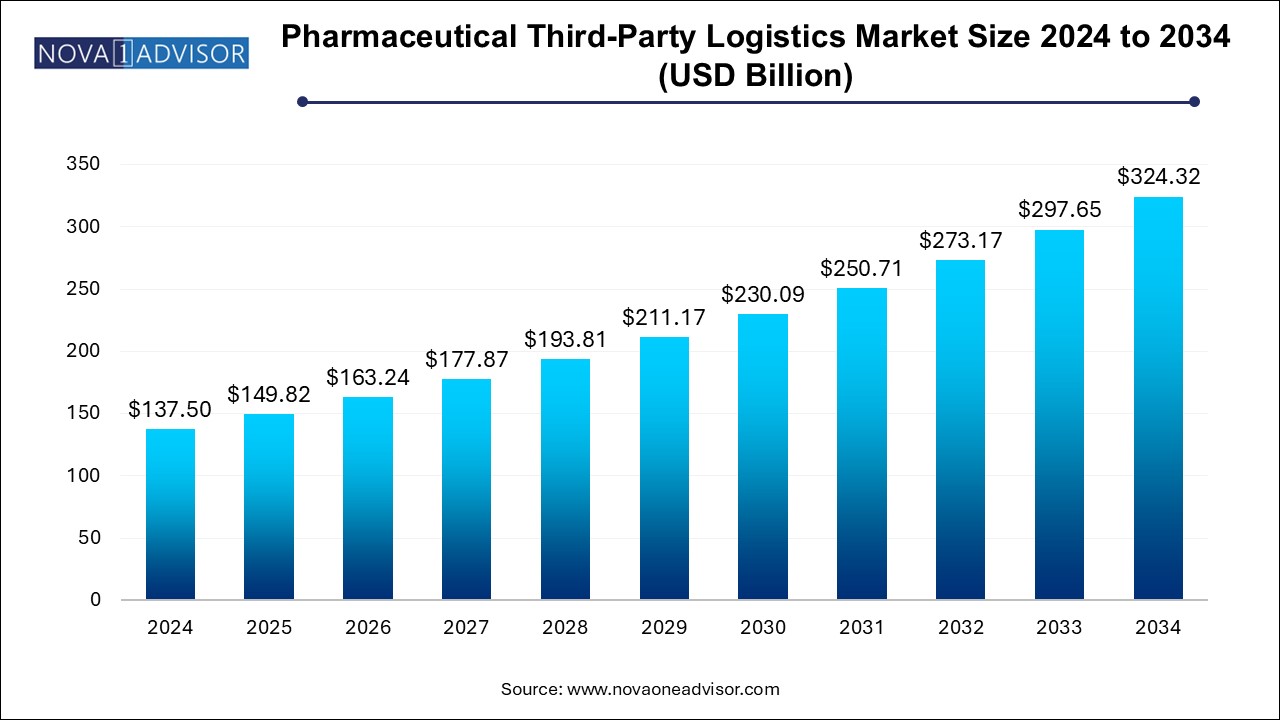
The pharmaceutical third-party logistics market size was exhibited at USD 137.5 billion in 2024 and is projected to hit around USD 324.32 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 8.96% during the forecast period 2025 to 2034.
The U.S. pharmaceutical third-party logistics market size is evaluated at USD 40.2 billion in 2024 and is projected to be worth around USD 95.5 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 8.18% from 2025 to 2034.
-Market.jpg)
North America leads the pharmaceutical 3PL market, driven by a mature pharmaceutical industry, strong regulatory enforcement, and high demand for specialty drug distribution. The U.S. is home to top pharmaceutical companies and 3PL providers, including UPS Healthcare, AmerisourceBergen, and McKesson. The region’s dominance is reinforced by the presence of advanced cold-chain infrastructure, widespread adoption of DSCSA-compliant serialization, and growing demand for biologics and home-based therapies. With a robust investment landscape and innovation-driven logistics network, North America is expected to maintain its leadership position.
