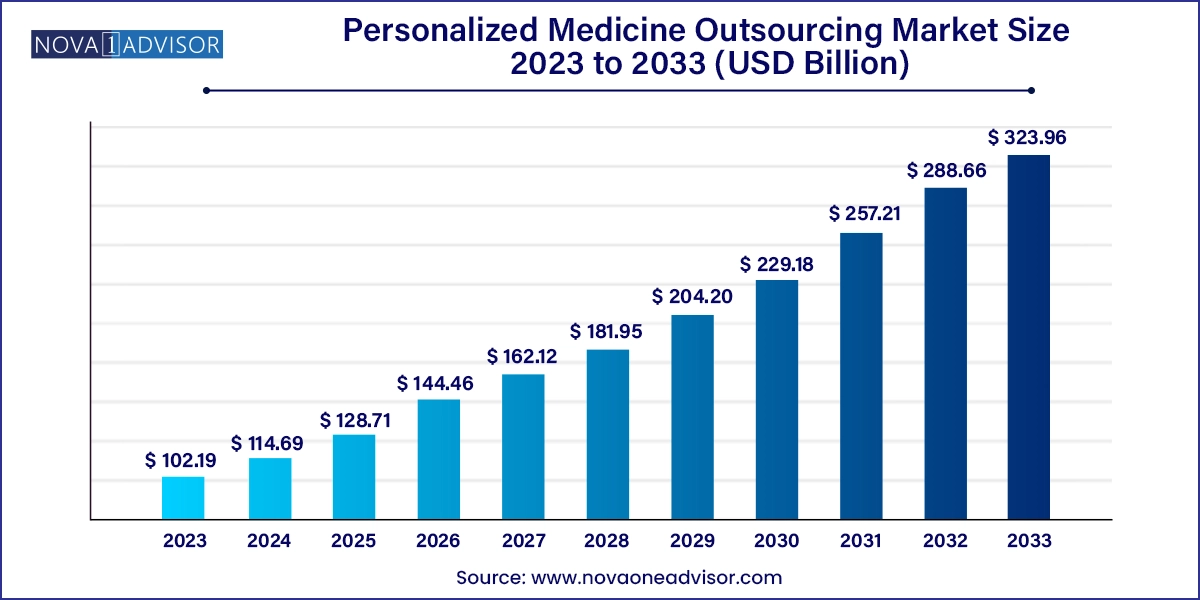
The global personalized medicine outsourcing market size was valued at USD 102.19 billion in 2023 and is anticipated to reach around USD 323.96 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 12.23% from 2024 to 2033.
The Personalized Medicine Outsourcing Market is rapidly evolving into one of the most dynamic and essential segments of the global healthcare and pharmaceutical industry. At the core of personalized medicine lies the concept of tailoring medical treatment to the individual characteristics, needs, and genetic profile of each patient. This paradigm shift from a one-size-fits-all approach to precision therapy has necessitated a complete transformation in how therapeutics are researched, developed, and manufactured—giving rise to a robust outsourcing ecosystem.
With personalized medicine involving highly specific, often complex therapeutic products such as monoclonal antibodies, cell and gene therapies, and targeted small molecule inhibitors, pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies increasingly rely on external partners for manufacturing, clinical development, and regulatory support. The complexity and high cost of these processes, combined with the need for rapid innovation, make outsourcing a strategic necessity rather than an option.
Contract development and manufacturing organizations (CDMOs), contract research organizations (CROs), and regulatory consultants offer the specialized knowledge, infrastructure, and scalability that enable drug developers to bring personalized therapies to market efficiently. This outsourcing trend spans across the product life cycle—from preclinical development and early-phase trials to large-scale commercial manufacturing and post-market surveillance.
The surge in clinical research across therapeutic areas such as oncology, rare genetic disorders, and infectious diseases further amplifies the demand for personalized medicine outsourcing. As regulatory bodies like the FDA, EMA, and PMDA adapt to accommodate emerging modalities, companies are under pressure to meet compliance while accelerating timelines. In this complex ecosystem, outsourcing partners play a pivotal role in enabling precision therapies to reach the right patients at the right time.
Increased Investment in Cell and Gene Therapy CDMOs: Rising number of cell and gene therapy trials has spurred demand for niche outsourcing firms with viral vector, plasmid, and cryopreservation expertise.
Integration of Artificial Intelligence in Drug Development: AI-powered platforms are transforming preclinical testing and patient stratification, making outsourced discovery services more efficient.
Growth of Decentralized Clinical Trials: Personalized medicine trials are increasingly being conducted through hybrid or fully decentralized models supported by outsourced patient monitoring and data collection services.
Regulatory Consultancy Outsourcing on the Rise: Companies are outsourcing regulatory documentation, interactions, and compliance planning to specialized service providers with personalized medicine expertise.
Specialized Manufacturing for Complex Biologics: Outsourcing firms are expanding modular, GMP-compliant facilities tailored for small-batch biologic and cell therapy production.
