The global personalized medicine market size was valued at USD 530.11 billion in 2023 and is anticipated to reach around USD 1,176.66 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 8.30% from 2024 to 2033.
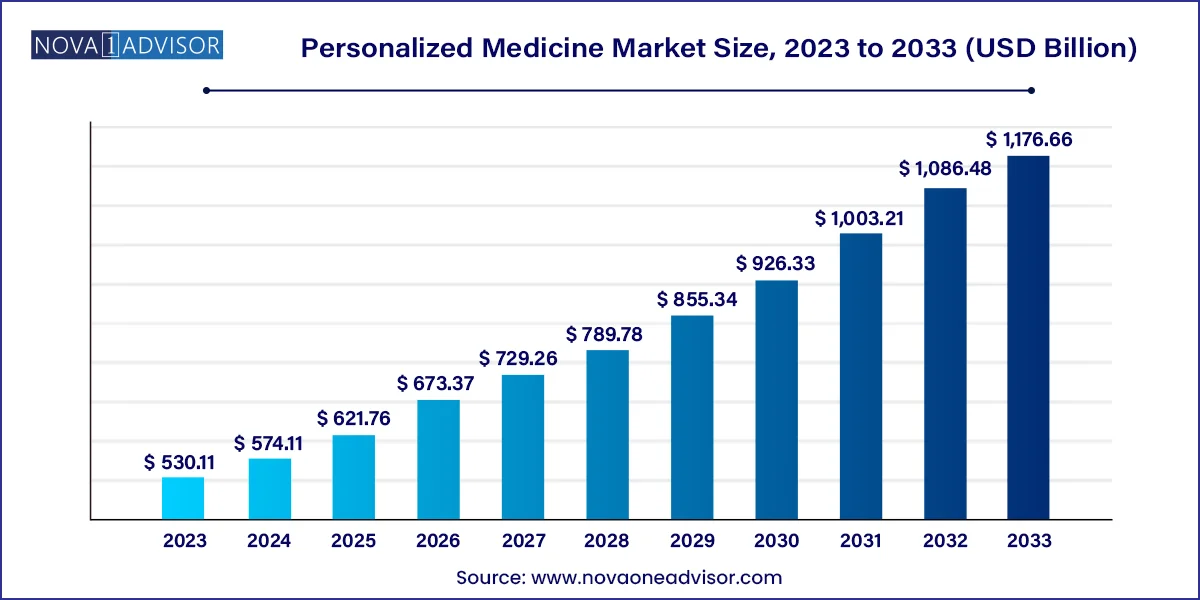
The U.S. personalized medicine market size was valued at USD 170.14 billion in 2023 and is expected to reach around USD 387.40 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 8.6% from 2024 to 2033.
North America dominated the personalized medicine market, largely due to advanced healthcare infrastructure, favorable reimbursement frameworks, and the presence of major genomic research companies. The United States leads in personalized drug approvals, with the FDA encouraging the development of companion diagnostics and breakthrough therapies. Initiatives such as the Precision Medicine Initiative and Cancer Moonshot have accelerated the integration of genomics into clinical care. Furthermore, the region is home to leading biotech firms, digital health startups, and academic research centers.
Asia-Pacific is expected to be the fastest-growing regional market, driven by expanding healthcare access, increasing investment in genomics, and government support for precision health programs. China and India are investing heavily in population genomics and AI-enabled health platforms. Japan's focus on geriatric genomics and South Korea's innovation in bioinformatics are also contributing to regional growth. The rise of telemedicine and mobile health apps in Asia-Pacific further supports the delivery of personalized care across diverse demographics.
The personalized medicine market represents one of the most dynamic and transformative areas of modern healthcare. Unlike traditional treatment paradigms that follow a one-size-fits-all model, personalized medicine involves tailoring medical treatment to individual characteristics such as genetic makeup, environmental exposures, and lifestyle choices. This approach enables higher efficacy, fewer side effects, and more informed clinical decisions. The market has gained significant momentum over the past decade, driven by advances in genomics, digital health, biomarker identification, and drug development technologies. From oncology and rare disease treatment to personalized nutrition and mental health care, the applications are expanding across the spectrum of healthcare.
