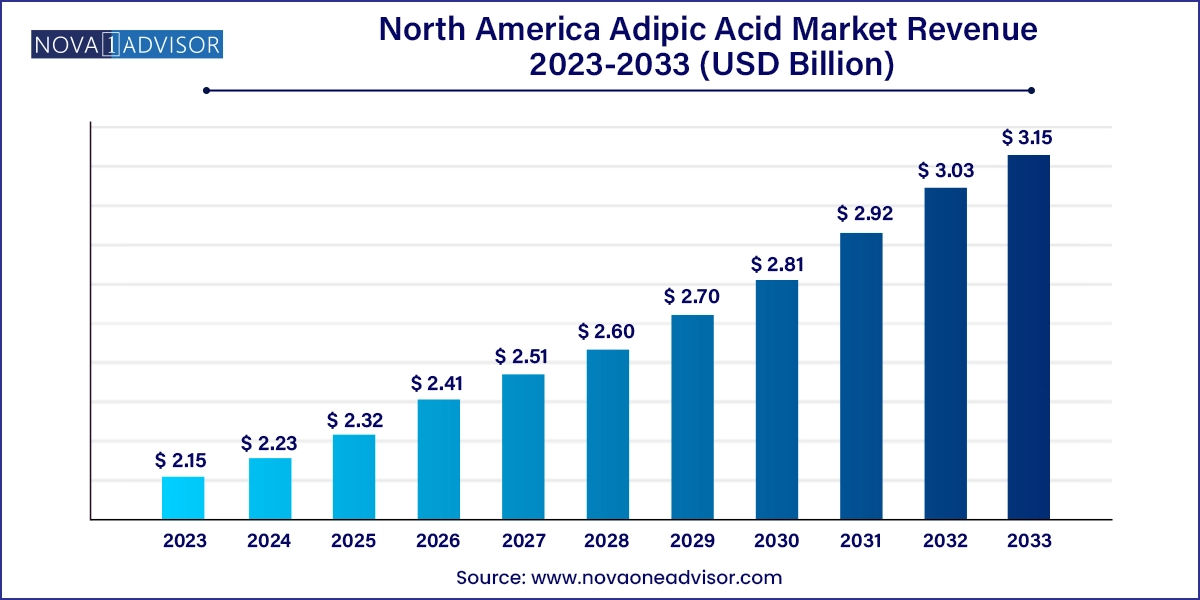
The North America adipic acid market size was exhibited at USD 2.15 billion in 2023 and is projected to hit around USD 3.15 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 3.9% during the forecast period 2024 to 2033.
The North America adipic acid market is a dynamic and evolving sector that plays a critical role in a broad array of industrial applications, particularly in the production of nylon 6,6, which is vital to automotive, textiles, and electronics industries. Adipic acid, a white crystalline compound, is classified as a dicarboxylic acid and is primarily synthesized from cyclohexane through oxidation processes involving nitric acid. It is the most commercially significant aliphatic dicarboxylic acid used in the polymer industry.
As of recent estimates, North America holds a substantial share of the global adipic acid market, driven by advanced industrial infrastructure, robust manufacturing capabilities, and a high demand for synthetic fibers and engineered plastics. The region also benefits from strong R&D capabilities, particularly in the United States, allowing companies to explore bio-based adipic acid alternatives and reduce environmental impact. Adipic acid's flexibility in formulation, strong performance characteristics, and compatibility with various chemical intermediates further enhance its market penetration across diverse sectors.
The market is significantly influenced by environmental regulations that affect the production of conventional adipic acid, which emits nitrous oxide a potent greenhouse gas. As a result, the market has witnessed increasing activity in green chemistry, with companies investing in bio-based routes to adipic acid production using glucose and biomass as raw materials.
This market’s growth trajectory is supported by an interplay of factors including the demand from the automotive and textile industries, the push for lightweight, fuel-efficient materials, and a rising emphasis on sustainable and biodegradable plastics. The market’s future is poised for transformation as companies aim to balance economic viability with environmental responsibility through innovative production technologies.
Shift Toward Bio-based Adipic Acid: Increasing environmental concerns and stringent emission regulations have catalyzed the transition toward bio-based adipic acid alternatives, primarily produced through renewable feedstocks like glucose.
Surging Demand from Automotive Sector: The automotive industry's need for lightweight materials to enhance fuel efficiency and reduce emissions is driving adipic acid consumption, particularly in the production of nylon 6,6-based components.
Recycling and Circular Economy Initiatives: Companies are exploring closed-loop recycling systems where waste nylon is depolymerized and re-converted into adipic acid, promoting circularity and reducing dependency on petrochemical sources.
