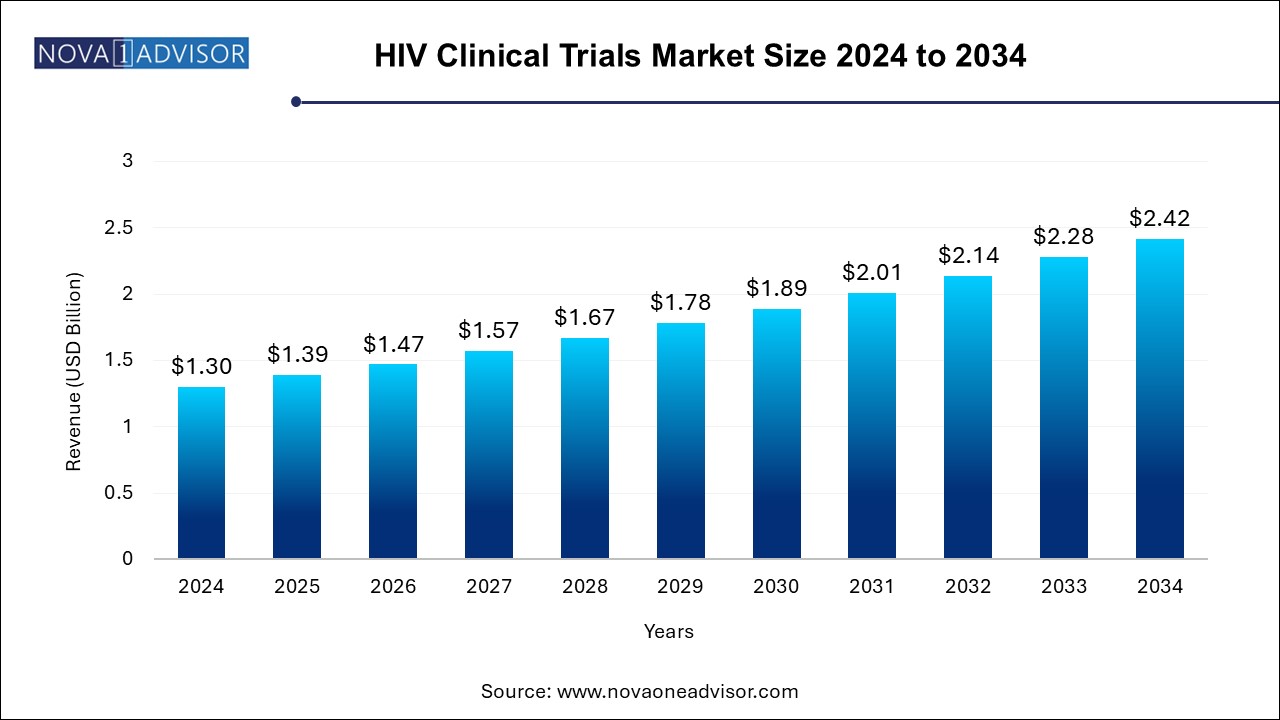
The HIV clinical trials market size was exhibited at USD 1.30 billion in 2024 and is projected to hit around USD 2.42 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 6.4% during the forecast period 2024 to 2034.
The HIV clinical trials market is a critical segment of global infectious disease research, representing sustained efforts to combat one of the world’s most persistent and devastating pandemics. Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) remains a major global health issue, with over 38 million people living with the virus as of 2024. Despite significant advancements in antiretroviral therapies (ARTs), a permanent cure or universally effective vaccine continues to elude researchers, necessitating continued innovation and investment in clinical trials.
Clinical trials serve as the cornerstone of new drug discovery, regimen optimization, vaccine development, long-acting injectables, and cure research for HIV. Over the years, the clinical trial landscape for HIV has expanded dramatically—from early Phase I safety trials to late-stage Phase III efficacy studies and long-term Phase IV post-marketing surveillance. Global partnerships between pharmaceutical companies, biopharmaceutical innovators, non-profit foundations, and public health agencies have accelerated the pace of HIV research.
Key regions such as North America, Sub-Saharan Africa, and Southeast Asia are leading hubs for HIV clinical research due to their well-established research infrastructure, diverse patient populations, and varying epidemiological profiles. Trial designs have become increasingly sophisticated, incorporating real-world evidence, patient-reported outcomes, and digital health tools to ensure efficiency and inclusivity. Moreover, the COVID-19 pandemic catalyzed adaptive and decentralized trial models, many of which are now being applied to HIV clinical studies.
