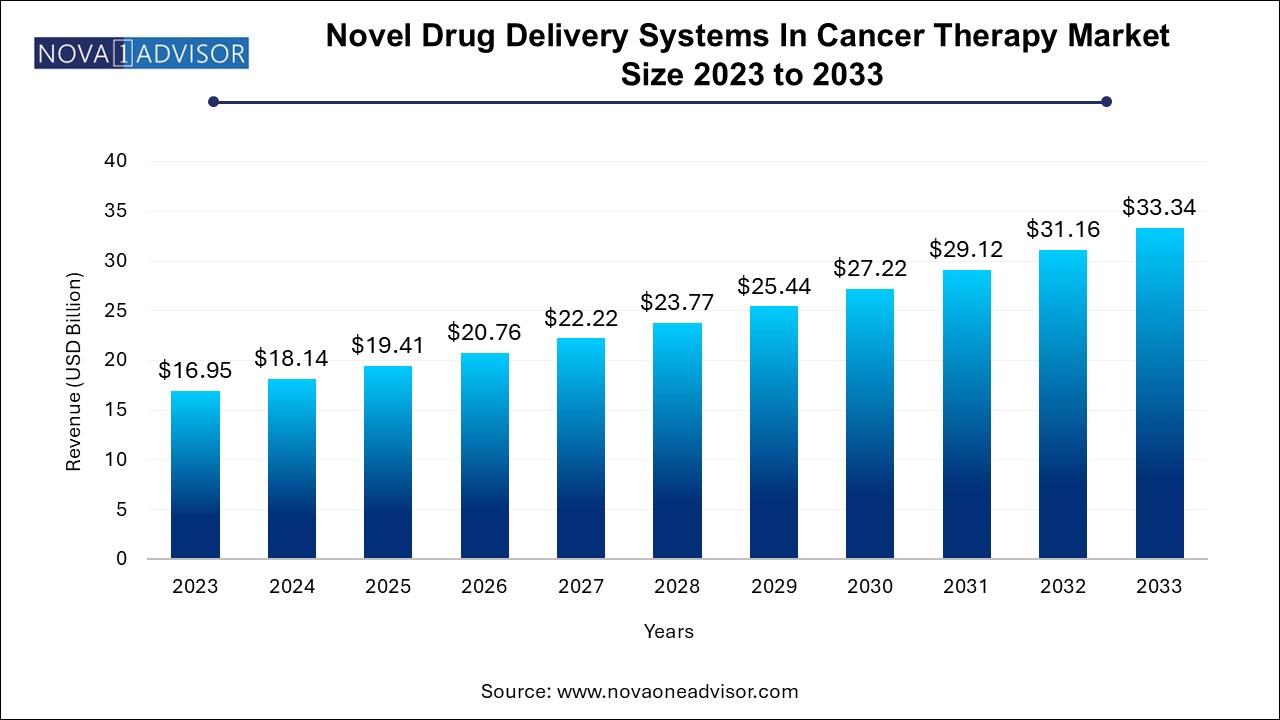
The novel drug delivery systems in cancer therapy market size was exhibited at USD 16.95 billion in 2023 and is projected to hit around USD 33.34 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 7.0% during the forecast period 2024 to 2033.
The Novel Drug Delivery Systems (NDDS) in Cancer Therapy Market represents a paradigm shift in oncology, addressing some of the most persistent challenges in cancer treatment—namely, the limited selectivity, systemic toxicity, and multidrug resistance associated with conventional chemotherapeutics. NDDS leverages innovative technologies and biocompatible materials to deliver anti-cancer agents with enhanced precision, prolonged circulation, controlled release, and minimal off-target effects. These systems aim to improve therapeutic efficacy while reducing adverse effects, thereby optimizing clinical outcomes and patient quality of life.
