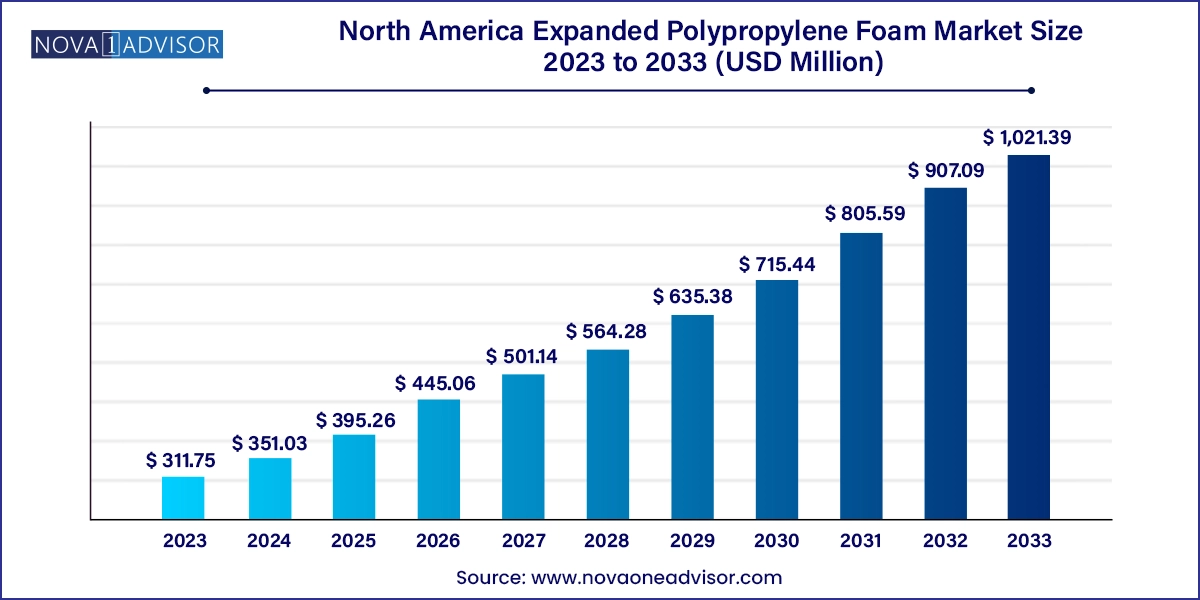
The North America expanded polypropylene foam market size was exhibited at USD 311.75 million in 2023 and is projected to hit around USD 1,021.39 million by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 12.6% during the forecast period 2024 to 2033.
Expanded Polypropylene (EPP) foam is a closed-cell bead foam known for its excellent strength-to-weight ratio, impact resistance, thermal insulation, and exceptional energy absorption properties. In North America, the demand for EPP foam has evolved from being a niche material in protective packaging to becoming a critical component in diverse industries such as automotive, construction, HVAC, consumer electronics, and healthcare.
EPP foam is chemically inert, recyclable, and highly versatile. These characteristics make it especially appealing in a region like North America, where sustainability, product safety, and cost-efficiency are increasingly influencing procurement decisions. With growing industrial modernization, EPP foam is being favored over traditional foams like polystyrene and polyurethane in many technical applications. Furthermore, North American industries have shown a strong inclination toward materials that support circular economy models, and EPP foam stands out as one of the most eco-friendly thermoplastic foams available.
The market has been propelled by the increasing adoption of lightweight materials across automotive manufacturing and construction. For automakers aiming to reduce vehicle weight without compromising crash performance or passenger comfort, EPP provides a perfect material solution. Similarly, in construction, the demand for insulation materials that deliver thermal efficiency, moisture resistance, and long-term durability is driving adoption in insulation panels, formworks, and underlayments.
As EPP foam becomes increasingly integrated into product development strategies across North America, its use is no longer limited to cost-saving or shock-absorbing features it is now part of design thinking aimed at improving performance, environmental impact, and end-user experience.
Lightweighting and Electrification in the Automotive Industry: Automakers are pushing EPP foam into core structural and interior components to reduce weight and accommodate battery-heavy EV designs.
Increased Adoption in Sustainable Packaging: With growing concerns over single-use plastics, reusable and recyclable EPP-based packaging is gaining traction in both consumer and industrial sectors.
Integration into Smart Building Solutions: EPP foam is being incorporated into energy-efficient construction technologies, including advanced thermal envelopes and modular insulation systems.
Growth of EPP Foam in Medical Equipment Protection: The material’s inertness and ease of sterilization are making it a reliable choice for packaging and supporting sensitive medical instruments.
