The global insulin delivery devices market size was valued at USD 19.14 billion in 2023 and is anticipated to reach around USD 36.61 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 6.7% from 2024 to 2033.
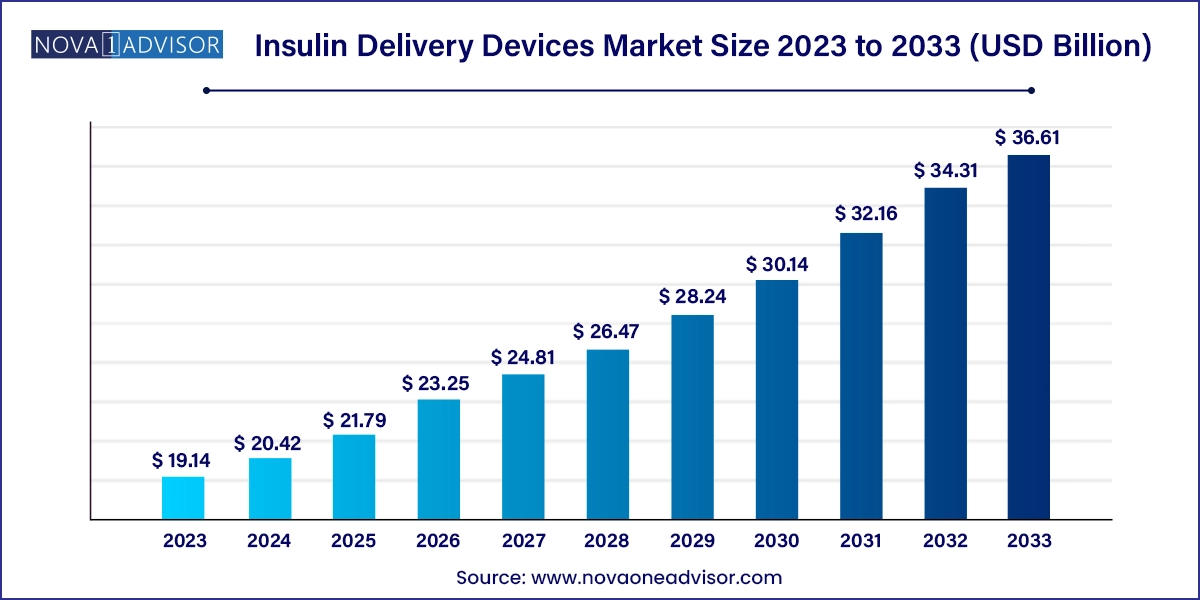
The U.S. insulin delivery devices market size was estimated at USD 4.85 billion in 2023 and is predicted to be worth around USD 9.81 billion by 2033, at a CAGR of 7.3% from 2024 to 2033.
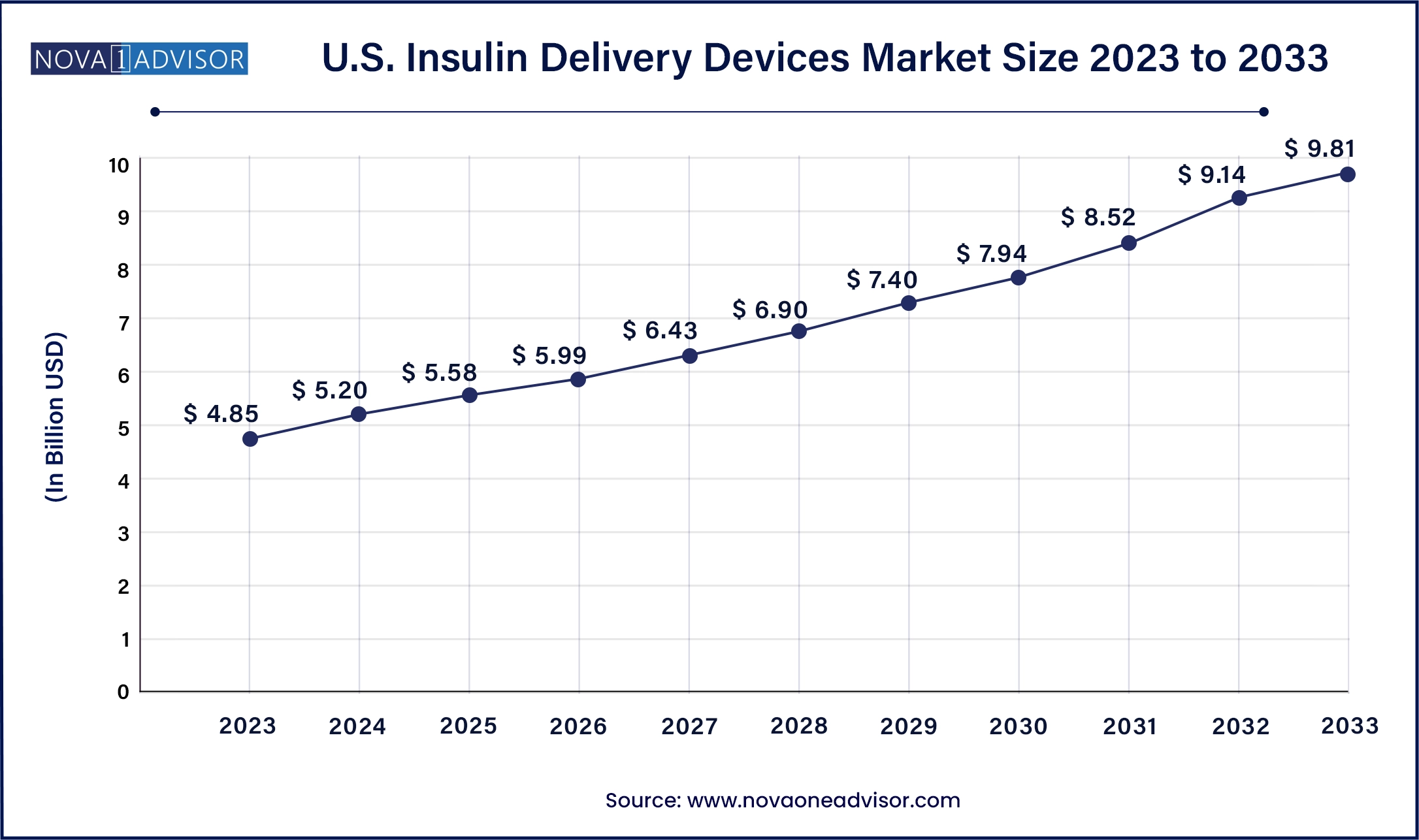
North America remains the leading region in the global insulin delivery devices market, largely due to the high prevalence of diabetes, advanced healthcare infrastructure, and the widespread adoption of innovative technologies. The United States, in particular, boasts a mature market with significant penetration of smart insulin pumps and digital monitoring tools. Companies like Medtronic, Tandem Diabetes Care, and Insulet Corporation are headquartered in the region and continue to drive innovation. Additionally, favorable reimbursement frameworks and government initiatives like Medicare coverage for insulin delivery devices further support market expansion.
Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing regional market, attributed to the rapid rise in diabetes cases, expanding healthcare access, and increasing urbanization. Countries like India and China, home to the world's largest diabetic populations, are witnessing increased demand for both low-cost and advanced insulin delivery systems. Government policies encouraging local production of medical devices, coupled with growing health awareness and the presence of domestic manufacturers, are fostering rapid growth. The emergence of middle-class populations with higher disposable incomes is also contributing to a surge in adoption of premium devices such as insulin pens and patch pumps.
