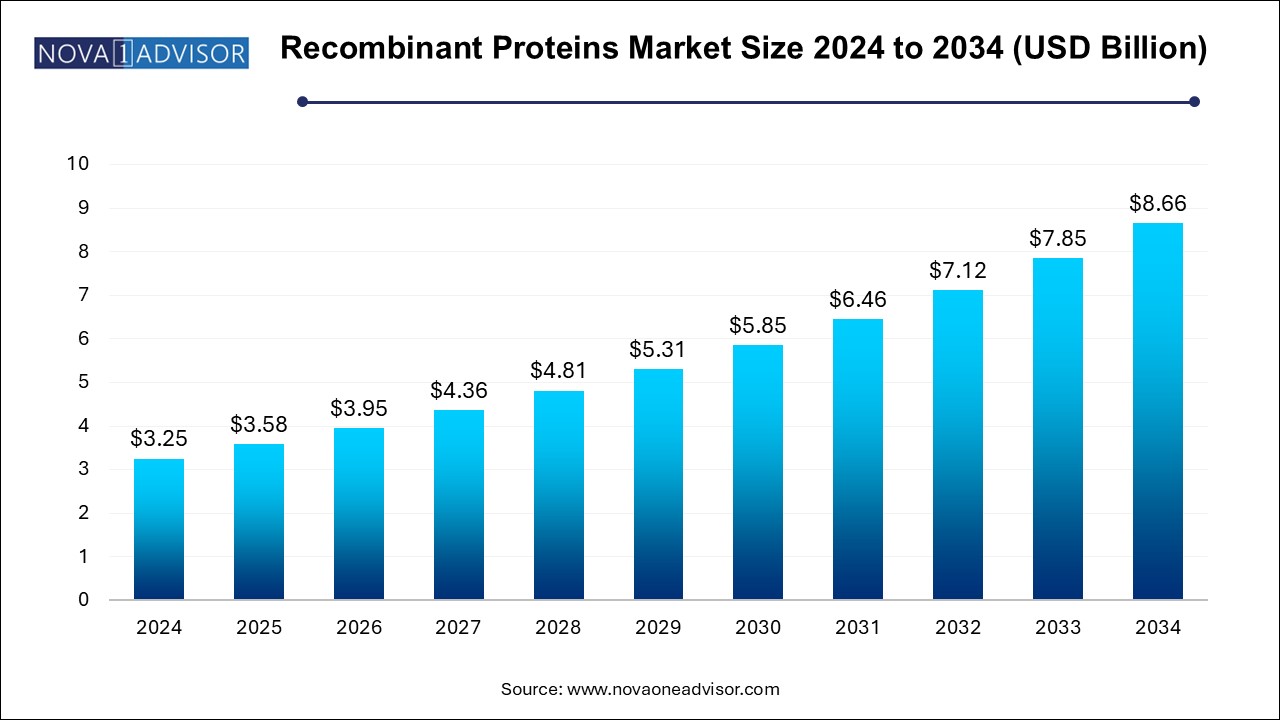
The recombinant proteins market size was exhibited at USD 3.25 billion in 2024 and is projected to hit around USD 8.66 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 10.3% during the forecast period 2025 to 2034.
