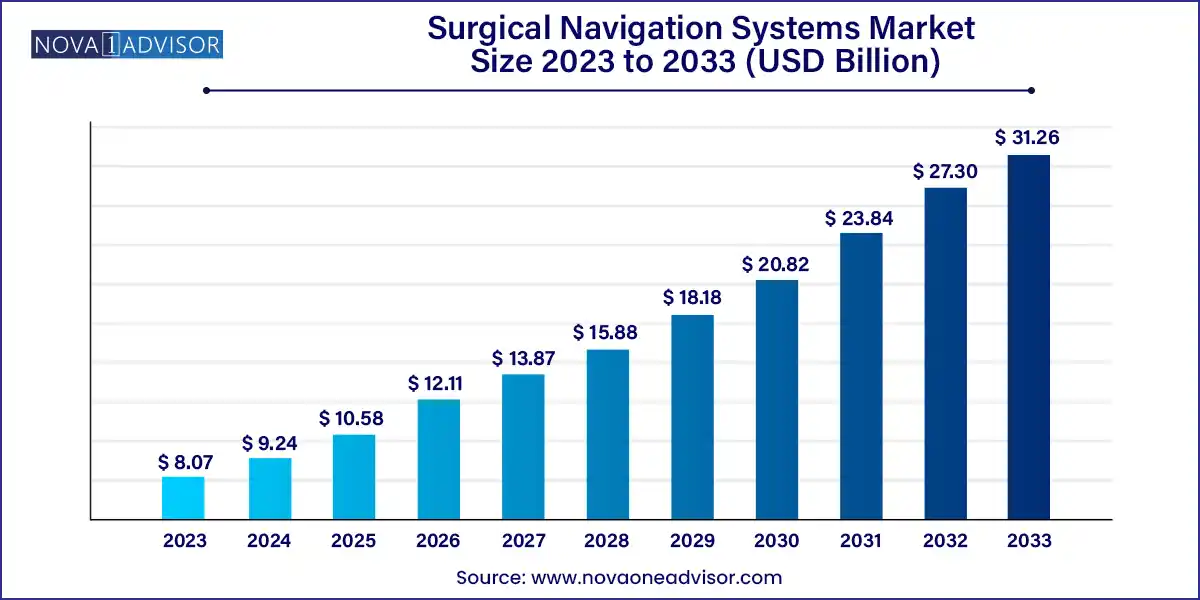
The global surgical navigation systems market size was exhibited at USD 8.07 billion in 2023 and is projected to hit around USD 31.26 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 14.5% during the forecast period of 2024 to 2033.
The Surgical Navigation Systems Market represents a rapidly advancing sector of the medical technology industry, delivering real-time visualization tools that assist surgeons in planning and executing complex procedures with greater accuracy and safety. Often referred to as computer-assisted surgery (CAS), surgical navigation leverages advanced imaging modalities such as MRI, CT, and fluoroscopy, coupled with real-time tracking sensors, to guide instruments with sub-millimeter precision during interventions.
These systems are increasingly integrated into neurosurgery, orthopedic, ENT, spinal, and dental surgeries, where precise anatomical orientation is critical. The market has evolved considerably over the past decade, moving from standalone consoles to fully integrated digital operating rooms that merge navigation, robotics, and artificial intelligence.
Rising demand for minimally invasive surgeries (MIS), an aging population requiring joint and spine care, and growing technological literacy among clinicians are driving the adoption of surgical navigation globally. Moreover, favorable reimbursement policies in developed economies and ongoing efforts to expand access in emerging regions provide fertile ground for sustained growth.
Integration with Robotics: Navigation systems are increasingly being paired with surgical robots for enhanced precision and automation.
AI-Enhanced Imaging and Predictive Analytics: Use of AI to support intraoperative decision-making and postoperative outcome prediction.
Miniaturization and Portability: Development of compact and mobile navigation systems suitable for ambulatory and resource-limited settings.
Augmented Reality (AR) & Mixed Reality (MR): Incorporation of AR/MR for immersive surgical training and in-procedure navigation.
Cloud-Based Data Sharing: Real-time sharing of surgical plans and outcomes across hospital networks and cloud platforms.
Customization for Specific Specialties: Tailored systems for ENT, dental, spine, and joint surgeries with modular features.
Remote Surgical Planning and Tele-mentoring: Surgeons in remote locations accessing navigation software and expert guidance via digital platforms.
Growing Adoption in Emerging Markets: Increased installations in tier-2 hospitals across Asia, Latin America, and the Middle East.
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 9.24 Billion |
| Market Size by 2033 | USD 31.26 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2024 to 2033 | CAGR of 14.5% |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Forecast Period | 2024-2033 |
| Segments Covered | Product, Disease Type, Surgery, End-user, Region |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) | Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Regional Scope | North America; Europe; Asia Pacific; Central and South America; the Middle East and Africa |
| Key Companies Profiled | Johnson & Johnson Services, Inc. (DePuy Synthes); Stryker; Zimmer Biomet; B. Braun Melsungen AG; Medtronic; KARL STORZ SE & Co. KG; Amplitude Surgical; Corin; Siemens Healthineers; Smith+Nephew. |
The dominant driver of the surgical navigation market is the accelerated demand for minimally invasive surgeries (MIS). These procedures result in smaller incisions, reduced blood loss, shorter recovery times, and lower infection risk. However, MIS also limits the surgeon’s direct view of anatomy, heightening the need for precise intraoperative visualization tools like navigation systems.