The global insulin delivery devices market is a vital component of the broader diabetes management industry, underpinning the daily therapeutic routines of millions of individuals living with diabetes. As diabetes continues to rise as a global health crisis, the demand for efficient, accurate, and user-friendly insulin delivery systems has reached unprecedented levels. Insulin therapy remains a cornerstone for managing both Type I and advanced Type II diabetes, making insulin delivery devices indispensable tools in maintaining blood glucose control, reducing complications, and improving quality of life.
Insulin delivery devices encompass a wide array of technologies, ranging from traditional syringes and pens to technologically advanced pumps and jet injectors. These devices have undergone remarkable evolution over the past decade. While early models emphasized functionality, today's market favors integrated solutions offering convenience, automation, and minimal user intervention. This shift is particularly driven by the increasing prevalence of diabetes, with the International Diabetes Federation (IDF) estimating over 540 million adults living with diabetes worldwide in 2024 a number expected to surpass 640 million by 2030.
Globally, the market is being shaped by several critical factors, including growing awareness about diabetes management, advancements in insulin formulations, and patient-centric innovation in device technology. In developed economies, digital insulin pumps with Bluetooth-enabled monitoring are setting new standards for glycemic control, while in emerging regions, affordable pen and syringe-based solutions remain essential for broad access.
Healthcare providers, manufacturers, and policymakers are also recognizing the importance of structured insulin delivery in preventing long-term complications such as neuropathy, nephropathy, and retinopathy. The inclusion of insulin devices in public reimbursement schemes and private insurance coverage has further fueled their adoption, especially among newly diagnosed Type II diabetics requiring injectable therapy. As technological innovation continues to bridge the gap between convenience and efficacy, the insulin delivery devices market is poised for continued growth and transformation.