Technological Innovations in Catalyst Development: New catalysts that minimize nitrous oxide generation during adipic acid synthesis are being developed, thereby improving process efficiency and environmental performance.
Integration with Specialty Chemicals: Adipic acid is increasingly being integrated into specialty chemical formulations such as plasticizers, resins, and lubricants, broadening its market potential.
Increased Strategic Alliances: Key players are engaging in mergers, acquisitions, and partnerships to strengthen R&D, develop green products, and expand their regional presence, particularly in the U.S. and Mexico.
Digitalization and Process Automation: Leading manufacturers are adopting Industry 4.0 tools to streamline adipic acid production, improve yield, and monitor emissions in real time.
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 2.23 Billion |
| Market Size by 2033 | USD 3.15 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2024 to 2033 | CAGR of 3.9% |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Forecast Period | 2024-2033 |
| Segments Covered | Application, Region |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) | Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Key Companies Profiled | Ascend Performance Materials; INVISTA; Química Delta; Dow Chemical Company; SAE Manufacturing Specialties Corp; Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc.; GJ Chemical; Toronto Research Chemicals; MilliporeSigma; CJ Chemicals; Reagents. |
One of the primary drivers of the North America adipic acid market is the increased focus on automotive lightweighting, a strategy adopted by automakers to enhance fuel efficiency and meet stringent emission standards. Adipic acid is a critical precursor in the production of nylon 6,6, which is renowned for its strength, heat resistance, and durability. Nylon 6,6 is used in engine covers, radiator end tanks, air intake manifolds, and other high-performance components.
As automakers transition away from metals and conventional polymers to advanced, lightweight engineering plastics, adipic acid consumption is experiencing a notable surge. For instance, General Motors, Ford, and Tesla have invested heavily in lightweight material integration, reducing vehicle weight by up to 10% in certain models. This reduction translates directly into better fuel economy and lower emissions, thus boosting adipic acid demand. Furthermore, electric vehicles (EVs) also benefit from nylon-based parts due to their thermal insulation and noise reduction properties.
Despite its wide application, the adipic acid market in North America faces considerable restraints due to environmental and regulatory challenges. The conventional production process of adipic acid emits nitrous oxide (N₂O), a greenhouse gas nearly 300 times more potent than carbon dioxide in terms of global warming potential. Regulatory bodies such as the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in the United States have imposed stringent controls on industrial emissions, pushing producers to upgrade facilities or invest in mitigation technologies.
Additionally, public scrutiny of petrochemical-based processes is intensifying, leading to delays in permitting and greater compliance costs. The high capital expenditure required to switch to eco-friendly production methods, such as bio-based synthesis, further constrains smaller manufacturers. In 2023, several chemical plants in North America faced operational limitations due to tightening emissions norms, directly impacting the adipic acid supply chain. These regulatory pressures are likely to persist, affecting production costs and market dynamics.
An emerging opportunity in the North American adipic acid market lies in the commercialization of bio-based and renewable alternatives. As sustainability becomes central to industrial and consumer decision-making, bio-adipic acid produced using glucose, lignocellulosic biomass, or muconic acid offers a low-carbon, biodegradable option. The U.S. Department of Energy and private enterprises have invested significantly in bio-chemistry, recognizing its potential to decouple chemical production from fossil fuels.
Start-ups and research institutions in the U.S. and Canada are at the forefront of innovations in green adipic acid production. For instance, companies like Verdezyne and Rennovia (before its closure) made progress in creating high-purity bio-based adipic acid at commercial scale. If these bio-production processes can be cost-competitive and meet quality benchmarks, they could disrupt the traditional petrochemical-dominated market. The adoption of bio-adipic acid also aligns with carbon neutrality goals and ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance) commitments, offering manufacturers a strong competitive edge.
Nylon 6,6 Fiber dominated the application segment in the North America adipic acid market, owing to its extensive use in the automotive, electronics, and textile industries. Nylon 6,6 derived from adipic acid offers exceptional thermal stability, tensile strength, and abrasion resistance. It is used in high-performance applications, including vehicle under-the-hood parts, tire reinforcements, and engineering plastics. In North America, especially the U.S., automotive OEMs heavily rely on nylon 6,6 to meet safety and regulatory standards while achieving lightweighting goals. This segment's dominance is underpinned by the mature automotive sector and consistent demand from high-performance applications.