Asia Pacific is the fastest-growing region, supported by expanding pharmaceutical manufacturing in China and India, rising biologics demand, and growing investment in healthcare logistics. The region's lower labor and real estate costs make it attractive for 3PL infrastructure development. Countries like Singapore and South Korea are emerging as cold-chain logistics hubs. Moreover, the rising prevalence of chronic diseases, growing middle-class population, and regulatory harmonization are encouraging multinational pharma companies to partner with regional 3PLs for scalable distribution strategies.
The pharmaceutical third-party logistics (3PL) market plays a pivotal role in the global pharmaceutical value chain, serving as the backbone of drug distribution by ensuring the timely, secure, and compliant movement of pharmaceutical products from manufacturers to end-users. With rising complexity in drug portfolios—including temperature-sensitive biologics, cell and gene therapies, and personalized medicine—logistics is no longer a back-end operational function but a strategic component of pharmaceutical delivery.
Pharmaceutical manufacturers increasingly partner with specialized 3PL providers to outsource critical supply chain functions such as warehousing, order fulfillment, inventory management, regulatory compliance, and cold-chain logistics. This allows manufacturers to focus on core R&D and commercialization, while leveraging the 3PL's expertise in transportation optimization, risk mitigation, and adherence to evolving global regulatory requirements.
The pharmaceutical 3PL market spans various services, from traditional storage and distribution to advanced serialization, DSCSA compliance, and real-time track-and-trace capabilities. 3PL providers are rapidly adopting digital technologies, including IoT sensors, AI-driven forecasting, and blockchain-based supply chain transparency, to enhance service offerings and reduce disruptions. This is especially crucial for high-value, high-risk products such as biologics, vaccines, and temperature-sensitive specialty drugs.
The growing global demand for biologics, rapid growth in e-pharmacy, expansion of personalized therapies, and increasing regulatory scrutiny are reshaping the contours of the pharmaceutical logistics ecosystem. In this evolving landscape, 3PLs are becoming strategic partners, not just logistical vendors, as they bridge the gap between innovation and accessibility.
Growth in Cold Chain Logistics: Surge in biologics, vaccines, and cell/gene therapies is driving investment in temperature-controlled transport and storage.
DSCSA and Serialization Compliance: Increasing adoption of serialization and digital track-and-trace solutions to meet regulatory mandates.
Blockchain Integration for Transparency: Pharmaceutical companies are piloting blockchain platforms with 3PLs to ensure supply chain integrity.
Adoption of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and IoT: AI is being used for demand forecasting, while IoT sensors are monitoring temperature and shock during transit.
Customization of Logistics for Personalized Medicine: Gene and cell therapy distribution is demanding cryogenic storage, time-sensitive delivery, and reverse logistics.
Rise of Title Model Services: Pharmaceutical companies increasingly opt for title model distribution, where 3PLs take temporary ownership of inventory to manage supply chain complexity.
Outsourcing Among Small and Mid-sized Biotechs: Emerging pharma companies are increasingly outsourcing full-scale logistics operations to reduce CapEx and accelerate time-to-market.
Integration of e-commerce Fulfillment Models: DTC (direct-to-consumer) channels, especially in chronic care and over-the-counter products, are influencing last-mile logistics strategies.
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 149.82 Billion |
| Market Size by 2034 | USD 324.32 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2025 to 2034 | CAGR of 8.96% |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025-2034 |
| Segments Covered | Product, Temperature, Therapeutic Area, Manufacturer Size, Service |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) | Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Regional scope | North America; Europe; Asia Pacific; Latin America; MEA |
| Key Companies Profiled | CEVA Logistics; Cencora Corporation (ICS); DB SCHENKER; Kuehne+Nagel; Kerry Logistics Network Limited; Cardinal Health; McKesson Corporation; EVERSANA, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Knipper Health |
A primary driver of the pharmaceutical 3PL market is the rising global demand for biologics and specialty pharmaceuticals, which require stringent logistics support due to their complexity, sensitivity, and regulatory requirements. Unlike traditional small-molecule drugs, biologics such as monoclonal antibodies, therapeutic proteins, and vaccines are temperature-sensitive and often need refrigerated or cryogenic handling throughout the supply chain.