Expansion of EPP Foam into Aerospace Interiors: Aircraft manufacturers are exploring EPP foam for its vibration-dampening and energy-absorbing properties, particularly in interior panels and cabin accessories.
Digital Manufacturing and Design Customization: 3D modeling and CNC machining are allowing greater design flexibility in EPP components, particularly in custom-fit packaging and prototyping.
Circular Economy Initiatives: Manufacturers are investing in EPP recycling programs, closing the loop by reprocessing scrap into new foam products.
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 351.03 Million |
| Market Size by 2033 | USD 1,021.39 Million |
| Growth Rate From 2024 to 2033 | CAGR of 12.6% |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Forecast Period | 2024-2033 |
| Segments Covered | Product, Application, Region |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) | Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Country scope | U.S.; Canada; Mexico |
| Key Companies Profiled | BASF SE; Sonoco Products Company; Magna International, Inc.; Woodbridge; Clark Foam Products Corporation; PDM Foam (Signode Industrial Group LLC); Knauf Industries; Bradford Company |
One of the key forces pushing the North America EPP foam market forward is the automotive industry’s consistent pursuit of lightweight, durable, and safe materials. As vehicles are expected to meet stringent fuel economy standards and safety regulations, EPP foam has emerged as a key enabler of such requirements. It is now widely used in seating systems, headrests, bumpers, door panels, and underbody components.
Electric vehicle (EV) platforms, in particular, have amplified the importance of EPP foam. EVs require lightweight components to compensate for heavy batteries, and EPP not only delivers on weight reduction but also provides necessary impact resistance to protect energy systems. Moreover, with EPP being recyclable, it supports car manufacturers’ efforts to build eco-friendly, sustainable vehicles that comply with green mobility goals.
Despite its excellent properties, the widespread use of EPP foam is somewhat restrained by the capital-intensive nature of its production. EPP manufacturing requires steam chest molding equipment, pressure-controlled autoclaves, and well-regulated expansion processes. These requirements increase the initial setup cost for manufacturers and limit the number of producers capable of scaling efficiently.
Moreover, the base resin polypropylene is itself subject to price volatility linked to crude oil markets. When polypropylene prices surge, the production cost of EPP foam becomes less competitive compared to lower-cost alternatives like expanded polystyrene (EPS). This cost challenge is particularly significant in price-sensitive sectors such as consumer packaging and electronics.
The rise of omnichannel retail and sustainability-conscious logistics practices is opening a high-potential opportunity for reusable and returnable packaging systems. EPP foam’s resistance to repeated impact, water, and chemicals makes it an ideal material for developing crates, totes, insulated containers, and inserts that can be reused across multiple shipping cycles.
Large e-commerce and grocery retailers in North America are exploring cold-chain delivery and protective transport solutions that are both sustainable and efficient. EPP foam boxes that maintain thermal insulation while withstanding rough handling and cleaning processes are emerging as a preferred choice. Companies implementing closed-loop logistics systems are showing increased interest in EPP foam as a long-term cost-saving investment over disposable packaging.
High-density EPP foam dominates the product category due to its superior mechanical properties, high load-bearing capacity, and suitability for safety-critical applications. It finds its highest demand in the automotive sector, particularly in seating cores, bumper systems, and underbody protection components. High-density variants are also preferred in reusable logistics crates, military applications, and formwork in construction, where the material is required to withstand dynamic loading over extended periods. Its ability to offer maximum energy absorption without permanent deformation makes it indispensable in safety-critical design.