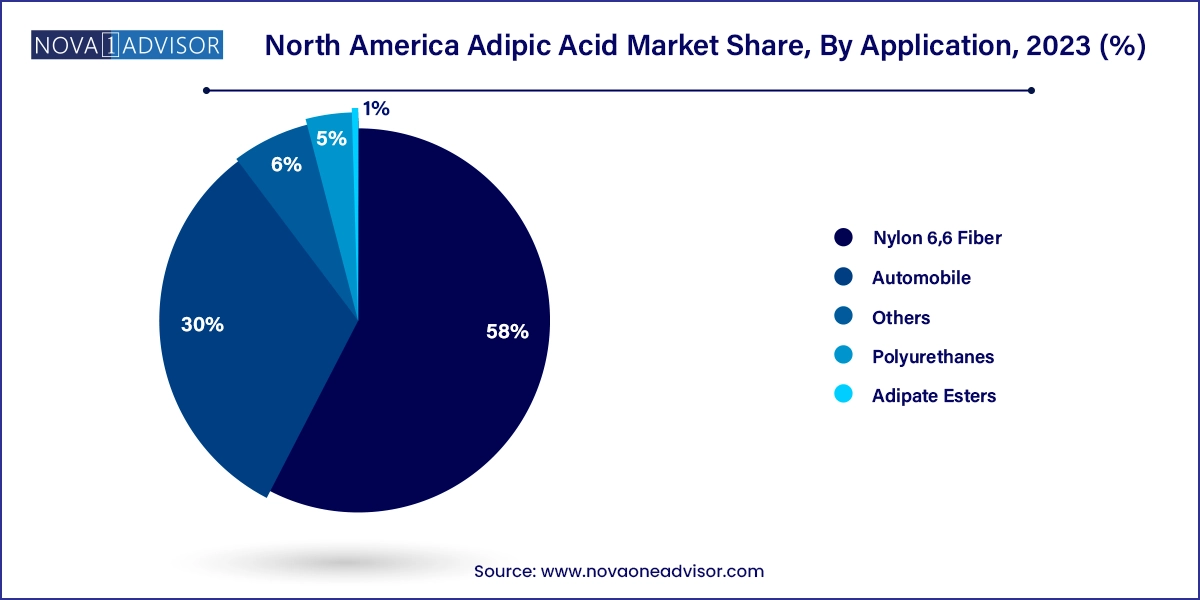
Conversely, polyurethanes emerged as the fastest-growing segment, driven by expanding use in construction, insulation, and footwear applications. Polyurethane foams made from adipic acid-based polyols are crucial for energy-efficient building solutions, contributing to LEED certifications and green architecture. Moreover, the shift toward comfortable, durable footwear and sportswear in Mexico and the U.S. has accelerated the demand for polyurethane elastomers. As consumers demand versatile, sustainable materials, this segment is expected to witness robust growth, supported by both regulatory pushes for insulation and innovation in wearable consumer products.
The United States leads the North America adipic acid market, both in production and consumption. It houses major chemical manufacturers, advanced R&D facilities, and a large base of end-user industries such as automotive, packaging, and construction. The U.S. government’s push for electric vehicle adoption and energy-efficient infrastructure amplifies the demand for adipic acid-derived materials. In 2024, the Department of Energy announced new funding for bio-based industrial chemical research, further reinforcing innovation in this space.
Canada represents a growing hub for bio-based chemical innovation, supported by strong government initiatives, academic-industry collaboration, and investments in sustainable technologies. Although smaller in market share compared to the U.S., Canada has witnessed increasing imports of adipic acid for use in polyurethane-based insulation materials due to harsh weather and energy conservation mandates.
Mexico is emerging as a manufacturing powerhouse, particularly for automotive parts and footwear, two key application areas for adipic acid. Lower production costs and favorable trade agreements like USMCA (United States-Mexico-Canada Agreement) make Mexico a strategic base for adipic acid downstream applications. Industrial clusters in Monterrey and Guadalajara are witnessing growth in adipic acid consumption for synthetic fiber and polyurethanes.
February 2025 – Invista, a major producer of adipic acid and nylon 6,6 intermediates, announced the successful deployment of a nitrous oxide abatement technology at its Texas facility, reducing greenhouse gas emissions by over 85%.
December 2024 – BASF expanded its investment in bio-based adipic acid research by partnering with North American biotech startups. The collaboration aims to commercialize a fermentation-based process using renewable glucose.
September 2024 – Ascend Performance Materials disclosed plans to upgrade its Alabama plant, investing over $100 million to enhance adipic acid production capacity and sustainability metrics.
July 2024 – Solvay announced a strategic partnership with a Canadian university to research and scale bio-adipic acid production using muconic acid fermentation pathways.
April 2024 – ExxonMobil Chemical entered the market for bio-based monomers, including adipic acid, signaling a pivot toward sustainable specialty chemicals and expanding their North American product offerings.
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2033. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the North America adipic acid market
Application
Country