The global precision genomic testing market size was valued at USD 14.65 billion in 2023 and is anticipated to reach around USD 57.59 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 14.67% from 2024 to 2033.
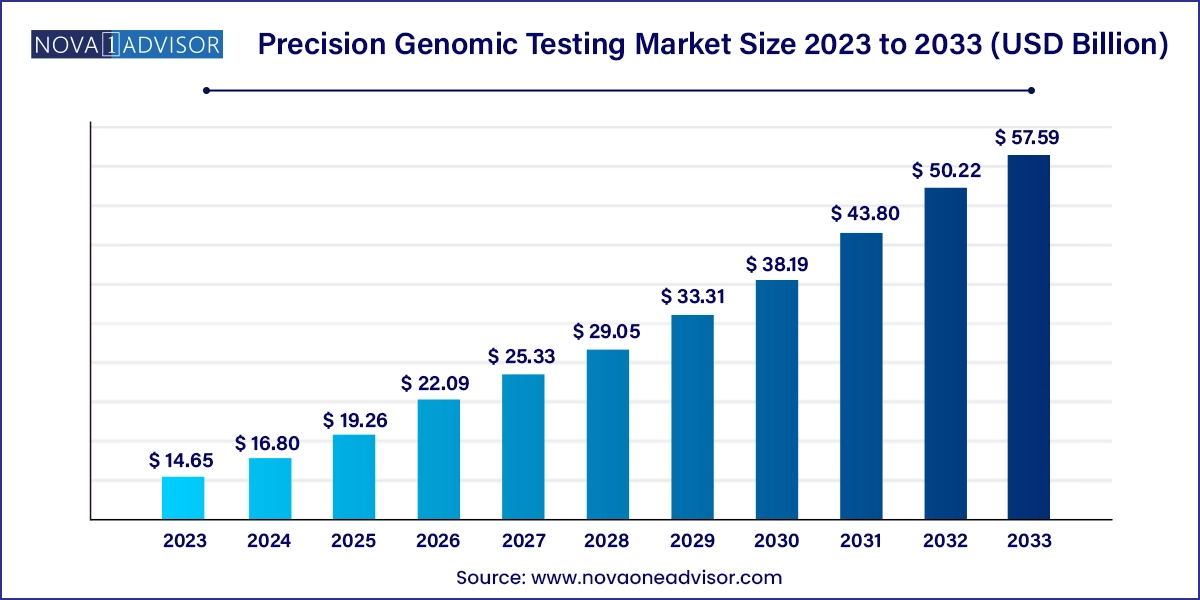
The U.S. Precision genomic testing market size was exhibited at USD 4.23 billion in 2023 and is projected to hit around USD 16.93 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 14.87% during the forecast period 2024 to 2033.
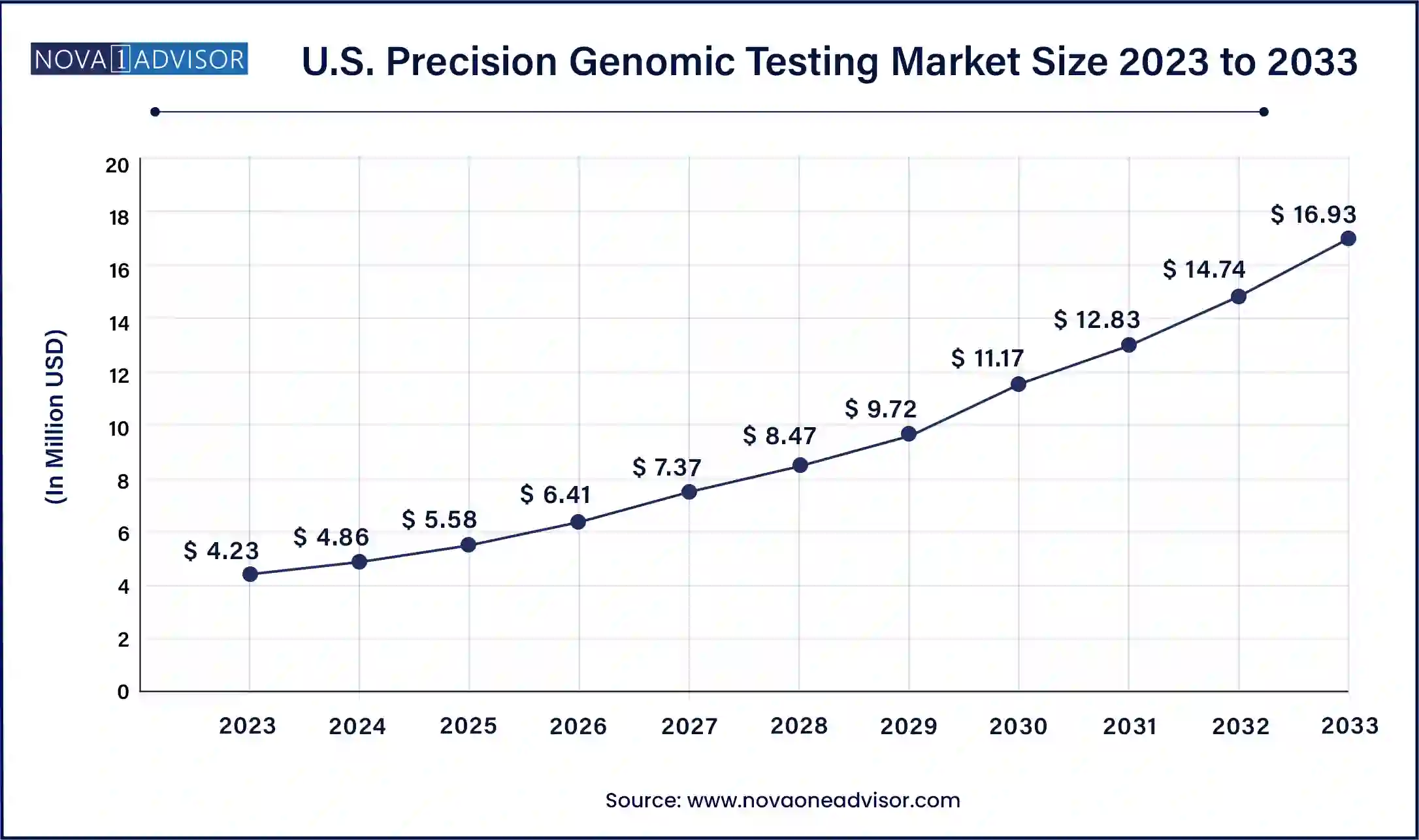
North America, particularly the United States, dominated the precision genomic testing market due to its advanced healthcare infrastructure, strong reimbursement ecosystem, and concentration of leading genomics companies. The region boasts a large number of genetic testing laboratories, academic institutions, and biotech innovators. Programs like the NIH’s “All of Us” Research Program aim to sequence one million American genomes to advance personalized medicine. Furthermore, favorable FDA regulatory pathways for genomic diagnostics have encouraged the launch of novel tests and expanded access to clinical sequencing services.
