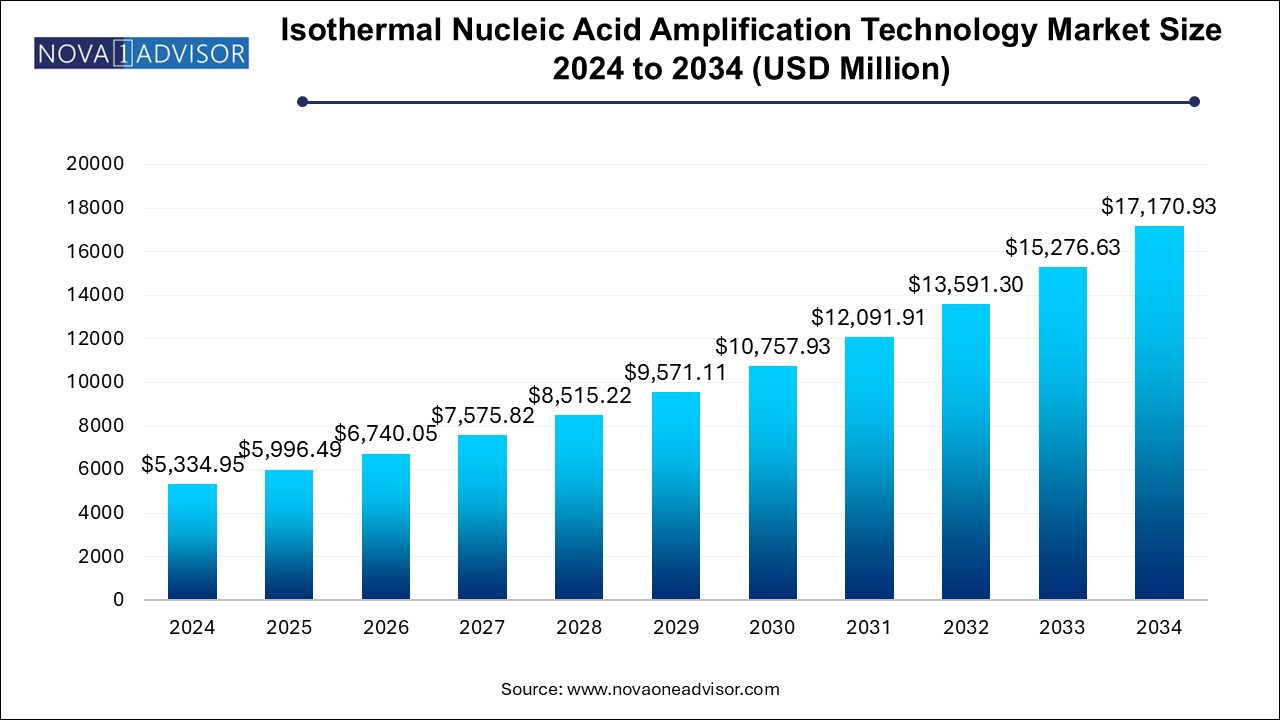
The global isothermal nucleic acid amplification technology (INAAT) market size was exhibited at USD 5,334.95 million in 2024 and is projected to hit around USD 17,170.93 million by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 12.4% during the forecast period of 2024 to 2034.
The Isothermal Nucleic Acid Amplification Technology (INAAT) market is emerging as a critical force in the global molecular diagnostics ecosystem. Unlike traditional polymerase chain reaction (PCR) that requires thermal cycling, INAAT enables the amplification of nucleic acids at a constant temperature. This simplification reduces the need for expensive equipment, cuts down turnaround time, and offers point-of-care applicability in resource-constrained settings.
INAAT platforms are particularly valuable in rapid, field-deployable diagnostics for infectious diseases such as tuberculosis, HIV, malaria, and, more recently, COVID-19. Additionally, the technology is being increasingly explored for cancer diagnostics, blood screening, and genetic disorder testing. Techniques such as Loop-mediated Isothermal Amplification (LAMP), Recombinase Polymerase Amplification (RPA), and Transcription-Mediated Amplification (TMA) are seeing expanding use in clinical, veterinary, and agricultural domains.