The increasing prevalence of drug-resistant HIV strains, challenges related to adherence to daily ART regimens, and demand for simplified, long-acting treatment options are fostering new clinical trials for innovative therapies. As the global healthcare community moves closer to the ambitious UNAIDS 95-95-95 targets—aiming for 95% of people living with HIV to know their status, 95% of those diagnosed to be on treatment, and 95% of those on treatment to achieve viral suppression—clinical trials are playing an indispensable role in shaping next-generation treatment and prevention strategies.
Rise of Long-acting Injectables: Clinical trials are increasingly focusing on extended-release ART regimens such as cabotegravir and rilpivirine to reduce pill burden and improve adherence.
Decentralized Clinical Trials (DCTs): The shift toward virtual monitoring, home-based sample collection, and e-consenting platforms is enabling more flexible and inclusive trial participation.
Focus on Functional Cures: Trials investigating latency-reversing agents, immune modulation, and gene editing technologies (like CRISPR) are gaining momentum.
Preventive Vaccine Research: Multinational Phase IIb and III trials for HIV vaccines, including mRNA-based candidates, are expanding globally.
Inclusion of Underrepresented Populations: Gender-diverse participants, pediatric populations, and individuals from high-burden geographies are being prioritized in study designs.
Integration of Digital Health Tools: Wearables, mobile health apps, and telehealth consultations are being used for adherence tracking and data capture in real-time.
Public-private Collaborations: Collaborations between NIH, WHO, Gates Foundation, and pharmaceutical companies are accelerating multicentric trial rollouts.
Use of Surrogate Endpoints: Trials are adopting surrogate endpoints such as viral reservoir reduction, immunologic response markers, and biomarkers to expedite development timelines.
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 1.39 Billion |
| Market Size by 2034 | USD 2.42 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2024 to 2034 | CAGR of 6.4% |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2024-2034 |
| Segments Covered | Phase, Study Design, Sponsor, Region |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) | Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Regional Covered | North America; Europe; Asia Pacific; Latin America; MEA |
| Key Companies Profiled | PPD Inc.; IQVIA Inc.; Parexel International Corporation; ICON plc; Syneos Health; WuXi AppTec; Janssen Global Services, LLC; Gilead Sciences, Inc.; Bionor Holding AS; Charles River Laboratories; GSK plc.; SGS SA |
Increasing Global HIV Burden and the Urgent Need for Innovative Therapies
A primary driver of the HIV clinical trials market is the persisting burden of the disease and the complex challenges in current treatment paradigms. While current ART regimens have revolutionized HIV management by suppressing viral loads and prolonging life expectancy, they fall short of offering a cure. Furthermore, the need for daily adherence to medication, stigma associated with pill-taking, drug resistance, and long-term side effects continue to affect the quality of life for people living with HIV.
As a result, there is a global push to develop more effective, durable, and tolerable treatment options. Trials involving long-acting injectables, broadly neutralizing antibodies (bNAbs), immune checkpoint inhibitors, and latency reversal agents are underway to address these gaps. With increasing financial support from government agencies like the NIH, PEPFAR, and global pharmaceutical companies, the momentum in HIV trial activity is accelerating. The urgency to eliminate HIV as a public health threat by 2030, as outlined in the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), continues to catalyze innovation and drive trial initiation across the globe.
Ethical and Logistical Challenges in Participant Recruitment and Retention
Despite increasing interest and funding in HIV clinical research, significant challenges remain in participant recruitment and long-term retention. HIV trials often require lengthy follow-up, strict inclusion criteria, and invasive procedures such as biopsies or frequent blood draws, which deter potential participants. Moreover, the stigma surrounding HIV still exists in many parts of the world, which may discourage individuals from enrolling in trials due to fear of disclosure or discrimination.
Additionally, recruiting from key populations—such as men who have sex with men (MSM), transgender individuals, and sex workers—requires culturally sensitive outreach, which is not always adequately addressed. In rural or resource-limited settings, infrastructure limitations, regulatory delays, and logistical barriers can further complicate trial execution. These challenges increase dropout rates and prolong recruitment timelines, leading to delays in trial completion and higher operational costs for sponsors.