NDDS platforms span a wide array of product types, including nanoparticles (such as liposomes, polymer-based nanocarriers, micelles, and dendrimers), embolization particles (used in interventional oncology), and stimuli-responsive delivery vehicles that release drugs in response to tumor microenvironment cues like pH, temperature, or enzymes. Among these, liposomes and polymer-based systems have gained the most traction, with several formulations approved for clinical use—such as Doxil (liposomal doxorubicin) and Abraxane (albumin-bound paclitaxel).
The market’s growth is catalyzed by the rising global cancer burden, increasing investment in precision medicine, growing awareness of nanotechnology-based therapeutics, and robust pipeline activity in both academia and industry. Additionally, the demand for localized, targeted, and image-guided delivery approaches has driven the adoption of embolization particles in hepatocellular carcinoma and metastatic colorectal cancers.
As oncology continues to evolve into a personalized and multi-modal discipline, NDDS plays a critical role in expanding therapeutic windows, overcoming resistance mechanisms, and facilitating combinational therapies such as chemo-immunotherapy and radiotherapy-enhanced drug delivery.
Surge in nanotechnology-based drug carriers such as liposomes, polymers, and micelles for encapsulating hydrophobic chemotherapeutics and biologics.
Development of multifunctional drug delivery platforms capable of simultaneous diagnosis (theranostics), targeting, and treatment.
Expansion of embolization therapy, especially drug-eluting beads for liver and uterine cancers, improving locoregional drug concentration.
Clinical integration of personalized and companion diagnostics for matching patients with targeted NDDS-based therapies.
Collaborations between pharma and nanotech companies to accelerate commercialization of nanoparticle-based formulations.
Adoption of pH- and enzyme-responsive delivery systems, enabling tumor-specific drug release and reducing systemic toxicity.
Research into immunomodulatory NDDS, which deliver checkpoint inhibitors, cytokines, or vaccines directly to the tumor microenvironment.
Emergence of AI and modeling tools to optimize nanoparticle design and predict biodistribution and clearance profiles.
Increasing approval of liposomal and polymeric formulations, with expanding indications for hematologic and solid tumors.
Integration of NDDS with radiology and interventional oncology, enabling image-guided drug delivery and therapy monitoring.
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 18.14 Billion |
| Market Size by 2033 | USD 33.34 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2024 to 2033 | CAGR of 7.0% |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Forecast Period | 2024-2033 |
| Segments Covered | Product, Region |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) | Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Regional scope | North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, MEA |
| Key Companies Profiled | Bristol-Myers Squibb Company (Celgene Corporation); Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd; Johnson & Johnson Services, Inc.; Galen Limited; Shire (Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited); Samyang Holdings Corporation; Merrimack Pharmaceuticals; Spectrum Pharmaceuticals, Inc. |
One of the most compelling drivers of the novel drug delivery systems market is the escalating global incidence of cancer and the pressing need for safer, more targeted therapies. According to the World Health Organization, cancer accounted for nearly 10 million deaths in 2020, with projections indicating continued growth due to aging populations, environmental exposures, and lifestyle factors.
Traditional chemotherapy, although effective in certain contexts, is plagued by limitations such as poor tumor selectivity, systemic toxicity, and drug resistance. NDDS addresses these challenges by enabling site-specific drug delivery, enhancing tumor penetration, and minimizing exposure to healthy tissues. For instance, liposomal formulations like Doxil have demonstrated reduced cardiotoxicity compared to conventional doxorubicin, while maintaining anticancer potency.
Moreover, NDDS can be tailored to target specific tumor markers or microenvironmental conditions, aligning with the broader trend toward precision oncology. As oncologists and patients seek therapies that are both effective and tolerable, the demand for NDDS continues to rise across various tumor types and stages.
Despite the advantages of NDDS, one of the key restraints inhibiting rapid market growth is the regulatory and manufacturing complexity associated with these systems. Unlike conventional small molecules, NDDS products involve intricate formulations, often comprising biodegradable polymers, surface ligands, and encapsulated actives—all of which require meticulous design, characterization, and scale-up processes.