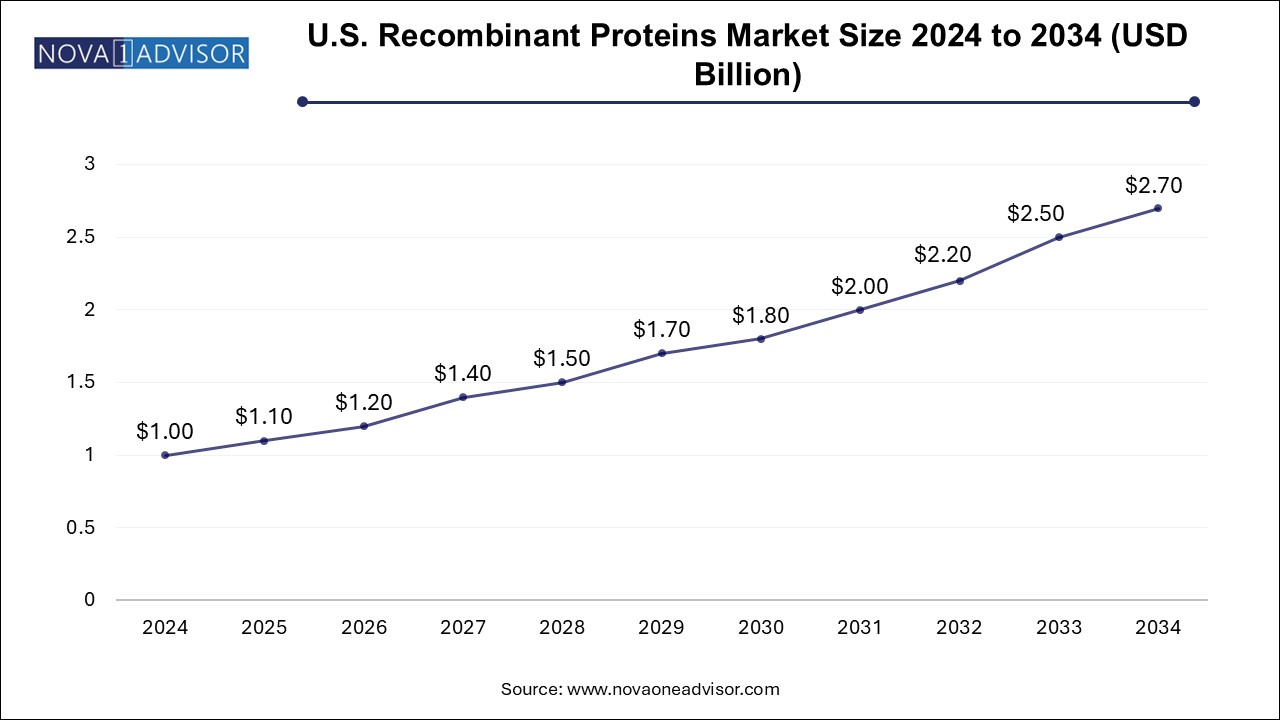
The U.S. recombinant proteins market size is evaluated at USD 1.0 billion in 2024 and is projected to be worth around USD 2.7 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 9.44% from 2025 to 2034.
North America, particularly the United States, dominates the recombinant proteins market due to its mature biopharmaceutical industry, robust R&D infrastructure, and high healthcare expenditure. The region houses many of the world’s leading biotech and pharmaceutical companies engaged in biologics development and protein-based therapeutics. The FDA’s supportive regulatory environment and fast-track approvals for innovative protein drugs have further accelerated commercial activity.
Asia Pacific is the fastest-growing region, driven by increasing healthcare investments, expanding biotech ecosystems, and supportive government policies in countries like China, India, Japan, and South Korea. China’s biopharmaceutical industry is undergoing rapid modernization with heavy investment in recombinant vaccine and biologic drug production. Local firms are actively licensing global protein technologies and setting up GMP-compliant manufacturing facilities.
India, known for its biosimilar production, is investing in indigenous recombinant protein manufacturing for insulin, erythropoietin, and diagnostics. In Japan and South Korea, academic collaborations and public-private partnerships are accelerating innovation in protein engineering and personalized medicine. The region’s cost advantages, skilled labor, and growing clinical trial capacity make it a key strategic zone for global players.
The recombinant proteins market has emerged as a foundational pillar of modern biotechnology, enabling critical advancements across therapeutic, diagnostic, and research landscapes. Recombinant proteins—engineered using recombinant DNA technology—mimic or enhance native biological processes, offering unprecedented specificity, scalability, and therapeutic potential. These proteins are produced by inserting genes encoding specific proteins into host systems such as bacteria, yeast, mammalian, or insect cells, allowing for controlled, high-yield protein expression.
The field has evolved from producing single therapeutic proteins, such as insulin and erythropoietin, to now encompassing a wide range of cytokines, hormones, antibodies, and antigens. The rising incidence of chronic diseases, including cancer, autoimmune disorders, and metabolic syndromes, coupled with increasing R&D in biologics, has fueled a surge in demand for recombinant protein technologies. The role of recombinant proteins in precision medicine, vaccine development, and cell & gene therapy is also expanding rapidly.
Furthermore, recombinant proteins are vital tools in the discovery and validation of new drugs, especially in assays for drug-target interactions and toxicology profiling. Their precision and reproducibility also make them indispensable in diagnostic assays. The global recombinant proteins market is thus poised for robust growth, supported by technological innovations in protein expression systems, bioinformatics-driven design, and a favorable regulatory environment for biologics.