Expansion of Rare Disease Focus: Orphan drug development is growing, leading to higher outsourcing in trial design, biomarker discovery, and regulatory submissions.
Adoption of Companion Diagnostic Co-Development Models: Increasing number of CDMOs and CROs are offering integrated services that include diagnostic assay validation and biomarker-based trial design.
| Report Attribute | Details |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 114.69 Billion |
| Market Size by 2033 | USD 323.96 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2024 to 2033 | CAGR of 12.23% |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Forecast Period | 2024 to 2033 |
| Segments Covered | Phase, application, service, type, end-use, region |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) | Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Report Coverage | Revenue forecast, company ranking, competitive landscape, growth factors, and trends |
| Key Companies Profiled | Parexel International (MA) Corporation; Syneos Health; Catalent, Inc; ICON plc; Lonza; Syngene International Limited; HCL Technologies Limited; Infosys Limited; Fujirebio; Aurigene Pharmaceutical Services Ltd. |
Rising Complexity of Therapeutic Modalities Demands Specialized Outsourcing
The growing complexity of therapeutic modalities in personalized medicine is a primary driver of outsourcing demand. Unlike traditional pharmaceuticals, personalized therapies often involve intricate biological systems, targeted mechanisms, and the integration of genomic data. For instance, CAR-T therapies require autologous cell manipulation and highly specific production timelines, while monoclonal antibodies must meet exacting quality standards and be manufactured in cleanroom environments.
Pharmaceutical companies—especially emerging biotechs—often lack the infrastructure and regulatory knowledge to handle these complexities in-house. Outsourcing to specialized CDMOs and CROs allows them to access state-of-the-art facilities, advanced analytics, and regulatory compliance frameworks without the capital burden. These service providers also facilitate rapid scale-up, batch production, and tech transfer processes, which are critical in meeting expedited approval timelines, such as those under orphan drug or fast-track designations.
Intellectual Property and Data Security Concerns in Outsourcing Partnerships
While outsourcing brings efficiency and scalability, it also raises concerns over intellectual property (IP) protection and data confidentiality, especially in the highly proprietary field of personalized medicine. Many of these therapies are built around unique genetic markers, biomarker targets, or cell lines that constitute the core intellectual assets of pharmaceutical and biotech firms.
Collaborating with external vendors across multiple geographies and jurisdictions increases the risk of IP leakage or non-compliance with data protection laws such as GDPR, HIPAA, or national biosafety regulations. For instance, genomic data collected during a clinical trial might be stored in a different country, raising legal and ethical challenges. Smaller firms are particularly vulnerable due to limited legal resources, which may lead to cautious outsourcing behavior or additional legal costs for contract negotiation and monitoring.
Expansion of Personalized Medicine in Emerging Markets
The expansion of personalized medicine into emerging markets such as India, China, Brazil, and Southeast Asia presents a major growth opportunity for outsourcing. These regions offer large patient pools, diverse genetic populations for research, and a growing infrastructure for clinical trials and biologics manufacturing. Governments are actively supporting biotechnology innovation through tax incentives, investment grants, and regulatory modernization.
Outsourcing firms that can establish local partnerships or set up operations in these regions stand to gain significant market share. For example, China’s NMPA and India’s CDSCO are accelerating clinical trial approvals for novel personalized therapies, boosting demand for localized CRO and CDMO services. Moreover, the growing presence of skilled professionals, coupled with cost advantages, makes these regions attractive hubs for clinical development, regulatory consulting, and small-scale personalized therapeutic production.
Clinical phases, particularly Phase II and Phase III, dominate the personalized medicine outsourcing market. These phases involve targeted patient populations, biomarker-driven endpoints, and close regulatory oversight—all of which necessitate the expertise of CROs and CDMOs. Oncology trials, for instance, often rely on genetic stratification and adaptive trial designs, increasing the need for outsourced data management, companion diagnostic development, and patient recruitment services. As a result, pharmaceutical and biotech firms routinely partner with outsourcing firms to accelerate development timelines and ensure trial success.
Preclinical phase outsourcing is growing at the fastest pace, driven by the increasing complexity of early-stage research in personalized medicine. With new modalities such as mRNA therapeutics, RNAi-based drugs, and gene editing technologies, preclinical models must be highly specialized. Outsourcing providers now offer in vitro assays, CRISPR libraries, and transgenic animal models tailored to specific disease pathways. Companies like Charles River Laboratories and WuXi AppTec are expanding capabilities in genomics-enabled discovery and toxicity testing, making preclinical outsourcing a strategic priority for innovators.
Oncology was the leading application segment in the personalized medicine outsourcing market due to the high volume of targeted cancer therapies in development. Personalized approaches in oncology leverage genetic mutations such as EGFR, BRAF, or HER2 to identify responsive patient populations. Outsourcing partners support these efforts by managing biomarker validation, companion diagnostic development, and complex manufacturing protocols. Contract manufacturers also provide scalable, GMP-compliant production for monoclonal antibodies and antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs), which dominate the precision oncology pipeline.