Regulatory bodies like the FDA and EMA demand comprehensive data on particle size distribution, drug loading efficiency, release kinetics, and stability, which adds to development timelines and costs. Additionally, batch-to-batch variability, challenges in sterilization and storage, and the need for specialized analytical equipment create hurdles for manufacturers, particularly small biotech firms.
Moreover, the lack of harmonized international regulatory pathways for nanomedicines and embolic agents further complicates global market access. Overcoming these technical and regulatory barriers requires investment in standardized protocols, academic-industry partnerships, and clear guidance from health authorities.
A major opportunity for market players lies in the integration of novel drug delivery systems with combination therapy strategies, particularly chemo-immunotherapy and radiotherapy. As cancer treatment shifts toward multi-modal approaches, NDDS offers an ideal platform for co-delivering synergistic agents or enhancing the effectiveness of immunotherapies.
For example, polymeric nanoparticles are being designed to co-deliver paclitaxel and PD-L1 inhibitors, improving both cytotoxic and immune-mediated effects. Similarly, micellar formulations can incorporate radiosensitizers or angiogenesis inhibitors alongside chemotherapy, increasing treatment precision and tumor regression rates.
Beyond therapeutic synergy, NDDS can help modulate the tumor microenvironment (e.g., reducing hypoxia or reversing immunosuppression), thereby improving patient responsiveness to combination protocols. Companies that innovate in this space and demonstrate clinical efficacy are likely to benefit from higher reimbursement rates, competitive differentiation, and regulatory support for breakthrough designations.
Nanoparticles accounted for the largest market revenue share of 87.0% in 2023, owing to their extensive clinical utility, high biocompatibility, and modular design capabilities. Among nanoparticles, liposomes and polymers are the most widely used carriers for chemotherapeutic drugs. Liposomal platforms such as Doxil, Myocet, and Onivyde are FDA-approved for treating various solid tumors, offering benefits like prolonged circulation time and reduced toxicity. Polymeric nanoparticles, on the other hand, allow for sustained release and targeted delivery of hydrophobic drugs, siRNA, or peptides. These systems are gaining momentum in treating brain, breast, and pancreatic cancers, where conventional drugs fail to achieve effective concentrations.
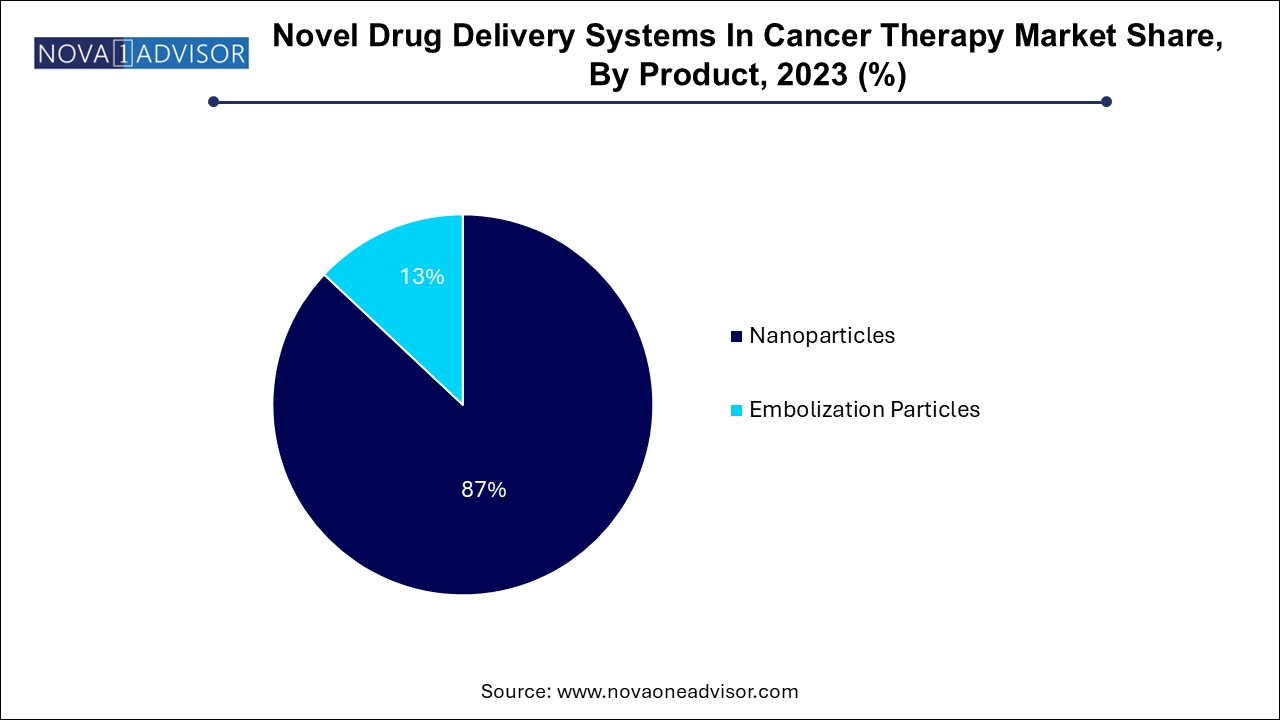
Embolization particles projected to grow at the fastest CAGR of 10.7% over the forecast period. especially in interventional oncology for localized therapy. Drug-eluting beads have become standard for transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) in hepatocellular carcinoma and liver metastases. These beads provide sustained local drug release while blocking tumor vasculature. PVA particles and liquid embolics are widely used for vascular malformations and pre-surgical devascularization of tumors. With increasing adoption of image-guided procedures and catheter-based delivery systems, the embolization segment is poised for substantial growth.