Integration of AI and Machine Learning in Protein Design and Expression Optimization
Rising Demand for Recombinant Immune Checkpoint Proteins in Cancer Immunotherapy
Increased Application in Cell & Gene Therapy Development
Expansion of Customized Protein Engineering Services by CDMOs
Growing Use of Recombinant Antigens in Infectious Disease Diagnostics
Surge in Recombinant Enzyme Applications in Rare Disease Treatment
Advancements in Mammalian and Yeast Expression Systems for Complex Protein Production
Collaboration Between Academic Institutions and Biotech Firms for Novel Protein Development
Increased Use in Regenerative Medicine and Tissue Engineering
Expansion of Protein Arrays for High-Throughput Screening in Drug Discovery
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 3.58 Billion |
| Market Size by 2034 | USD 8.66 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2025 to 2034 | CAGR of 10.3% |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025-2034 |
| Segments Covered | Product, Application, End use, Host Cell, Region |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) | Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Regional scope | North America; Europe; Asia Pacific; Latin America; MEA |
| Key Companies Profiled | Sino Biological, Inc.; R&D Systems, Inc.; GenScript; Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc.; Merck KGaA; Thermo Fisher Scientific; Proteintech Group, Inc.; Enzo Life Sciences, Inc.; Abnova Corporation; RayBiotech Life Inc.; STEMCELL Technologies Inc. |
A key driver propelling the recombinant proteins market is the rapid expansion of biologics and personalized medicine, areas where recombinant proteins play a central role. Biologics such as monoclonal antibodies, fusion proteins, and cytokine therapies rely on recombinant protein production for both development and large-scale manufacturing. Their high target specificity and ability to be engineered for therapeutic precision make them ideal for conditions like cancer, rheumatoid arthritis, and multiple sclerosis.
Moreover, the rise of personalized medicine requires tailored therapeutic approaches based on genetic and molecular profiles—often supported by recombinant proteins that mimic patient-specific targets or deliver customized immune responses. For example, recombinant checkpoint proteins like PD-1 and CTLA-4 are crucial in checkpoint blockade therapies, while tumor-specific antigens are used in cancer vaccines and CAR-T cell therapies. The ongoing shift toward individualized treatment paradigms ensures sustained growth and innovation in this segment.
Despite strong market potential, high production costs and complex downstream processes remain significant restraints for the recombinant proteins market. Producing recombinant proteins—especially large, glycosylated or multimeric forms—requires optimized expression systems, stringent purification protocols, and often, post-translational modifications. These factors increase manufacturing costs and prolong development timelines.
Additionally, maintaining product consistency, stability, and bioactivity during scale-up is technically demanding and subject to rigorous regulatory scrutiny. Small and mid-sized biotech companies, in particular, face challenges in balancing cost-efficiency with quality control. Moreover, the need for cold-chain logistics and specialized storage infrastructure adds to operational overhead. Addressing these challenges requires continued investment in process optimization, platform technologies, and modular biomanufacturing.
A promising opportunity lies in the emerging role of recombinant proteins in advanced therapeutics such as regenerative medicine, gene editing, and stem cell therapy. Recombinant growth factors and cytokines, for instance, are instrumental in guiding cell differentiation, proliferation, and tissue regeneration. Bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs), fibroblast growth factors (FGFs), and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) are increasingly used in orthopedic repair, wound healing, and cardiovascular regeneration.
In addition, recombinant proteins are being used as delivery agents or effectors in CRISPR-based gene editing and mRNA therapeutics. For instance, recombinant Cas enzymes and nucleases are enabling precision gene modification, while recombinant enzymes are being incorporated into lipid nanoparticles for controlled drug delivery. As these next-generation therapies gain regulatory approval and commercial traction, the demand for high-quality, GMP-compliant recombinant proteins will rise exponentially.
The cytokines & growth factors segment held the largest share of 24.6% of the market in 2024. due to their central role in modulating immune responses, cell growth, and signaling pathways. Subcategories such as interferons (IFNs) and interleukins (ILs) are widely used in cancer immunotherapy, antiviral therapies, and vaccine adjuvants. For example, recombinant IFN-alpha is approved for hepatitis C treatment, while IL-2 has shown efficacy in renal cell carcinoma and melanoma. These proteins are also essential components of immunoassays and vaccine research, ensuring consistent demand from both therapeutic and research sectors.
