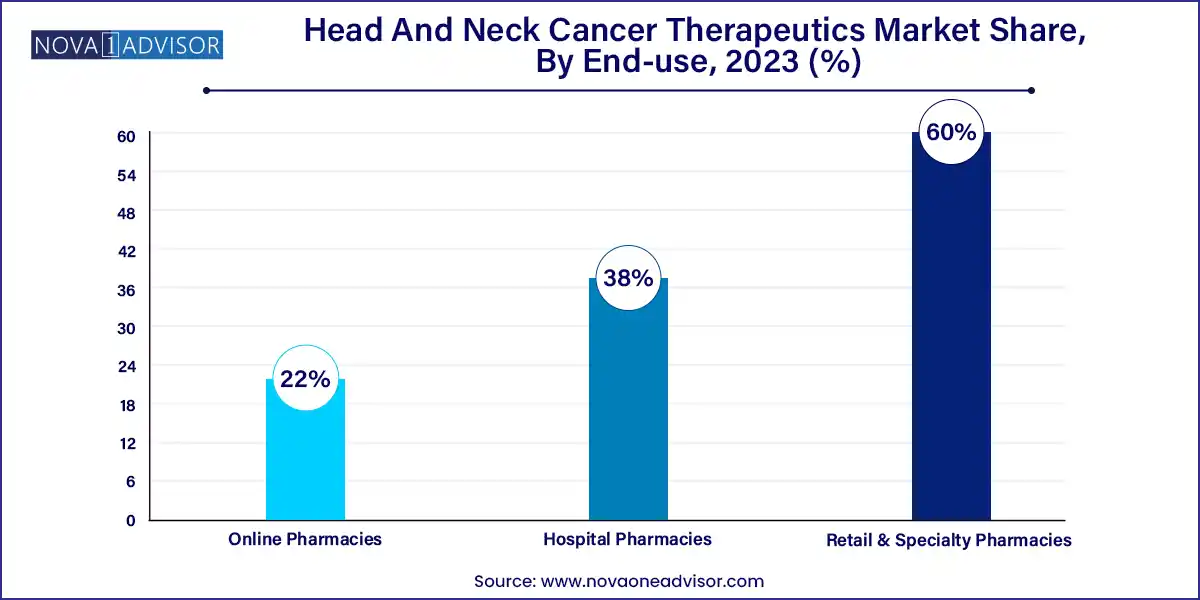
Online pharmacies are emerging as a growing channel, especially for oral cancer therapeutics. In regions with expanding digital health ecosystems, patients are using telemedicine platforms for follow-ups and medication delivery. This channel is particularly useful in urban areas and for maintenance therapies that require long-term adherence.
North America dominates the head and neck cancer therapeutics market, supported by advanced healthcare systems, high awareness levels, and early adoption of immunotherapies. The U.S., in particular, benefits from rapid FDA approvals, widespread insurance coverage, and a large base of HPV-related oropharyngeal cancer cases. The presence of global pharmaceutical giants like Merck & Co., BMS, and Eli Lilly further anchors market leadership in the region.
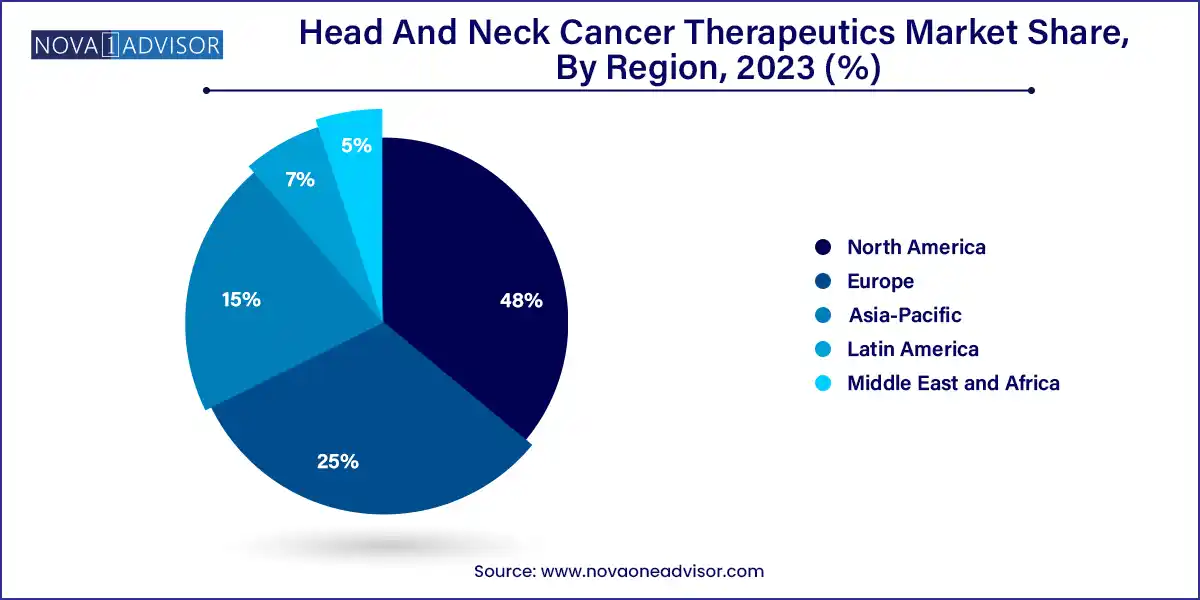
Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing region, with rising cancer incidence in India, China, and Southeast Asia. Cultural practices such as betel nut chewing and tobacco use contribute significantly to the high burden of HNCs. Governments are responding with expanded screening programs and oncology infrastructure development. Pharma companies are entering these markets with both originator drugs and generics, supported by local manufacturing hubs.
Merck & Co. (April 2025): Received FDA approval to expand Keytruda’s indication as a first-line monotherapy for recurrent/metastatic HNC in patients with high PD-L1 expression.
AstraZeneca (March 2025): Began a Phase III trial combining durvalumab (PD-L1 inhibitor) with radiation therapy in newly diagnosed locally advanced HNC.
Eisai Co. Ltd. (February 2025): Partnered with a biotech firm to co-develop a novel tyrosine kinase inhibitor aimed at HPV-negative HNC.
Eli Lilly (January 2025): Announced the availability of a biosimilar to cetuximab in the European market, targeting cost-sensitive healthcare systems.
Roche (December 2024): Introduced a liquid biopsy tool to detect treatment response in HNC patients undergoing immunotherapy.
This report forecasts revenue growth at global, regional, and country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2033. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the global head and neck cancer therapeutics market.
Therapy Type
Route of Administration
Channel
By Region