In orthopedic procedures such as total knee arthroplasty (TKA) or spinal fusion, surgical navigation significantly improves alignment accuracy and reduces revision rates. Similarly, in neurosurgery, it aids in targeting tumors or vascular malformations while preserving functional brain areas.
As more healthcare institutions aim to improve surgical outcomes and reduce complications, the integration of navigation systems is becoming standard in high-stakes specialties. Their use also aligns with value-based care initiatives, which reward quality and efficiency.
A prominent restraint is the high initial capital expenditure associated with acquiring surgical navigation systems. Advanced systems with integrated imaging, robotics, and software often cost hundreds of thousands of dollars, excluding maintenance and training costs.
Furthermore, integrating these systems into existing operating room (OR) workflows can be challenging. Hospitals need to train surgeons, nurses, and technical staff, while also updating infrastructure to support digital systems. Smaller hospitals and ambulatory surgical centers (ASCs) often lack the budget or staff to support such adoption, particularly in emerging markets.
This cost barrier is gradually being addressed by leasing models, refurbished systems, and modular designs, but it remains a hurdle for broader adoption in mid- and low-income settings.
The most promising opportunity lies in AI-enhanced and cloud-connected surgical navigation systems. By leveraging real-time imaging and historical patient data, these systems can provide personalized surgical guidance, highlight potential complications, and even recommend optimal surgical paths.
Additionally, cloud integration enables surgeons to access preoperative plans remotely, collaborate with peers, and contribute to shared learning platforms. This digital infrastructure is especially valuable for training new surgeons, managing multi-site hospital systems, and expanding navigation into rural or resource-scarce environments.
The rise of software-as-a-service (SaaS) in surgical navigation is also opening new business models, reducing upfront costs and making systems more accessible to smaller institutions.
Orthopedic surgery dominates the market, driven by the demand for high-precision tools in knee, hip, and spinal procedures. These systems help align implants accurately, reduce surgical revisions, and optimize joint biomechanics. With the rise in aging populations and sports injuries, orthopedic navigation remains a staple in high-volume surgical centers.
Neurosurgery is the fastest-growing application segment, particularly for brain tumor resections, epilepsy surgeries, and functional procedures such as deep brain stimulation (DBS). The need for sub-millimeter accuracy and real-time feedback makes navigation systems indispensable in this field. The trend is further fueled by rising brain cancer prevalence and increased neurosurgical volumes in tertiary care centers.
Hospitals remain the largest end-users, benefiting from comprehensive surgical departments, capital investment budgets, and advanced imaging infrastructure. Navigation systems are widely installed in neurosurgical, orthopedic, and ENT departments of tertiary care hospitals globally.
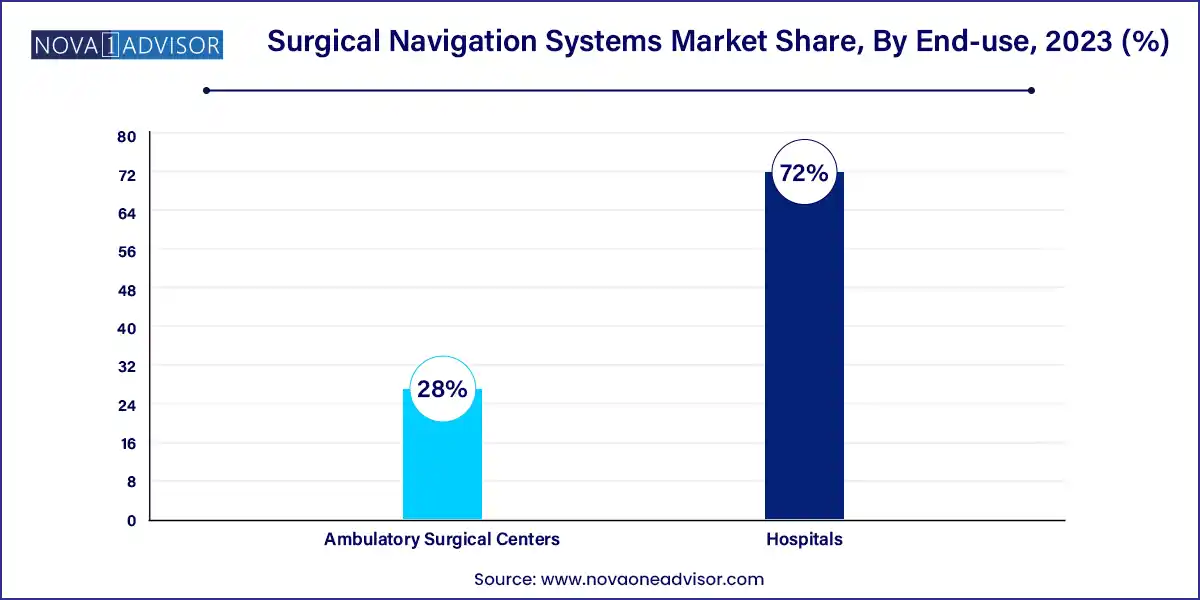
Ambulatory Surgical Centers (ASCs) are the fastest-growing end-use segment, propelled by the shift toward outpatient MIS procedures. Compact and portable navigation systems are particularly attractive for ASCs seeking to offer specialized orthopedic or ENT surgeries. Their rapid adoption is supported by reduced turnaround times, patient preference, and cost-efficiency.