Advancements in Personalized HIV Therapy and Precision Medicine
An emerging opportunity in the HIV clinical trials market lies in the development of personalized treatment strategies. With advances in genomics, proteomics, and data analytics, researchers are now able to classify patients based on viral subtypes, host genetic factors, immune profiles, and treatment history to tailor therapy accordingly. Clinical trials that explore individualized ART regimens, resistance testing-guided therapy adjustments, and genotype-specific interventions are gaining prominence.
Moreover, gene therapy platforms such as CRISPR/Cas9 and CAR-T cell technologies are offering hope for functional cures in select patient subsets. Trials focusing on autologous stem cell transplantation and CCR5 gene editing have shown early promise. These precision approaches are not only transforming the scientific landscape but also attracting significant investment from biotech firms, venture capitalists, and academic consortia, thereby creating substantial growth potential in the HIV clinical trials domain.=
Phase III trials dominate the HIV clinical trials market, owing to their critical role in evaluating treatment efficacy, safety, and long-term outcomes on a large scale. Phase III studies often involve thousands of participants across multiple countries, testing novel ART regimens, vaccines, or adjunctive therapies. Given the global impact of HIV, Phase III trials are typically supported by international agencies such as UNAIDS and conducted through global research networks. The successful completion of Phase III trials is pivotal for regulatory approval, market entry, and adoption into treatment guidelines.
Phase II trials are the fastest-growing phase segment, reflecting a surge in exploratory studies of novel treatment mechanisms, therapeutic vaccines, and long-acting agents. These trials aim to determine optimal dosing, immunologic response, and virologic suppression across different demographics. The rise in adaptive trial designs—where results from Phase II studies guide modifications or progress to pivotal Phase III stages—is accelerating innovation and reducing time-to-market for promising candidates. With increasing investment in early clinical development, Phase II activity is expanding significantly.
Pharmaceutical and biopharmaceutical companies are the leading sponsors, contributing significantly to trial funding, design, and global execution. These sponsors are focusing on developing next-generation ARTs, combination therapies, and functional cures. Companies such as Gilead Sciences, ViiV Healthcare, and Johnson & Johnson are actively running global multicenter trials, often in collaboration with academic research institutions and government bodies. Their financial resources and R&D capabilities enable them to support extensive trial networks and long-term follow-up studies.
Non-profit organizations are emerging as the fastest-growing sponsor segment, with entities such as the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, International AIDS Vaccine Initiative (IAVI), and amfAR playing crucial roles in funding early-phase and community-based trials. These organizations often focus on preventive measures, pediatric trials, and studies targeting high-risk populations in low-income regions. Their partnerships with governments and universities ensure trials are ethically conducted, locally relevant, and accessible to underserved communities.
The interventional studies segment held the largest revenue share of over 46.0% in 2024 and it is expected to register the second-fastest CAGR during the forecast period. representing a majority of trials focused on testing new HIV treatments, vaccines, and prophylactic approaches. These trials involve actively administering a drug or intervention to assess efficacy and safety under controlled conditions. The surge in long-acting injectables and therapeutic vaccine candidates has bolstered the number of interventional trials in recent years. Regulatory authorities also favor interventional data when making approval decisions, reinforcing the importance of this study design.