Among growth factors, VEGF, FGF, EGF, and TGF-beta are prominent due to their applications in tissue regeneration and angiogenesis studies. The increasing application of growth factors in stem cell expansion and bioprinting is further boosting this segment. On the other hand, recombinant enzymes—particularly kinases and metabolic enzymes—are witnessing the fastest growth. Their utility in metabolic disorders, rare enzyme deficiencies, and as components of diagnostic kits is expanding. Enzyme replacement therapies (ERTs), such as those for Gaucher or Fabry disease, also underscore the therapeutic relevance of this product segment.
The therapeutics segment dominated the global market with a share of 34.2% in 2024. driven by the surge in biologic drug development and increasing regulatory approvals. Within therapeutics, biologics such as monoclonal antibodies and fusion proteins are produced using recombinant protein technologies. Recombinant hormones, insulin analogs, and hematopoietic growth factors are also well-established therapies with global patient bases. The subsegment of vaccines is witnessing renewed interest due to recombinant protein-based COVID-19 vaccines like Novavax’s NVX-CoV2373, which employ spike protein subunits.
Meanwhile, cell and gene therapies are the fastest-growing subsegment within therapeutics. Recombinant proteins are used to engineer CAR-T cells, modulate immune responses, or deliver therapeutic genes. For example, recombinant antigens and cytokines are used to prime dendritic cells or enhance T-cell expansion. In gene therapy, proteins like TALENs, ZFNs, and CRISPR-Cas enzymes are used to edit genomic sequences. As the number of approved and pipeline therapies grows, the demand for recombinant proteins in these advanced applications is expected to surge.
The Pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies represent the dominant end-use segment due to their role in therapeutic protein development, clinical research, and manufacturing. These companies use recombinant proteins extensively in preclinical assays, biomarker discovery, target validation, and pharmacodynamic studies. With the biologics pipeline growing steadily, demand for recombinant proteins as therapeutic agents, assay components, and companion diagnostics is robust across the sector.
However, academic and research institutes are witnessing rapid growth in demand. Universities and national labs are deploying recombinant proteins for translational research, regenerative medicine trials, and drug screening studies. Government and private grants supporting genomics, proteomics, and personalized medicine initiatives have significantly increased protein usage in experimental protocols. Additionally, diagnostic laboratories are integrating recombinant antigens into immunoassays for infectious diseases, autoimmune disorders, and cancer screening.
The Mammalian cell systems, such as CHO (Chinese hamster ovary) and HEK (human embryonic kidney) cells, are the preferred hosts for producing complex recombinant proteins that require post-translational modifications. These systems are essential for manufacturing therapeutic monoclonal antibodies, fusion proteins, and glycosylated hormones. The high fidelity of protein folding and glycosylation in mammalian systems ensures bioactivity and reduces immunogenicity, making them indispensable in drug development.
At the same time, yeast and fungi-based expression systems are the fastest-growing segment due to their scalability, cost-effectiveness, and ability to produce recombinant proteins with minimal endotoxin contamination. Systems like Pichia pastoris and Saccharomyces cerevisiae are widely used for producing enzymes, vaccine antigens, and diagnostic reagents. These systems offer higher yields than bacterial systems while being more capable of performing post-translational modifications. With increasing demand for low-cost production platforms, especially in diagnostics and industrial enzyme sectors, this segment is expected to witness substantial growth.
March 2025: Thermo Fisher Scientific launched a new recombinant cytokine panel for use in multiplex immunoassays targeting immuno-oncology research applications.
February 2025: Sino Biological Inc. announced the construction of a new recombinant protein production facility in Suzhou, China, aimed at scaling up antibody and antigen manufacturing for global supply.
January 2025: GenScript Biotech Corporation introduced a high-throughput platform for recombinant enzyme screening tailored to rare metabolic disorder drug development.
December 2024: Abcam plc collaborated with academic institutions to develop a library of recombinant immune checkpoint proteins for oncology therapeutic development.
November 2024: Merck KGaA expanded its recombinant protein production capacity in its Darmstadt facility to meet increasing global demand for vaccine and biologic manufacturing.
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2034. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the recombinant proteins market
By Product
By Application
By End Use
By Host Cell
By Regional