Optical navigation systems lead the market, known for their high precision and robust performance in open and MIS procedures. These systems use infrared cameras to track surgical instruments, delivering accurate feedback in orthopedic and neurosurgical applications. Their widespread use and reliability have made them the gold standard in developed markets.
Electromagnetic systems are growing fastest, offering more flexibility in small or deep surgical fields, such as ENT or spine. These systems are less susceptible to line-of-sight issues and can be integrated into smaller OR setups. With improvements in sensor miniaturization and shielding, EM-based navigation is gaining momentum, especially in endoscopic and sinus procedures.
North America leads the surgical navigation systems market, supported by robust healthcare infrastructure, early technology adoption, and strong reimbursement frameworks. The U.S. accounts for the majority of installations, particularly in orthopedic and spine centers. The region is also home to key players like Medtronic, Stryker, and Zimmer Biomet, who continuously innovate and train clinicians in advanced navigation.
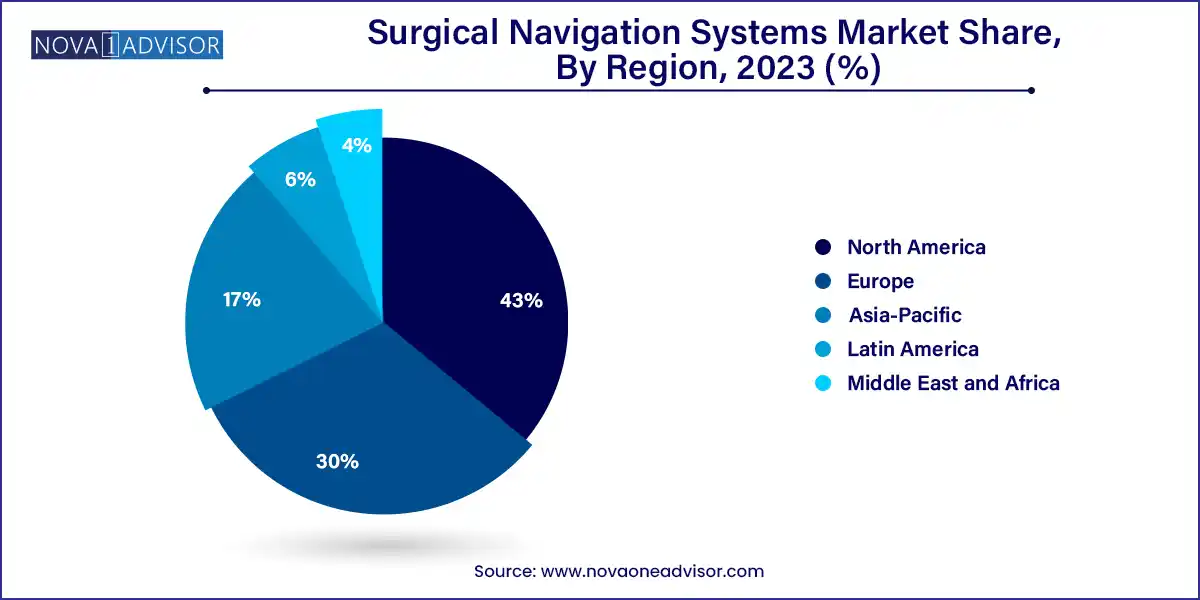
Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing region, driven by rising healthcare expenditure, expanding medical tourism, and government investments in modernizing hospitals. Countries like China, India, and South Korea are experiencing a surge in elective surgeries, especially for spine, joint, and dental care. Furthermore, local manufacturers are emerging with cost-effective systems tailored for regional markets.
Stryker (March 2025): Launched the next-generation version of its orthopedic navigation platform with AI-enhanced analytics for joint replacement.
Brainlab (April 2025): Unveiled a mixed reality-guided navigation suite for cranial and ENT surgeries at the Global Neurosurgery Conference.
Medtronic (February 2025): Expanded its StealthStation product line with cloud integration for remote surgical planning and multi-site case sharing.
Zimmer Biomet (January 2025): Announced partnership with a Chinese hospital chain to deploy ROSA-guided orthopedic systems across Asia.
Fiagon GmbH (March 2025): Introduced a new electromagnetic navigation system tailored for outpatient ENT procedures, emphasizing miniaturization and ease of use.
This report forecasts revenue growth at global, regional, and country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2033. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the global surgical navigation systems market.
Application
Technology
End-use
By Region