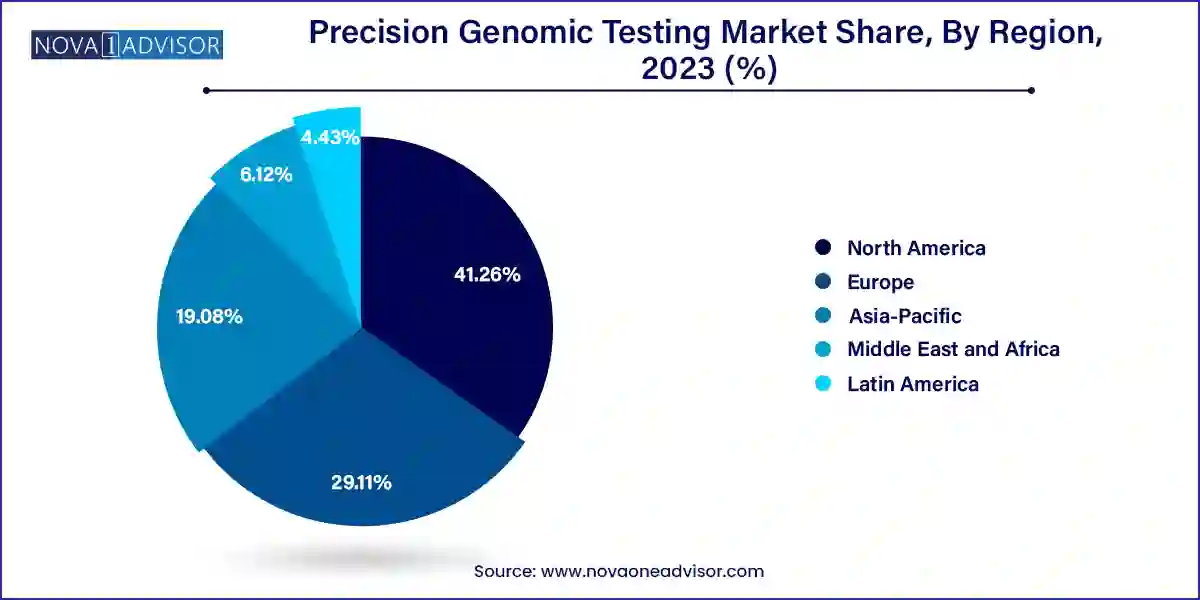
Asia-Pacific is witnessing the fastest growth in the precision genomic testing market, fueled by rising healthcare expenditures, government genomics initiatives, and increased clinical trial activity. Countries like China, India, and South Korea are making significant investments in genomics infrastructure. China’s Genomics 2030 initiative and India’s GenomeIndia project are creating national platforms for population-scale sequencing. Moreover, regional startups and research centers are forming partnerships with global players to improve local access to affordable, high-quality genomic testing. The region's large, diverse population and increasing burden of chronic diseases make it a key target for precision medicine strategies.
The Precision Genomic Testing Market represents a transformative advancement in the way we understand, diagnose, and treat diseases. By analyzing an individual’s unique genetic makeup, precision genomic testing enables healthcare providers to tailor interventions with a level of specificity previously unattainable. This growing field combines cutting-edge biotechnology, data science, and clinical knowledge to offer personalized insights into disease susceptibility, drug response, and therapeutic planning.
The global healthcare industry has gradually moved away from a one-size-fits-all approach toward personalized medicine, where precision genomic testing serves as a foundational pillar. These tests can identify mutations, chromosomal abnormalities, and gene expression patterns that may influence disease risk or therapy effectiveness. From diagnosing rare diseases in neonates to informing immunotherapy plans for cancer patients, precision genomic testing is becoming integral to modern healthcare.
A key growth driver has been the declining cost of next-generation sequencing (NGS) technologies, which have made whole-genome and exome sequencing increasingly accessible. Combined with AI-powered bioinformatics tools, genomic testing now delivers faster, more accurate interpretations. Government initiatives and collaborations between academic institutions and biotechnology companies have further expanded access to genomic testing and enhanced public awareness.
The COVID-19 pandemic also played a crucial role in accelerating molecular diagnostic adoption, with significant infrastructure investment in laboratories and increased public familiarity with genetic testing. This surge in genomic literacy is expected to sustain demand across various applications—from oncology and reproductive health to neurology and cardiology.
Rapid Decline in Sequencing Costs: Continued decrease in per-genome sequencing costs is democratizing access to high-throughput genomic testing.
Rise of Direct-to-Consumer Genomic Testing: Growth of consumer-facing platforms offering ancestry, health risk, and carrier screening services.
Integration with Artificial Intelligence: AI and machine learning are increasingly used to interpret complex genomic datasets and provide clinical decision support.
Pharmacogenomics Advancements: Precision prescribing based on genomic profiles is gaining adoption in oncology, psychiatry, and cardiovascular care.
Expansion of Liquid Biopsy: Non-invasive genomic testing through blood samples is growing in cancer diagnostics and recurrence monitoring.
Adoption in Reproductive and Prenatal Screening: Growth of preimplantation and non-invasive prenatal testing (NIPT) using genomic techniques.
Data Sharing and Interoperability Platforms: Emergence of genomic databases and cloud-based infrastructures to facilitate research and clinical collaboration.