North America novel drug delivery systems in cancer therapy market dominated the global novel drug delivery systems in cancer therapy market in 2023 with 43.4% owing to its robust oncology infrastructure, advanced R&D ecosystem, and supportive regulatory landscape. The U.S., in particular, leads in terms of clinical trials, product approvals, and academic-industry collaborations. The presence of established players such as Bristol Myers Squibb, Johnson & Johnson, and Celgene, along with emerging nanotech startups, has fostered innovation and rapid product commercialization. Additionally, favorable reimbursement policies for nanoparticle-based therapies and embolization procedures have facilitated market penetration across both academic hospitals and private oncology clinics.
Asia Pacific is the fastest-growing region, driven by rising cancer prevalence, government investment in precision medicine, and increasing awareness about novel therapeutic options. Countries like China, India, Japan, and South Korea are witnessing growing adoption of NDDS platforms in both public hospitals and private cancer centers. In China, for example, companies are developing indigenous liposomal formulations and embolization products under national initiatives like “Made in China 2025.” Meanwhile, India’s pharma sector is exploring cost-effective polymer-based nanocarriers for generic oncology drugs, improving affordability and access. Strategic partnerships between local firms and global players are further enhancing technology transfer and regulatory alignment.
March 2025: Y-mAbs Therapeutics announced FDA Fast Track Designation for its investigational drug delivery platform targeting CNS tumors using nanoliposome-encapsulated radiotherapeutics.
January 2025: TriSalus Life Sciences launched its Pressure-Enabled Drug Delivery™ system in select U.S. cancer centers, enhancing intravascular delivery of chemotherapy for liver and pancreatic tumors.
November 2024: Medtronic expanded its embolization product line with the acquisition of a biodegradable microsphere startup, targeting interventional oncology applications in Asia and Europe.
September 2024: Bristol Myers Squibb entered a collaboration with Nanobiotix to develop radio-enhancing nanoparticles in combination with immuno-oncology agents for advanced head and neck cancer.
July 2024: CSPC Pharmaceutical Group received Chinese regulatory approval for its PEGylated liposomal irinotecan formulation, marking the first nanocarrier-based therapy developed and commercialized domestically.
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2033. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the novel drug delivery systems in cancer therapy market
Product
Regional