Rising Adoption of Smart Insulin Pens and Connected Pumps: Devices integrated with mobile apps and real-time data logging are becoming preferred solutions, especially in tech-forward healthcare systems.
Shift Toward Tubeless and Patch Insulin Pumps: These offer enhanced mobility, discretion, and comfort, particularly appealing to younger Type I diabetic patients.
Increased Demand for Safety Pen Needles: Safety-engineered pen needles are gaining traction due to heightened focus on infection control and needle-stick injury prevention.
Preference for Disposable Devices in Low-Income Regions: Cost-effective, single-use pens and syringes are being heavily utilized in emerging markets.
Home-Based Insulin Administration on the Rise: The growth in homecare settings is encouraging innovation in devices suitable for self-administration with minimal training.
Combination with Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGMs): Integrated therapy systems that sync insulin pumps with CGMs are enabling better glycemic control and reducing hypoglycemic episodes.
Direct-to-Consumer Sales via E-commerce Channels: Online platforms are simplifying the procurement of insulin pens, needles, and pumps, expanding access across geographies.
| Report Attribute | Details |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 20.42 Billion |
| Market Size by 2033 | USD 36.61 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2024 to 2033 | CAGR of 6.7% |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Forecast Period | 2024 to 2033 |
| Segments Covered | By Product, By Application, By End User, and By Distribution Channels |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) | Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Report Coverage | Revenue forecast, company ranking, competitive landscape, growth factors, and trends |
| Key Companies Profiled | Novo Nordisk A/S, Wockhardt Ltd., Medtronic, F. Hoffmann-La Roche, Ltd., Abbott Laboratories, Sanofi, Eli Lilly and Company, Biocon Ltd., Ypsomed AG, Becton, Dickinson and Company. |
A primary driver of the insulin delivery devices market is the alarming rise in global diabetes prevalence, particularly in middle- and low-income nations. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), diabetes is among the top 10 causes of death and continues to grow at an accelerated pace. Urbanization, sedentary lifestyles, and dietary changes have led to a dramatic rise in obesity and Type II diabetes, even among younger age groups.
In Type I diabetes, which necessitates lifelong insulin therapy, insulin pumps and pens are essential. Similarly, a significant proportion of Type II patients eventually require insulin therapy due to pancreatic beta-cell exhaustion. The sheer volume of patients transitioning from oral anti-diabetics to insulin has created a sustained demand for delivery devices. For example, in India and China alone, tens of millions of patients initiate insulin each year driving demand for cost-effective, safe, and easy-to-use devices. The growing recognition of insulin’s role in early intervention is further strengthening the market base.
Despite robust demand, one of the significant restraints in the insulin delivery devices market is the high cost and limited accessibility of advanced delivery technologies, particularly in low- and middle-income countries. While digital insulin pumps and smart pens offer superior precision, their price often remains prohibitive for a vast section of the diabetic population.
For instance, the upfront and maintenance costs of tubeless insulin pumps like Omnipod or integrated sensor-pump systems can exceed several thousand dollars annually. Even in developed markets like the U.S., reimbursement hurdles and insurance limitations deter widespread use. Additionally, in rural and underserved regions, lack of awareness and inadequate infrastructure further limit the distribution and proper usage of these devices. These disparities contribute to uneven market penetration and hinder optimal outcomes across geographies.
A significant opportunity lies in the integration of digital health technologies and artificial intelligence (AI) with insulin delivery systems. The rise of smart diabetes management platforms that link insulin devices with mobile apps, wearable sensors, and cloud-based monitoring portals is transforming patient care. These digital ecosystems allow patients to receive real-time feedback, dose recommendations, and alerts for missed doses or hypoglycemic events.
Companies are already developing AI-enabled platforms that utilize historical data to optimize insulin dosing schedules. For instance, Tandem Diabetes' t:slim X2 insulin pump with Control-IQ technology uses an algorithm to adjust insulin delivery automatically, based on predicted glucose levels. As telemedicine and remote monitoring become more prevalent, healthcare providers can now adjust patient therapies without requiring in-person visits—improving convenience, compliance, and outcomes. These smart integrations not only improve patient engagement but also reduce healthcare system burden, creating strong commercial incentives for adoption.
Insulin pens dominated the product segment of the market, owing to their ease of use, portability, and widespread availability. Reusable and disposable insulin pens have become the preferred choice among both newly diagnosed and long-term patients. Pens offer more accurate dosing than syringes, are more discreet, and require less technical skill, making them especially suitable for elderly and pediatric patients. Their ergonomic design and ability to dial doses precisely also reduce the chances of under- or overdosing. Leading manufacturers like Novo Nordisk and Sanofi have capitalized on this preference by launching next-generation insulin pens with dose memory and Bluetooth connectivity.