Focus on Rare Disease Diagnosis: Genomic testing is proving crucial in identifying rare genetic disorders that are otherwise difficult to diagnose.
| Report Attribute | Details |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 16.80 Billion |
| Market Size by 2033 | USD 57.59 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2024 to 2033 | CAGR of 14.67% |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Forecast Period | 2024 to 2033 |
| Segments Covered | Product, application, technology, end use, region |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) | Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Report Coverage | Revenue forecast, company ranking, competitive landscape, growth factors, and trends |
| Key Companies Profiled | Illumina, Inc.; Color Genomics, Inc.; Amgen, Inc.; 24 genetics; Circle DNA; F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd.; Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc.; AncestryDNA; Agilent Technologies, Inc.; QIAGEN N.V. |
Increasing Adoption of Genomic Testing in Oncology
One of the most significant drivers of the precision genomic testing market is its transformative impact in oncology. Cancer is inherently a genetic disease, with mutations in DNA playing a central role in its development and progression. Precision genomic testing allows for the identification of specific biomarkers and gene alterations that guide personalized treatment decisions.
For instance, patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) can be tested for mutations in genes like EGFR, ALK, and ROS1 to determine the most effective targeted therapy. Similarly, BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutation testing has become standard in breast and ovarian cancer management. As more targeted therapies and immunotherapies enter the market, demand for companion diagnostic tests continues to surge. This integration of genomic testing into routine oncology care is propelling significant investment and innovation in the sector.
Data Privacy and Ethical Concerns Surrounding Genetic Information
While the potential of precision genomic testing is vast, one of the key constraints is the concern around data privacy, ownership, and ethical usage. Genomic data is inherently personal and sensitive. Improper storage, access, or misuse of such data can have serious implications for individual privacy and trust.
Cases of unauthorized data sharing, cyberattacks on genomic databases, or the potential for genetic discrimination in insurance and employment raise valid societal concerns. Furthermore, many countries still lack robust regulatory frameworks for genomic data protection. These uncertainties create hesitation among consumers, healthcare providers, and institutions, slowing broader adoption. Companies must prioritize transparent data governance models, encryption technologies, and informed consent protocols to mitigate these concerns.
Expansion into Preventive and Wellness Genomics
As healthcare systems worldwide transition toward preventive care, a major opportunity lies in the integration of precision genomic testing into wellness and preventive health strategies. By identifying genetic predispositions to chronic conditions like diabetes, hypertension, or neurodegenerative diseases, individuals can take proactive measures to delay or prevent disease onset.
Companies are increasingly offering genomic wellness panels that assess metabolic function, nutritional needs, and lifestyle factors influenced by genes. Employers and insurers are also exploring the integration of genomic screening into workplace health programs. Moreover, national genomic initiatives, like Singapore’s Precision Health Research program, aim to embed genomics in primary care and public health frameworks. This preventive approach holds the potential to revolutionize health management and significantly reduce long-term medical costs.
Consumables held the largest share of the market due to their recurring use in genomic testing workflows. Kits, reagents, and plasmids are essential for DNA extraction, amplification, sequencing, and analysis. Unlike capital equipment, consumables must be replenished for every testing cycle, making them a consistent revenue source. The increasing volume of diagnostic and research-based genomic tests, especially in high-throughput environments like hospitals and laboratories, continues to drive demand for high-quality consumables. Major suppliers like Illumina, Thermo Fisher Scientific, and Qiagen provide tailored kits for oncology, hereditary conditions, and reproductive health, sustaining the segment’s dominance.
Services, however, are emerging as the fastest-growing segment. With the rise of outsourced testing models, particularly in emerging regions, service providers offer end-to-end genomic testing solutions—from sample collection to bioinformatics interpretation. Clinical laboratories, CROs, and DTC testing firms are expanding service portfolios that cover everything from raw data analysis to actionable clinical reports. Cloud-based platforms now offer genomic interpretation-as-a-service, enabling faster scalability without large infrastructure investments. This service-led approach aligns with the increasing demand for integrated, easy-to-access genomic testing experiences.