Rare diseases are gaining momentum as the fastest-growing segment, with more than 7,000 conditions classified under this category, many of which are genetic. The high unmet need and regulatory incentives like orphan drug exclusivity and fast-track approvals make rare disease development a key area of focus for biotech firms. However, limited patient pools and complex study designs necessitate specialized CRO support. Companies like PPD and ICON offer decentralized trial capabilities, digital biomarker integration, and regulatory expertise in orphan indications, making outsourcing vital to rare disease innovation.
Contract development services dominated the market as pharmaceutical and biotech companies outsource drug formulation, analytical method development, and preclinical research for personalized products. These services ensure that drugs are optimized for delivery, stability, and therapeutic effectiveness before they enter clinical trials. Many CDMOs now provide integrated development platforms that include early-stage R&D, regulatory consulting, and clinical trial material preparation—enabling a seamless transition from concept to clinical evaluation.
Contract manufacturing is growing rapidly as more personalized therapies progress toward commercial stages. The rise of biologics and ATMPs (advanced therapy medicinal products) like CAR-T cells has driven demand for specialized manufacturing facilities with capabilities in sterile fill-finish, viral vector production, and cold-chain logistics. Flexible manufacturing systems, modular cleanrooms, and continuous bioprocessing are being adopted to accommodate small-batch, high-complexity production. This shift is accelerating investment in global GMP manufacturing capacity, particularly for cell and gene therapies.
Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) dominated the therapeutic product segment, reflecting their established role in personalized medicine for autoimmune diseases, cancers, and inflammatory conditions. These biologics require sophisticated development and production infrastructure, leading to outsourcing of expression system development, purification processes, and quality control. Contract manufacturers are scaling up facilities to meet the demand for biosimilars and novel mAb therapies with enhanced specificity and reduced immunogenicity.
Cell & gene therapy is the fastest-growing type due to an explosion of clinical activity and investment in regenerative medicine. These therapies involve manipulating patient-derived cells or delivering gene-editing tools like CRISPR, posing substantial logistical, manufacturing, and regulatory challenges. Specialized outsourcing partners like Catalent, Lonza, and Thermo Fisher Scientific offer expertise in viral vector production, cell expansion, and cryopreservation. The complexity of these therapies makes outsourcing a strategic necessity, especially for startups and academic spin-offs aiming for commercialization.
Pharmaceutical companies held the dominant position in the market due to their extensive drug pipelines and global commercialization requirements. These firms engage outsourcing partners at every stage—from target identification and trial design to manufacturing and lifecycle management. The need to accelerate product timelines and reduce operational burden makes outsourcing an essential part of their R&D strategy.
Biotechnology companies, often smaller and innovation-focused, are the fastest-growing end users. Lacking internal resources for large-scale development or GMP production, they rely heavily on outsourcing partners. Emerging biotechs are at the forefront of cell therapy, RNA therapeutics, and gene-editing platforms, making them ideal candidates for integrated CDMO/CRO services. This reliance is fostering long-term strategic alliances between biotechs and outsourcing firms, often resulting in shared IP development and risk-sharing models.
North America, especially the United States, leads the global personalized medicine outsourcing market. The region benefits from the presence of major pharmaceutical companies, advanced clinical research infrastructure, and a strong regulatory framework supporting innovative therapies. The FDA's proactive stance on personalized treatments and companion diagnostics has accelerated development timelines, increasing demand for outsourcing services. Leading CDMOs and CROs headquartered in the U.S., including Thermo Fisher Scientific, Charles River, and Catalent, continue to expand capacity to support the booming cell and gene therapy market.
Asia-Pacific is witnessing the fastest growth in personalized medicine outsourcing due to increasing clinical trial activity, favorable regulatory changes, and growing biotech ecosystems. Countries like China, India, and South Korea are investing heavily in precision medicine initiatives, supported by government funding and foreign investment. Outsourcing firms are establishing local facilities to offer clinical development, biomanufacturing, and regulatory support tailored to these markets. Cost efficiency, large patient pools, and improving compliance environments make Asia-Pacific an attractive destination for global outsourcing in personalized healthcare.
April 2025 – Lonza Group announced the opening of a new cell and gene therapy manufacturing facility in Singapore to expand its Asia-Pacific capabilities.
February 2025 – Thermo Fisher Scientific acquired a U.S.-based CDMO specializing in mRNA-based personalized vaccines, strengthening its RNA therapeutic outsourcing services.
December 2024 – Catalent entered into a multi-year agreement with a European biotech firm to support the development and manufacture of rare disease gene therapies.
October 2024 – WuXi AppTec launched a cloud-based platform for integrated preclinical and clinical development tailored for personalized medicine pipelines.
August 2024 – PPD (a Thermo Fisher company) partnered with a Japanese pharma company to conduct decentralized oncology trials using genomic stratification.
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2033. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the Personalized Medicine Outsourcing market.
By Phase
By Application
By Service
By Type
By End-use
By Region