For example, mRNA vaccines like Pfizer-BioNTech's COVID-19 vaccine require ultra-low temperature storage and real-time temperature monitoring, a task that only highly specialized 3PLs can manage. Furthermore, the growth of biosimilars and high-value specialty drugs in oncology, immunology, and neurology has intensified the demand for temperature-controlled storage, secured delivery, and stringent product integrity assurance during transit.
To meet these demands, 3PL providers are investing heavily in specialized infrastructure, including GMP-compliant cold rooms, validated packaging, dry ice/cryogenic transport systems, and IoT-based monitoring tools. This expansion is not limited to large pharmaceutical companies—mid-sized firms and biosimilar developers are also contributing significantly to the volume, expanding the logistics footprint across markets.
Despite growth opportunities, the pharmaceutical 3PL market faces significant barriers due to high capital investment and complex regulatory compliance. To serve biopharma clients effectively, logistics providers must establish GDP (Good Distribution Practice)-compliant facilities, acquire temperature-controlled fleets, implement validated IT systems, and maintain stringent quality assurance protocols. These requirements are not only capital-intensive but also entail ongoing costs for maintenance, audit readiness, and certification renewals.
Furthermore, the market is governed by evolving regulations—such as the Drug Supply Chain Security Act (DSCSA) in the U.S. and the Falsified Medicines Directive (FMD) in Europe—which demand serialization, traceability, and tamper-evidence at every node in the supply chain. Compliance failures can result in costly recalls, shipment holds, or legal penalties. Smaller 3PL firms may struggle to keep pace, leading to market consolidation. Thus, while demand is growing, the barrier to entry and cost of compliance remain key restraints for new entrants and expansion plans.
A transformative opportunity in the pharmaceutical 3PL market is the emergence of logistics models tailored for cell and gene therapies (CGTs). These personalized therapies often involve the collection of patient-specific cells, their modification in GMP facilities, and rapid return for reinfusion—typically within narrow timeframes and under strict temperature-controlled conditions.
This highly intricate and sensitive logistics workflow has created demand for specialized “vein-to-vein” and “needle-to-needle” solutions that combine cryogenic shipping, chain-of-identity tracking, redundant transport routes, and rapid communication systems. 3PL providers that can build capabilities around this emerging niche—such as cryo-packaging, remote temperature validation, real-time GPS monitoring, and contingency routing—stand to become strategic partners in the personalized medicine revolution.
As more CGTs receive FDA approval and enter commercial distribution, logistics providers with pre-built cryogenic infrastructure, regulatory expertise, and proven SOPs (Standard Operating Procedures) will be uniquely positioned to capture this lucrative, high-value market segment.
The Branded pharmaceuticals dominated the pharmaceutical 3PL market in 2024, owing to their high demand, complex regulatory handling, and premium pricing. These products often require tailored logistics strategies to ensure quality and regulatory compliance during transport. Given the high financial value of branded drugs—especially in oncology, cardiovascular, and neurology—pharma companies rely heavily on specialized 3PL partners for inventory control, theft prevention, serialization, and secure distribution across healthcare networks and pharmacies. The long patent lifecycle of branded products ensures a stable logistics demand with emphasis on service quality and traceability.
Meanwhile, cell and gene therapy products are the fastest-growing product segment, given their precision medicine focus and extreme logistical demands. These therapies require cryogenic temperatures (as low as -196°C), real-time location tracking, and specialized handling from collection to delivery. Unlike traditional products, CGTs often involve small batches or even single-patient shipments, making efficiency and reliability paramount. 3PL providers are investing in specialized packaging, route optimization, and compliance protocols to cater to this niche, high-growth segment that is expected to expand significantly over the next decade.
The Refrigerated logistics held the largest market share, driven by the widespread demand for cold-chain distribution in biologics, vaccines, and specialty drugs. Temperatures typically maintained between 2°C to 8°C are required for monoclonal antibodies, insulin, and select antibiotics. Refrigerated logistics ensures product integrity through the use of temperature-controlled containers, real-time temperature sensors, and cold storage warehousing facilities. Regulatory requirements and increasing quality audits further reinforce the dominance of this segment, especially in hospital and clinical trial supply chains.