Oncology continues to dominate the application segment, accounting for the largest volume of precision genomic tests globally. Genomic biomarkers such as KRAS, HER2, and PD-L1 guide treatment decisions, while companion diagnostics enable targeted therapy selection. With cancer cases on the rise and the oncology pipeline rich in targeted therapeutics, genomic profiling has become essential in clinical oncology. Tests like FoundationOne CDx and Guardant360 are frequently used to match patients with immunotherapies and targeted drugs. Moreover, tumor mutational burden (TMB) and microsatellite instability (MSI) tests are gaining clinical relevance, expanding oncology’s genomic footprint.
In contrast, rare diseases represent the fastest-growing application segment. Genomic testing offers a lifeline for patients with undiagnosed, inherited disorders by providing clarity through whole exome or genome sequencing. Rare diseases often go years without a diagnosis, leading to poor outcomes and high costs. Precision genomics offers faster, more accurate diagnostic options, particularly for pediatric and neonatal populations. Global initiatives like the “Solve-RD” project in Europe and the “Undiagnosed Diseases Network” in the U.S. are leveraging genomics to uncover new disease pathways, reinforcing the segment’s rapid growth.
Next-generation sequencing (NGS) was the most dominant technology in the precision genomic testing market. NGS technologies enable high-throughput analysis of entire genomes or targeted regions with unprecedented speed and cost-effectiveness. Its widespread use in oncology, infectious disease testing, pharmacogenomics, and reproductive health has made NGS the standard for precision diagnostics. Companies like Illumina, BGI, and Thermo Fisher dominate this space, offering platforms and consumables for research and clinical use. Additionally, advancements like single-cell sequencing and long-read technologies are extending NGS applications into more complex areas of biology.
CRISPR/Cas systems, while still in the emerging stage, are experiencing the fastest growth. Originally developed as gene-editing tools, CRISPR technologies are now being applied to diagnostics through platforms like SHERLOCK and DETECTR. These CRISPR-based systems allow rapid, portable, and low-cost genomic detection of pathogens and mutations, especially in point-of-care settings. Moreover, their specificity and adaptability make them attractive for future decentralized genomic diagnostics, especially in resource-limited environments. As regulatory frameworks solidify and clinical trials progress, CRISPR technologies are poised to disrupt traditional genomic testing methodologies.
Diagnostic laboratories led the market due to their central role in processing large volumes of clinical genomic tests. Equipped with sophisticated instrumentation, trained personnel, and bioinformatics capabilities, these labs perform a wide range of tests spanning oncology panels, carrier screening, NIPT, and pharmacogenomics. Centralized diagnostic labs also drive test standardization, quality assurance, and result interpretation, making them the go-to for hospitals, physicians, and DTC companies. Giants like Labcorp, Quest Diagnostics, and Eurofins have extensive networks supporting precision genomic testing at scale.
Hospitals and clinics represent the fastest-growing end-use segment as genomic testing moves closer to the point of care. With increasing awareness among clinicians and better reimbursement policies, hospitals are integrating genomic testing into routine diagnostics for oncology, prenatal care, and chronic disease management. Academic medical centers are leading the charge by establishing genomics departments and precision medicine programs. This shift toward decentralization, supported by user-friendly instruments and software, is making genomic testing more accessible within the clinical workflow.
March 2025 – Illumina Inc. launched its next-gen sequencing platform, NovaSeq X Plus, in India through a collaboration with MedGenome, expanding clinical genomics access across South Asia.
January 2025 – Color Health secured a major partnership with a U.S. hospital system to provide genetic screening services to over 100,000 employees and patients.
November 2024 – BGI Genomics expanded its CRISPR-based diagnostic services in Southeast Asia with the introduction of portable point-of-care testing kits.
October 2024 – Invitae Corporation introduced a new integrated genetic testing and counseling platform designed for oncology clinics in the U.S. and Canada.
August 2024 – Thermo Fisher Scientific acquired a minority stake in a Japanese precision medicine startup to strengthen its presence in Asia.
Precision Genomic Testing Market Report Segmentation
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2033. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the Precision Genomic Testing market.
By Product
By Application
By Technology
By End Use
By Region