In clinical settings, the integration of companion diagnostics with therapeutics has enabled targeted therapies to be administered with precision, improving outcomes particularly in cancer care. At the consumer level, direct-to-consumer (DTC) genetic tests have revolutionized how individuals interact with their health data. Furthermore, the convergence of artificial intelligence (AI), bioinformatics, and telemedicine is supporting more scalable and efficient delivery of personalized care. Major pharmaceutical companies are increasingly developing therapies based on patient stratification using genetic, proteomic, and metabolomic profiling. The personalized medicine market is not only enhancing patient care but also reshaping business models, regulatory frameworks, and research strategies in life sciences.
Growth of Companion Diagnostics: Companion diagnostics are now routinely paired with targeted therapies, especially in oncology, to identify patients most likely to benefit from a treatment.
Direct-to-Consumer Genomic Testing Expansion: DTC testing services are gaining popularity, allowing consumers to access genetic information without a healthcare intermediary.
Integration of AI and Big Data Analytics: Machine learning models are analyzing massive datasets from patient genomes, EHRs, and clinical trials to support decision-making.
Rise in Telemedicine Adoption: Telemedicine platforms are becoming integral to delivering personalized care, especially in chronic disease management.
Advancements in Liquid Biopsy: Non-invasive blood-based tests are emerging as powerful tools for monitoring disease progression and therapy response.
Personalized Nutrition and Wellness: Nutrigenomics and microbiome analysis are guiding personalized dietary and lifestyle interventions.
Increasing Investment in Rare Disease and Orphan Drug Research: Personalized medicine is ideal for developing therapies for niche populations with specific genetic mutations.
| Report Attribute | Details |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 574.11 Billion |
| Market Size by 2033 | USD 1,176.66 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2024 to 2033 | CAGR of 8.30% |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Forecast Period | 2024 to 2033 |
| Segments Covered | Product, Application, End Use, Technology, Region |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) | Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Report Coverage | Revenue forecast, company ranking, competitive landscape, growth factors, and trends |
| Key Companies Profiled | GE Healthcare, Illumina, Inc., ASURAGEN, INC., Abbott, Dako A/S, Exact Sciences Corporation, Danaher Corporation (Cepheid, Inc.), Decode Genetics, Inc., QIAGEN, Exagen Inc., Precision Biologics, Celera Diagnostics LLC, Biogen, Genelex, IBM, Genentech, Inc., 23andMe, Inc. |
A primary driver of the personalized medicine market is the growing demand for targeted therapies, especially in oncology. Conventional chemotherapies often lead to broad cytotoxic effects, affecting both healthy and malignant cells. In contrast, targeted therapies act on specific molecular pathways involved in tumorigenesis. Personalized medicine enables these treatments by using genetic tests to identify mutations such as EGFR, HER2, or BRAF. For instance, the use of Trastuzumab in HER2-positive breast cancer patients has significantly improved survival rates. As healthcare systems strive for cost-effective solutions that maximize patient outcomes, the demand for such precise, biomarker-driven interventions continues to rise.
One of the most pressing challenges in personalized medicine is the issue of data privacy and ethical management of genetic information. As genomic and health data are shared across platforms for research and care coordination, there is a heightened risk of misuse or breaches. Unauthorized access to genetic data could lead to insurance discrimination, stigmatization, or exploitation. Moreover, questions persist regarding informed consent, data ownership, and the use of anonymized data in commercial research. Regulatory bodies like the GDPR in Europe and HIPAA in the United States have implemented frameworks to mitigate these risks, but inconsistencies across jurisdictions remain a barrier to seamless global integration.