The global demand for fast, cost-effective, and sensitive diagnostics is reshaping the diagnostic toolkit—driving uptake of isothermal technologies in hospitals, laboratories, and home-based testing platforms. As precision medicine and decentralized diagnostics gain momentum, INAAT will play a pivotal role in meeting the demand for near-patient testing that is rapid, accurate, and scalable.
Rise of Point-of-Care Testing (POCT): INAAT is gaining adoption in portable diagnostic kits, particularly in infectious disease management at clinics and rural centers.
Integration with Microfluidics and Lab-on-a-Chip Platforms: Combining INAAT with microfluidic technologies is enabling ultra-fast, low-volume diagnostics.
Adoption in COVID-19 and Respiratory Pathogen Testing: The COVID-19 pandemic catalyzed emergency use of INAAT methods like LAMP and NEAR for SARS-CoV-2 testing.
Growing Use in Veterinary and Agricultural Diagnostics: Isothermal techniques are being adapted to detect plant pathogens and animal diseases in field conditions.
Shift Toward Multiplexed and Automated INAAT Systems: Emerging platforms offer simultaneous detection of multiple pathogens or biomarkers.
Rapid Expansion in Low-Resource Settings: Organizations like WHO and UNICEF support INAAT deployment for TB and HIV diagnosis in underserved regions.
Rising Investment in Synthetic Biology and INAAT Toolkits: Biotech companies are developing customizable INAAT platforms for CRISPR-based diagnostics and synthetic gene circuits.
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 5,996.49 Million |
| Market Size by 2033 | USD 17,170.93 Million |
| Growth Rate From 2024 to 2033 | CAGR of 12.4% |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2024-2034 |
| Segments Covered | Product, Technology, Application, End-use, Region |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) | Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Regional Scope | North America; Europe; Asia Pacific; Central and South America; the Middle East and Africa |
| Key Companies Profiled | Alere, Inc.; bioMerieux SA; Eiken Chemical Co. Ltd; Hologic Inc.(Gen-Probe); Lucigen; Meridian Bioscience, Inc.; Ustar Biotechnologies Ltd.; QIAGEN; Quidel Corporation; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc; BD (Becton, Dickinson & Company); OptiGene Limited |
A significant driver of the INAAT market is the escalating demand for decentralized diagnostic solutions, especially in the context of infectious disease outbreaks and chronic disease monitoring. Unlike PCR-based methods, which require thermocyclers and trained personnel, INAAT’s ability to amplify DNA or RNA at a single temperature allows the creation of simple, portable devices that can deliver results in under 30 minutes.
This has proven particularly valuable during the COVID-19 pandemic, where rapid, on-site testing was essential for curbing transmission. For example, the Abbott ID NOW platform, based on NEAR (nicking enzyme amplification reaction), gained widespread use in airports, clinics, and care homes for its rapid SARS-CoV-2 detection. Such real-world utility has demonstrated the versatility of INAAT and catalyzed R&D investment across multiple diagnostic fields.
As healthcare systems globally shift toward home-based and community-level diagnostics, INAAT stands out as a key enabling technology due to its speed, sensitivity, and suitability for minimal-resource settings.
Despite its advantages, INAAT faces challenges in terms of specificity, false positives, and limited multiplexing capability, which constrain its use in complex diagnostics. Unlike PCR, where precise thermal cycling can be tightly controlled, isothermal methods rely on enzyme reactions that may be more prone to off-target amplification or background noise.
Furthermore, multiplexing simultaneous detection of multiple targets is difficult to achieve without cross-reactivity or signal interference. This limits INAAT’s scalability for comprehensive panels used in cancer screening or syndromic infectious disease panels. Also, standardization across different INAAT platforms is lacking, which creates variability in performance and regulatory approval delays.
Overcoming these limitations will require innovations in probe design, signal detection systems (e.g., fluorescence or electrochemical), and advanced bioinformatics tools for result interpretation.
A growing opportunity for INAAT lies in its application in oncology and genetic testing, where early and rapid detection is critical. While PCR and sequencing dominate current protocols, their reliance on centralized labs and high costs limits accessibility.
Emerging INAAT platforms are being adapted to detect cancer biomarkers such as miRNAs, circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA), and methylation patterns from blood or saliva samples. For instance, LAMP and RCA (rolling circle amplification) methods are being developed for ultra-sensitive detection of HPV-associated cervical cancer and EGFR mutations in lung cancer.
