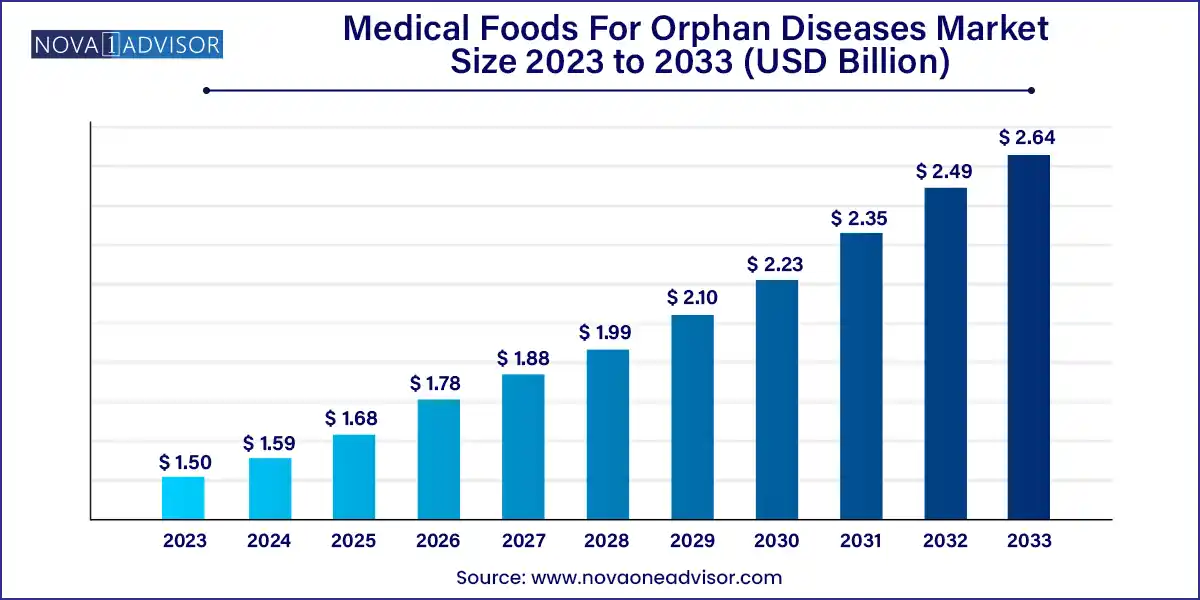
The global medical foods for orphan diseases market size was exhibited at USD 1.50 billion in 2023 and is projected to hit around USD 2.64 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 5.8% during the forecast period of 2024 to 2033.
The Medical Foods for Orphan Diseases Market is a highly specialized but increasingly essential segment within the broader medical nutrition industry. Medical foods are formulated specifically for the dietary management of diseases and conditions with distinct nutritional needs that cannot be met by normal diet alone. In the context of orphan diseases—rare diseases affecting fewer than 200,000 people in the U.S., or similarly rare in other regions—these foods play a critical therapeutic role.
Orphan diseases often involve complex metabolic disorders, enzyme deficiencies, or genetic abnormalities that hinder normal food processing or nutrient absorption. Conditions such as Phenylketonuria (PKU), Maple Syrup Urine Disease (MSUD), Homocystinuria, and Eosinophilic Esophagitis require lifelong dietary restrictions. Medical foods tailored to these patients help maintain metabolic balance, support growth, and prevent irreversible complications.
Unlike general nutritional supplements or functional foods, medical foods for orphan diseases must meet rigorous clinical, regulatory, and safety standards. They are typically administered under medical supervision and are often reimbursed by insurance or national healthcare systems. Given the rising number of diagnosed rare diseases and expanding newborn screening programs, this market is gaining momentum globally.
Precision Nutrition and Genomic Alignment: Customized medical foods are being developed based on genetic profiles of rare disease patients.
Expansion of Home-Based Nutritional Therapy: Increased demand for oral and enteral nutrition options compatible with homecare settings.
Rise in Newborn Screening Programs: Early detection of metabolic disorders fuels demand for lifelong dietary therapies.
Digital Therapeutic Integration: Companion apps for tracking intake, symptoms, and dietary compliance are becoming standard with medical foods.
Pediatric-Focused Product Innovation: Child-friendly formulations, flavors, and formats to improve adherence and acceptability.
Orphan Drug Synergies: Pharmaceutical companies developing orphan drugs are increasingly collaborating with medical food producers for holistic care.
Policy and Reimbursement Shifts: Government support and insurance coverage improvements are expanding patient access.