The integration of artificial intelligence into personalized medicine presents an expansive opportunity for market growth. AI-driven platforms can rapidly analyze complex datasets, including genomic sequences, proteomic profiles, imaging data, and clinical histories, to identify patterns and predict disease trajectories. For instance, IBM Watson has been used to suggest treatment protocols based on genomic markers in oncology. Startups are also developing AI tools for personalized drug response prediction and precision nutrition planning. As AI algorithms become more accurate and interpretable, they are expected to accelerate drug development pipelines, support clinician decision-making, and democratize access to personalized healthcare.
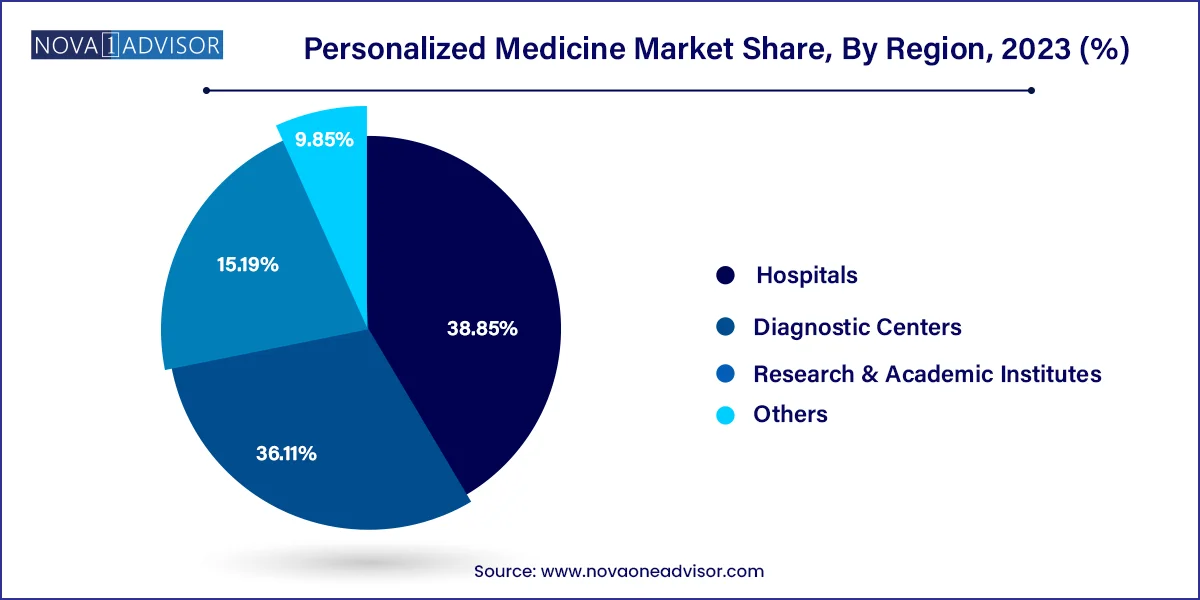
Personalized medicine therapeutics dominated the market in 2024, accounting for the largest revenue share due to the proliferation of targeted drugs and genomic medicine. These therapeutics are tailored to specific patient groups or even individuals based on molecular diagnostics. Pharmaceutical innovations in oncology, particularly in non-small cell lung cancer and melanoma, have contributed significantly to this segment. Drug development pipelines now routinely include genetic biomarker validation, enabling faster and more effective treatment approvals. Genomic medicine is also playing a vital role in managing rare diseases, where patient-specific therapies are being developed using gene editing and cell therapy techniques.
Personalized medicine diagnostics is expected to be the fastest-growing product segment, driven by rising demand for genetic testing, DTC diagnostics, and esoteric laboratory services. The affordability and accessibility of sequencing technologies have led to widespread adoption in both clinical and consumer settings. Esoteric lab tests, such as those identifying complex mutations or rare disorders, are increasingly used in specialized institutions. Moreover, DTC testing companies like 23andMe and AncestryDNA are expanding into health-related insights, enabling consumers to assess disease risk, carrier status, and pharmacogenetic compatibility from home.