Additionally, neonatal screening programs and rare disease diagnostics are beginning to incorporate INAAT for faster turnaround and early intervention. As personalized medicine expands, INAAT’s compatibility with CRISPR diagnostics and synthetic gene circuits opens the door for highly specific, low-cost precision diagnostics in outpatient and home care settings.
Reagents dominate the market, driven by their recurring use across diagnostic workflows. These include enzymes (e.g., polymerases, reverse transcriptases), primers, buffers, and detection dyes required for LAMP, RPA, or TMA reactions. With thousands of samples processed daily in reference labs and hospitals, the demand for high-quality, batch-consistent reagents continues to rise. Moreover, reagent innovation is at the forefront of improving reaction efficiency, reducing cross-reactivity, and enabling multiplexing capabilities in INAAT platforms.
Instruments are the fastest-growing segment, particularly with the development of portable and automated platforms. Compact INAAT analyzers integrated with touchscreens, battery-powered heating blocks, and cloud connectivity are increasingly adopted for decentralized testing. Companies are investing in open-source hardware and modular designs that can be rapidly adapted to new assays, allowing greater flexibility and lower capital investment compared to PCR thermocyclers.
LAMP (Loop-mediated Isothermal Amplification) dominates the technology landscape, thanks to its simplicity, speed, and visual detection capabilities. LAMP reactions typically complete within 30 minutes and can be read by color change or turbidity, making them ideal for resource-limited settings. They have been extensively validated for pathogens like Zika virus, SARS-CoV-2, E. coli, and malaria. The COVID-19 crisis accelerated global adoption, with several governments integrating LAMP into border testing protocols and home test kits.
RPA (Recombinase Polymerase Amplification) is the fastest-growing segment, due to its ultra-rapid reaction time (often under 20 minutes) and ambient temperature operation. RPA has been utilized in portable systems for tuberculosis, dengue, and foodborne pathogen detection. Its compatibility with lyophilized reagents and field-friendly formats makes it ideal for outbreak settings and remote diagnostics.
Infectious disease diagnostics dominate the application segment, constituting the primary area where INAAT is applied. Pathogen detection in diseases like COVID-19, HIV, chlamydia, TB, and hepatitis remains the key use case due to the global burden of communicable diseases. INAAT’s speed and sensitivity are particularly crucial in screening asymptomatic carriers, enabling immediate clinical decision-making. Programs in Africa, India, and Southeast Asia are actively incorporating INAAT in maternal health, HIV diagnosis, and TB surveillance.
Cancer diagnostics is the fastest-growing application, as liquid biopsy and molecular marker detection gain traction. INAAT techniques are being developed to amplify tumor-derived DNA and RNA with high sensitivity. LAMP and NASBA (Nucleic Acid Sequence-Based Amplification) assays are being tested for miRNA detection and epigenetic markers in cervical, prostate, and breast cancer. The ability to process samples outside centralized labs offers enormous promise for rural and community oncology care.
Hospitals dominate the end-use segment, as they remain the primary setting for patient diagnosis, especially during initial consultation or emergency care. Hospitals use INAAT platforms for immediate detection of respiratory, gastrointestinal, or urogenital infections, with platforms like ID NOW and GeneXpert becoming part of emergency and ICU workflows. The increasing focus on antimicrobial stewardship and faster triaging also drives hospital usage of rapid molecular tests.