E-commerce and Direct-to-Patient Models: Online pharmacies and subscription models are revolutionizing product delivery.
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 1.59 Billion |
| Market Size by 2033 | USD 2.64 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2024 to 2033 | CAGR of 5.8% |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Forecast Period | 2024-2033 |
| Segments Covered | Product, Route Of Administration, Application, Sales Channel, Region |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) | Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Regional Scope | North America; Europe; Asia Pacific; Central and South America; the Middle East and Africa |
| Key Companies Profiled | Abbott; Nestle; Danone; Mead Johnson & Company, LLC; Relief Therapeutics; Solace Nutrition; Ajinomoto Cambrooke, Inc. |
A primary growth driver for this market is the rising global burden of rare and inherited metabolic disorders. Enhanced diagnostic technologies, particularly expanded newborn screening programs, have dramatically improved early identification of these conditions. In countries like the U.S., Germany, and Japan, most newborns are now screened for over 30 rare diseases shortly after birth, leading to early dietary interventions.
Diseases such as PKU, Tyrosinemia, and Homocystinuria, if left untreated, can lead to severe neurological damage, developmental delays, and even death. Medical foods help prevent these outcomes by restricting or supplementing specific nutrients (e.g., phenylalanine-free formulas for PKU patients). As survival rates and life expectancy improve for rare disease patients, long-term adherence to medical nutrition regimens becomes vital sustaining demand for specialized products.
Despite promising growth, the market faces a significant hurdle in the form of limited affordability and inconsistent global access. Medical foods for rare diseases are often expensive due to complex formulation, clinical validation, and regulatory compliance. In lower- and middle-income countries, many of these products are not reimbursed, leaving families to bear the full cost of therapy.
Additionally, there is often limited awareness among physicians and patients about the availability and importance of these products, particularly outside urban centers. Infrastructural barriers such as inadequate supply chains, cold chain dependencies, and low e-pharmacy penetration further restrict availability. These challenges create unmet needs and health disparities, especially in rural regions.
One of the most compelling opportunities in this market is the integration of medical foods into comprehensive, value-based care models for rare diseases. As healthcare shifts toward outcomes-based reimbursement, payers and providers are recognizing the role of dietary therapy in reducing hospitalization, delaying disease progression, and improving quality of life.
Pharmaceutical companies developing orphan drugs are increasingly exploring partnerships with medical food manufacturers to offer bundled therapeutic packages combining medication, nutrition, and digital monitoring. This model improves compliance and clinical outcomes, while creating new revenue streams for manufacturers.
Regulatory bodies are also moving toward recognizing medical foods as part of essential care, particularly in pediatric health. This creates new avenues for reimbursement, public procurement, and inclusion in treatment guidelines further enhancing market accessibility.
Powder-based formulations are the market leader, offering flexible dosing, longer shelf life, and ease of storage. Powders can be mixed into liquids or food, making them ideal for both home and institutional settings. They are also cost-effective to produce and transport, particularly in bulk packaging for hospitals and clinics.
Liquid formulations are gaining momentum, particularly for pediatric patients and tube feeding applications. Ready-to-drink formats ensure precise dosing, reduce preparation errors, and improve convenience. This segment is being driven by advancements in aseptic packaging and extended shelf-life technologies, allowing greater adoption in homecare and remote settings.
Phenylketonuria (PKU) remains the largest application segment, due to high global incidence and long-standing treatment protocols involving phenylalanine-free medical foods. Patients require strict protein intake control from infancy to adulthood. Companies like Cambrooke and Nutricia have developed specialized PKU product lines available globally, including low-protein flours and meal replacements.
Eosinophilic esophagitis and FPIES (Food Protein-Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome) are the fastest-growing segments, due to increased awareness and diagnosis of food-related allergic and inflammatory disorders. These conditions often require elemental formulas and amino acid-based medical foods, particularly for infants and young children with multiple food intolerances.
Institutional sales dominate the market, including hospitals, specialty clinics, and long-term care centers. Institutions account for bulk procurement and early-stage dietary management of newly diagnosed patients. In countries with national health programs, government tenders and subsidized supply chains boost institutional market share.
Online sales are the fastest-growing channel, fueled by e-pharmacy expansion, direct-to-patient services, and digital chronic care platforms. Patients and caregivers increasingly prefer home delivery and subscription models, especially for long-term dietary maintenance. E-commerce also supports better adherence through automated refills and remote support.