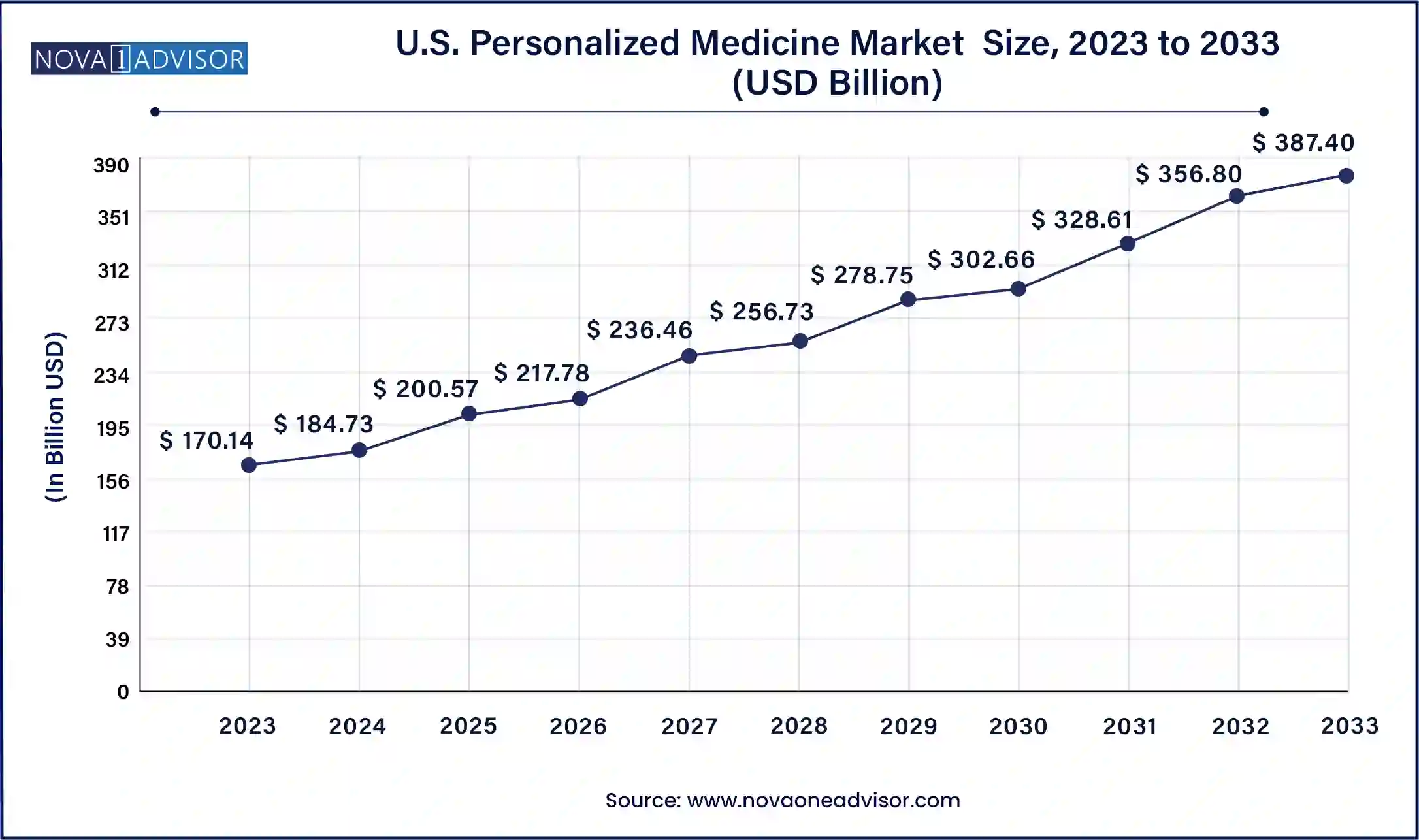
Hospitals were the leading end-users in 2024, due to their role in implementing clinical genomics, administering targeted therapies, and coordinating multidisciplinary care. Hospital networks have increasingly integrated molecular pathology and precision oncology units to enhance patient care. Large academic medical centers are also collaborating with pharmaceutical companies to conduct personalized medicine trials and integrate novel diagnostics.