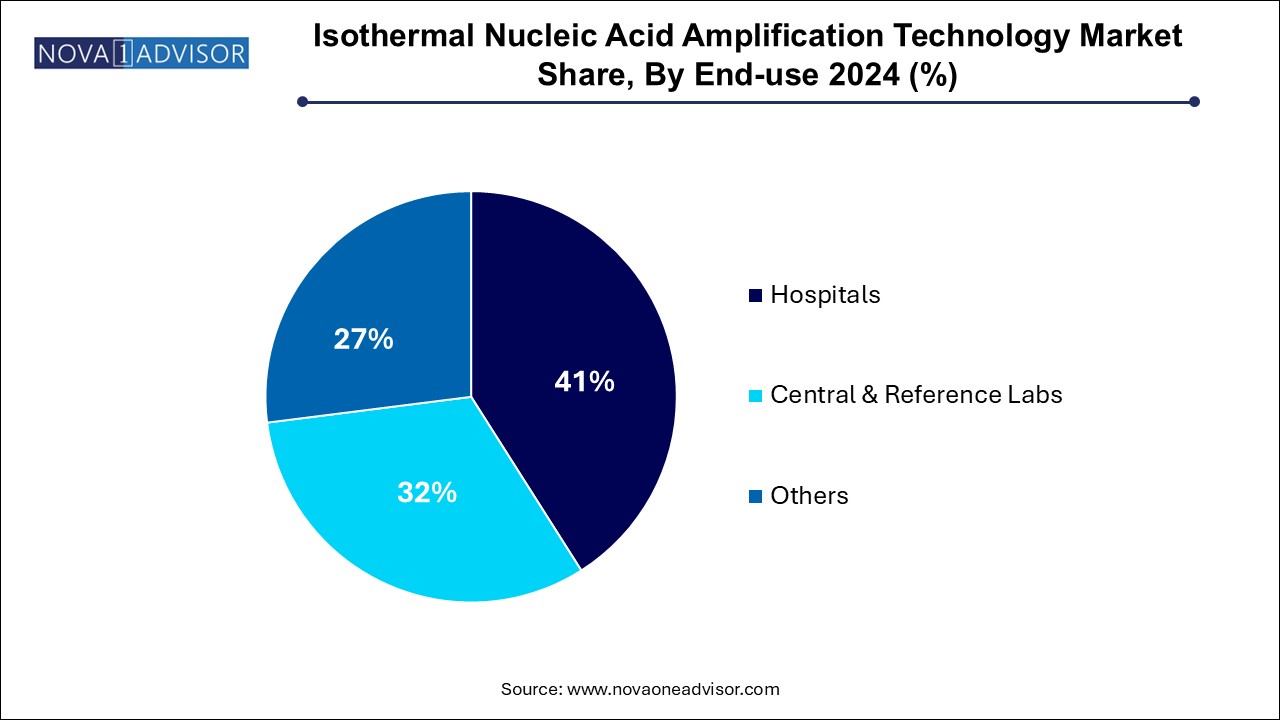
Central & reference laboratories are the fastest-growing, due to their role in processing high volumes of tests, especially during pandemics and national surveillance campaigns. These labs are expanding their INAAT capabilities to offer fast turnaround without overloading PCR lines. Public health agencies are increasingly using centralized INAAT systems for population-level disease tracking and outbreak response.
North America dominates the global INAAT market, with the U.S. leading in terms of R&D, clinical adoption, and regulatory approvals. The presence of major diagnostic companies like Abbott, Thermo Fisher Scientific, and Hologic, coupled with a robust academic ecosystem, drives innovation. During the COVID-19 pandemic, the U.S. FDA granted emergency use authorization (EUA) to multiple INAAT-based tests, which catalyzed widespread deployment. High healthcare spending, advanced laboratory infrastructure, and rising demand for molecular POC diagnostics ensure North America’s continued leadership.
Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing region, propelled by healthcare expansion, rising infectious disease burden, and government-supported screening programs. China, India, and Japan are investing in diagnostic independence, promoting local manufacturing of INAAT kits. Additionally, organizations like FIND, WHO, and the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation are funding pilot programs using INAAT for TB and HIV in rural Asia. The demand for decentralized testing in urban and rural populations makes APAC a high-potential growth region.
Abbott (April 2025): Expanded ID NOW testing menu to include multiplex detection of respiratory viruses (COVID-19, RSV, influenza A/B) using NEAR technology.
TwistDx (March 2025): Launched a new RPA master mix for ultra-rapid detection of dengue virus under ambient conditions for use in field hospitals.
Eiken Chemical Co., Ltd. (February 2025): Announced partnership with UNICEF to distribute LAMP-based malaria testing kits across sub-Saharan Africa.
Molbio Diagnostics (January 2025): Received CE marking for its Truenat LAMP platform for tuberculosis and drug-resistance detection, enhancing access in Europe and Africa.
Lucira Health (December 2024): Launched the next-gen at-home test platform combining INAAT with smartphone-based result tracking for flu and COVID-19.
This report forecasts revenue growth at global, regional, and country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2033. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the global isothermal nucleic acid amplification technology (INAAT) market.
By Product
By Technology
By Application
End-use
By Region