Oral administration dominates the market, particularly for pediatric and adolescent patients. Oral products such as flavored powders, drinks, and pills are preferred due to ease of use and palatability. These formulations cater to lifelong administration, allowing patients to integrate therapeutic nutrition into daily routines. Companies are investing in texture and flavor innovation to enhance adherence among children.
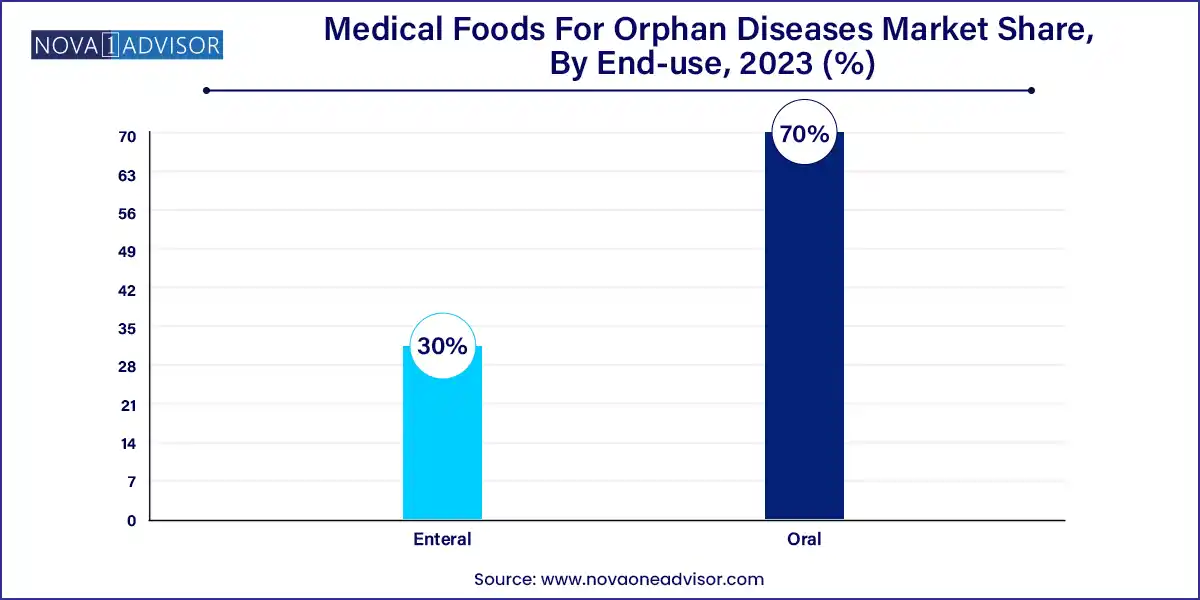
Enteral administration is the fastest-growing segment, especially among patients with severe conditions who cannot consume foods orally. Enteral medical foods are delivered via nasogastric or gastrostomy tubes, primarily in hospitals and homecare settings. This segment is critical for managing acute disease stages or complications like swallowing disorders in eosinophilic esophagitis and severe MSUD.
North America leads the global market, driven by robust newborn screening programs, high healthcare expenditure, and favorable reimbursement policies. The U.S. and Canada have well-established frameworks for diagnosing and managing orphan diseases with nutritional support. FDA and Health Canada approvals for medical foods have encouraged innovation, particularly for rare metabolic and neurological conditions.
Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing region, led by China, India, and Japan. Rising birth rates, increasing prevalence of genetic disorders, and expanding pediatric care infrastructure are fueling demand. Countries like Japan have well-integrated rare disease treatment protocols, while India is seeing increased public-private collaboration for rare disease registries and nutritional access. Government initiatives like the Ayushman Bharat program in India and China's National Rare Disease Registry are enabling wider patient identification and intervention.
Nutricia North America (April 2025): Announced a new range of PKU-specific ready-to-drink formulas for adolescent and adult patients, expanding their low-protein food product line.
Cambrooke Therapeutics (March 2025): Launched a mobile app for PKU and MSUD patients to track intake, symptoms, and reorder specialized medical foods.
Nestlé Health Science (February 2025): Entered into a joint venture with a biotech startup to develop amino acid-based formulas for pediatric eosinophilic GI disorders.
Mead Johnson Nutrition (January 2025): Introduced a hypoallergenic enteral formula tailored for FPIES, approved for use in neonatal ICUs in the U.S.
Vitaflo International (December 2024): Expanded distribution of its phenylalanine-free medical food in Latin America via a partnership with national health agencies.
This report forecasts revenue growth at global, regional, and country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2033. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the global medical foods for orphan diseases market.
Route of Administration
Product
Application
Sales Channel
By Region