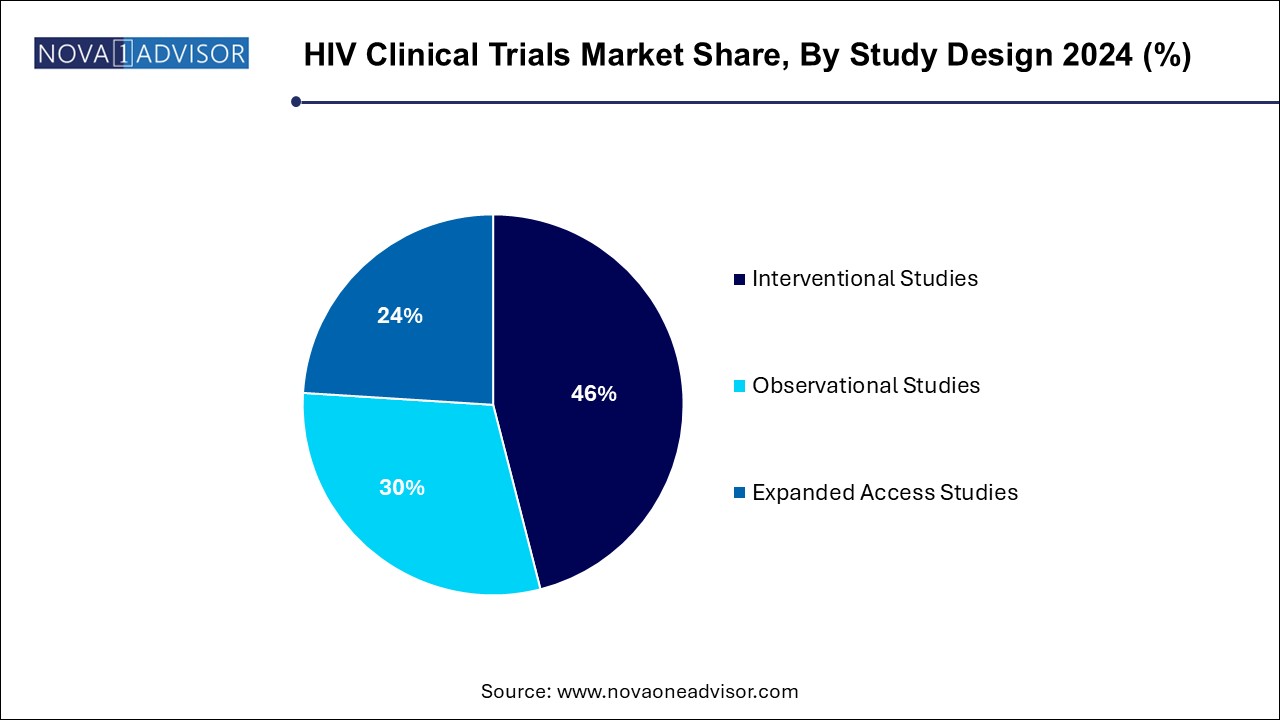
Expanded access studies are the fastest-growing segment, as compassionate use and early access programs are gaining regulatory and patient support. These studies allow individuals who do not qualify for traditional trials, or those with advanced or resistant HIV, to access investigational therapies. During public health crises or in regions with limited treatment options, expanded access studies offer critical care solutions and provide real-world evidence on drug performance. Pharmaceutical companies increasingly use this route to gather safety data and generate goodwill while awaiting trial completion.
North America remains the largest hub for HIV clinical trials, driven by a robust infrastructure, advanced regulatory frameworks, and significant investment in R&D. The United States, in particular, has a long-standing history of HIV research and continues to lead in terms of trial volume, funding, and innovation. The National Institutes of Health (NIH) and its Division of AIDS (DAIDS) fund a vast network of HIV clinical trials through the ACTG and HPTN networks. Major cities like New York, San Francisco, and Boston are home to world-class research institutions, contributing to both treatment and vaccine development trials.
Asia Pacific is the fastest-growing region for HIV clinical trials, owing to rising HIV prevalence, improved research capabilities, and increased government support. Countries like Thailand, India, China, and Vietnam are witnessing a surge in trial activity, especially in prevention, treatment-naïve populations, and vaccine research. With a large and genetically diverse patient base, Asia Pacific provides valuable epidemiological data for global product development. Multinational sponsors are increasingly establishing research partnerships in the region due to cost efficiency, rapid enrollment, and a growing pool of skilled investigators.
January 2025: Gilead Sciences announced the initiation of a global Phase III trial evaluating the safety and efficacy of a novel long-acting capsid inhibitor for HIV treatment.
February 2025: ViiV Healthcare published positive Phase IIb data on its injectable dual therapy regimen combining cabotegravir and a new maturation inhibitor, demonstrating high viral suppression rates.
March 2025: The NIH and Moderna launched a Phase I clinical trial in the U.S. to evaluate the safety of an mRNA-based HIV vaccine candidate.
April 2025: The Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, in collaboration with the WHO, funded a multi-country observational study examining ART resistance trends in sub-Saharan Africa.
April 2025: Johnson & Johnson paused further development of its HIV vaccine candidate following interim analysis from the Mosaico Phase III trial, citing insufficient efficacy in preventing transmission.
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2024 to 2034. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the HIV clinical trials market
By Phase
By Study Design
By Sponsor
By Regional