Among all products, tubeless insulin pumps are the fastest-growing sub-segment, reflecting increasing demand for convenience and wearable technology. Unlike traditional tethered pumps, tubeless versions such as Insulet’s Omnipod can be worn as a discreet patch, controlled wirelessly. They eliminate the need for external tubing, improving comfort and mobility. These pumps are particularly attractive to younger patients with Type I diabetes who seek flexibility in physical activity and travel. The growing market for pediatric diabetes management is also driving this segment, as parents opt for non-invasive, automated solutions to reduce management burden.
Home care settings dominate the insulin delivery devices market, driven by the global shift toward self-administration and decentralized care. With diabetes being a lifelong condition, most patients prefer managing insulin at home to reduce the inconvenience and costs associated with hospital visits. Devices such as pens, syringes, and even patch pumps are designed for intuitive use, requiring minimal medical training. Moreover, educational programs by diabetes educators and health insurers support this shift by empowering patients with the knowledge to self-manage safely.
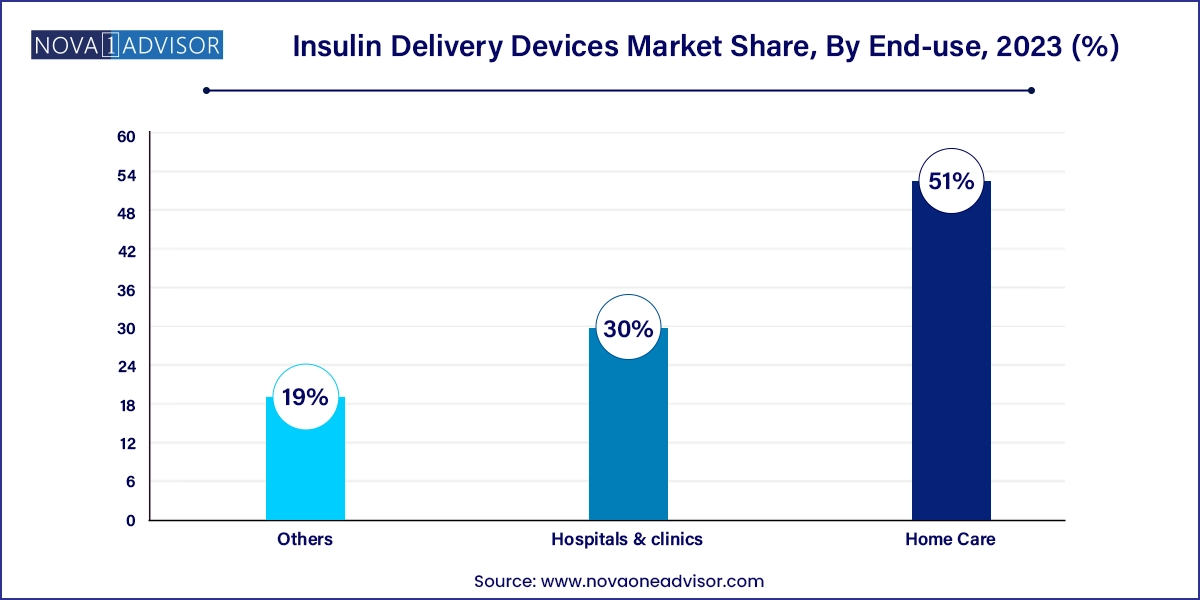
Hospitals and clinics represent the fastest-growing end-user segment, particularly in emerging countries where healthcare infrastructure is expanding rapidly. In-patient care often requires short-term insulin delivery, especially in gestational diabetes, surgical recovery, or acute illness. Additionally, hospital-driven device trials and brand partnerships play a vital role in familiarizing patients with new technologies, encouraging transition to at-home use post-discharge. Manufacturers are increasingly collaborating with hospital networks to bundle devices with insulin therapies and after-care services.
Retail pharmacies currently dominate the distribution channel segment, as they serve as a primary touchpoint for chronic care patients. Insulin pens, syringes, pen needles, and even pumps are widely available through retail channels, especially in urban centers. Pharmacists often serve as frontline advisors for insulin-naïve patients and assist with device demonstrations and troubleshooting.
Online sales are emerging as the fastest-growing distribution channel, driven by the COVID-19-induced digital health boom and increased patient preference for home delivery. E-commerce platforms, both general and pharmacy-specific, now offer subscription models, device bundles, and auto-refill services. Additionally, telehealth platforms are incorporating direct prescription-to-home-delivery models for insulin devices, reducing friction and expanding access especially in rural areas.
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2033. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the Insulin Delivery Devices market.
By Product
By Application
By End User
By Distribution Channels
By Region