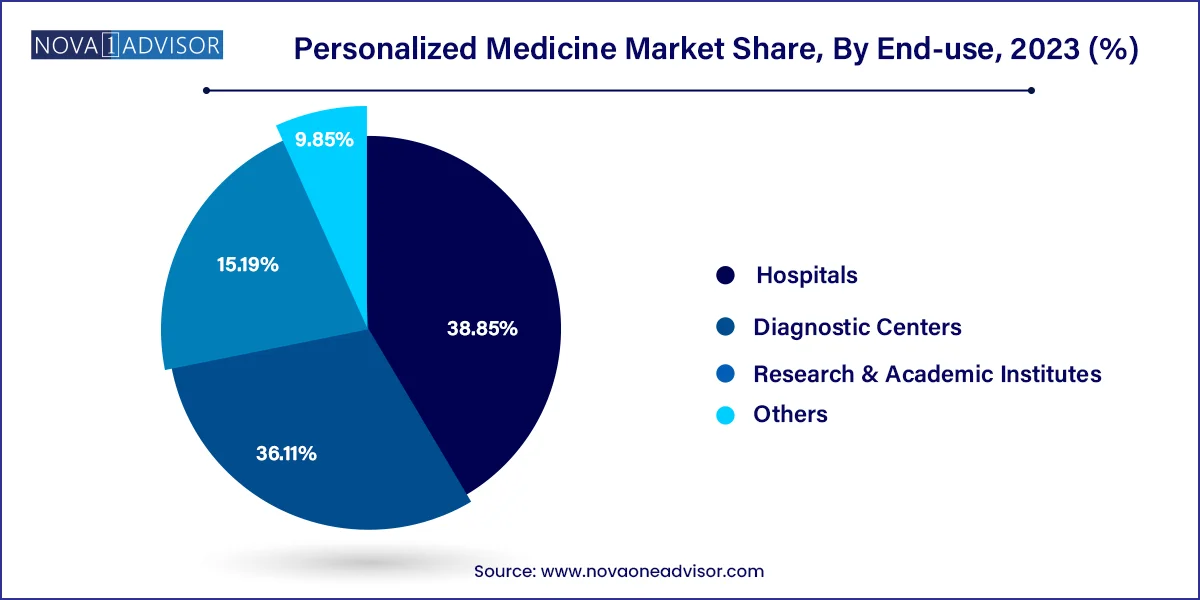
Research and academic institutes are the fastest-growing end-use segment, propelled by increasing government and private funding for personalized medicine projects. Institutions are spearheading multi-omics studies, bioinformatics tool development, and translational research initiatives. For example, the NIH's All of Us Research Program in the U.S. aims to collect genetic data from over one million Americans to support personalized medicine innovation.
The following are the leading companies in the personalized medicine market. These companies collectively hold the largest market share and dictate industry trends.
March 2025: Illumina launched the NovaSeq X system, reducing the cost of genome sequencing and enabling broader access to population-level genomic research.
February 2025: Roche partnered with Flatiron Health to integrate real-world evidence into personalized cancer treatment platforms using electronic health data.
January 2025: 23andMe received FDA clearance for its pharmacogenetics report, allowing consumers to assess drug metabolism variations directly.
December 2024: Tempus unveiled an AI-based clinical decision support tool for oncologists, helping select therapies based on real-time genomic data.
November 2024: GSK and NVIDIA announced a collaboration to accelerate drug discovery through AI-enabled genomic analysis using NVIDIA's Clara platform.
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2033. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the Personalized Medicine market.
By Product
By Application
By Technology
By End-use
By Region