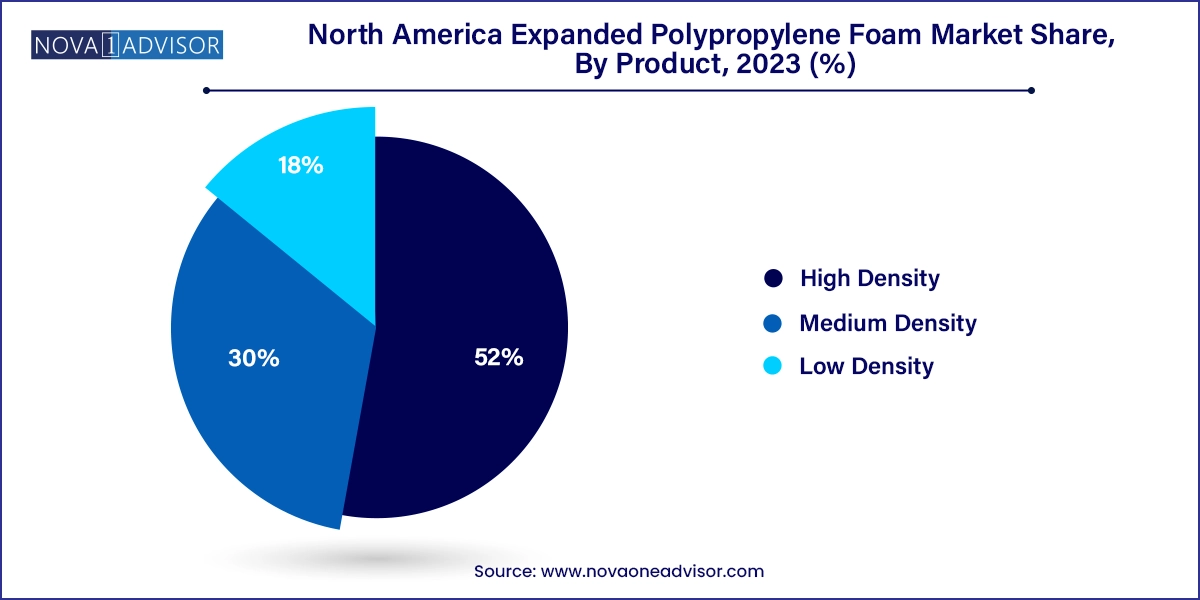
Medium-density EPP foam is the fastest-growing product segment, bridging the gap between cost and performance. It is seeing rapid uptake across packaging and HVAC applications. In consumer electronics, for example, medium-density foam is used in protective casings for laptops and smartphones, as it offers a balance of strength, cushioning, and cost-effectiveness. In HVAC, it is being applied in heat exchanger enclosures and air-handling systems where vibration resistance and thermal insulation are equally important. The material’s moderate density makes it easy to mold, enabling efficient customization for diverse industrial needs.
Automotive remains the dominant application segment, accounting for a large proportion of EPP foam consumption in North America. Its role in enhancing vehicle safety while reducing weight makes it a critical material for modern car design. From bumpers to instrument panels and door reinforcements, EPP foam offers crash resilience, thermal resistance, and durability. The trend of integrated modular seating systems in electric vehicles is further accelerating demand for molded EPP foam seats and lumbar supports, which improve comfort without adding significant mass.
Construction is the fastest-growing application segment, fueled by green building trends and growing demand for thermal insulation solutions. EPP foam is increasingly being utilized in floor underlayments, wall insulation boards, and structural components in prefab construction. Its moldability and ability to insulate while absorbing impact and sound make it a preferred solution for modern architecture. With the rising adoption of energy codes and net-zero building goals in states like California and New York, the construction sector’s appetite for durable, high-performance insulation is driving EPP foam’s penetration.
United States
The U.S. is the powerhouse of the EPP foam market in North America, primarily driven by its mature automotive, packaging, and aerospace industries. Automakers are pushing for lightweighting across their portfolios, and EPP is a strategic fit in both conventional and electric vehicle lines. The country's innovation ecosystem also supports rapid product development and material testing, which has enabled novel EPP applications in surgical trays, reusable retail packaging, and smart insulation panels.
In addition, the growth of e-commerce has led to a surge in demand for reliable, reusable packaging systems—particularly in grocery and meal delivery services. American packaging companies are increasingly developing EPP containers that maintain temperature for longer durations and withstand washing cycles. Aerospace and defense sectors are also adopting EPP foam in non-load-bearing cabin applications where insulation and vibration resistance are crucial.
Canada
Canada's adoption of EPP foam is strongly linked to its cold climate and the resulting demand for thermal insulation. Building codes in provinces such as Ontario and British Columbia now emphasize higher energy efficiency standards, pushing builders to opt for materials like EPP foam for roofing and underlayment. Furthermore, Canada's automotive manufacturing facilities, particularly those in Ontario and Quebec, are showing growing interest in EPP for vehicle interiors and safety systems.
There is also a budding market for medical-grade EPP foam in Canada. Medical device companies are employing it in diagnostic kit packaging and protective carriers for sensitive instruments, especially in decentralized and remote healthcare settings. Its non-toxic, moisture-resistant properties make it ideal for harsh environments and repeated use.
Mexico
Mexico’s role in the EPP foam market is rising, mainly as a manufacturing hub for North American automotive giants. As global carmakers expand assembly operations in Mexico to optimize supply chains, there is a trickle-down effect on local EPP suppliers. Components such as energy-absorbing seat inserts, headrests, and trunk liners are being increasingly sourced locally using EPP foam to reduce logistics costs and improve response times.
Moreover, Mexico's appliance and HVAC industries are expanding, creating new avenues for EPP foam applications. Domestic appliance brands are beginning to use EPP foam for insulation and vibration dampening in washing machines, refrigerators, and air conditioners. The combination of industrial growth and material adaptability is positioning Mexico as a promising contributor to the region’s EPP market.
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2033. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the North America expanded polypropylene foam market
Product
Application
Country