However, the cryogenic logistics segment is experiencing the fastest growth, especially following the approval of mRNA vaccines and the advancement of regenerative therapies. Cryogenic conditions (typically below -150°C) are required to store stem cells, CAR-T therapies, and other autologous or allogeneic cell-based products. The logistical complexity of maintaining such temperatures throughout transit—often requiring liquid nitrogen shippers and specialized validation—has driven innovation and infrastructure investments among 3PL firms. As the cell therapy pipeline expands, cryogenic logistics is anticipated to be a key revenue driver in the coming years.
The Oncology remained the leading therapeutic area in 2024, reflecting the market’s reliance on high-value, sensitive cancer treatments that demand precise storage and handling. Oncology drugs, including chemotherapy agents, targeted therapies, and immunotherapies, often require temperature-controlled environments and tight inventory control to prevent spoilage and ensure patient safety. High demand for personalized cancer treatments and continuous introduction of biologics has pushed logistics providers to specialize in oncology-specific transportation and warehousing solutions.
Simultaneously, neurology is one of the fastest-growing therapeutic segments, fueled by the development of innovative treatments for Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, epilepsy, and multiple sclerosis. Many of these drugs are biologic in nature, requiring refrigerated or cryogenic logistics. With the increasing prevalence of neurological disorders and the rise of neuroimmunology therapies, demand for safe and efficient delivery systems has intensified. Logistics partners are now developing dedicated pathways for neuro drugs, ensuring compliance with strict transit conditions and regulatory protocols.
The Storage and shipping services dominated the pharmaceutical 3PL market, reflecting the core function of warehousing and transportation in drug logistics. These services span ambient, cold, and frozen storage solutions, supported by validated processes for loading, transport, and temperature monitoring. Leading 3PLs offer multi-client, GDP-compliant warehouses near major metro areas and hubs, supported by real-time inventory tracking and automated systems to meet pharmaceutical storage standards.
In contrast, DSCSA and serialization services are the fastest-growing service category, driven by regulatory mandates to enhance drug traceability and prevent counterfeiting. The U.S. Drug Supply Chain Security Act (DSCSA) requires all prescription drugs to be serialized, trackable, and verified through the supply chain. This has led to 3PL providers investing in software platforms, scanning infrastructure, and cloud-based data reporting tools. Serialization is now being integrated into warehouse management systems and shipment protocols, making it a high-value add-on service for compliance-conscious clients.
Large pharmaceutical manufacturers accounted for the largest share, owing to their vast product portfolios, global distribution networks, and stringent compliance requirements. These companies often outsource significant portions of their logistics operations to 3PLs to reduce internal complexity, improve cost efficiency, and ensure access to global temperature-controlled networks. Partnerships are long-term and strategic, with service-level agreements (SLAs) and co-innovation initiatives to optimize last-mile delivery and reduce disruptions.
That said, small manufacturers are the fastest-growing segment, as more niche biotech startups and specialty pharma players enter the market. These companies lack the infrastructure and resources to manage their own logistics, making them highly reliant on full-service 3PL providers. They also tend to deal with specialized products—such as orphan drugs, biosimilars, or ATMPs—that require custom logistics solutions. 3PLs are now offering modular, flexible service models to cater to this segment, including clinical trial logistics, small-batch deliveries, and DTC support.
In March 2025, UPS Healthcare expanded its cold chain logistics capacity in the U.S. and Germany by adding cryogenic storage facilities to support cell and gene therapy distribution.
DHL Supply Chain launched a new Life Sciences Innovation Hub in Indiana in February 2025, integrating AI-based temperature monitoring and advanced serialization support.
In January 2025, FedEx Express announced partnerships with leading pharma manufacturers for integrated cold-chain services to distribute biologics and mRNA vaccines in remote areas.
Kuehne+Nagel, in November 2024, expanded its pharma distribution footprint in Asia with new GDP-certified facilities in India and China.
AmerisourceBergen, in December 2024, announced the launch of a blockchain-enabled track-and-trace system integrated with its 3PL services for secure pharmaceutical shipments.
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2034. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the pharmaceutical third-party logistics market
By Product
By Temperature
By Therapeutic Area
By Manufacturer Size
By Service
By Regional