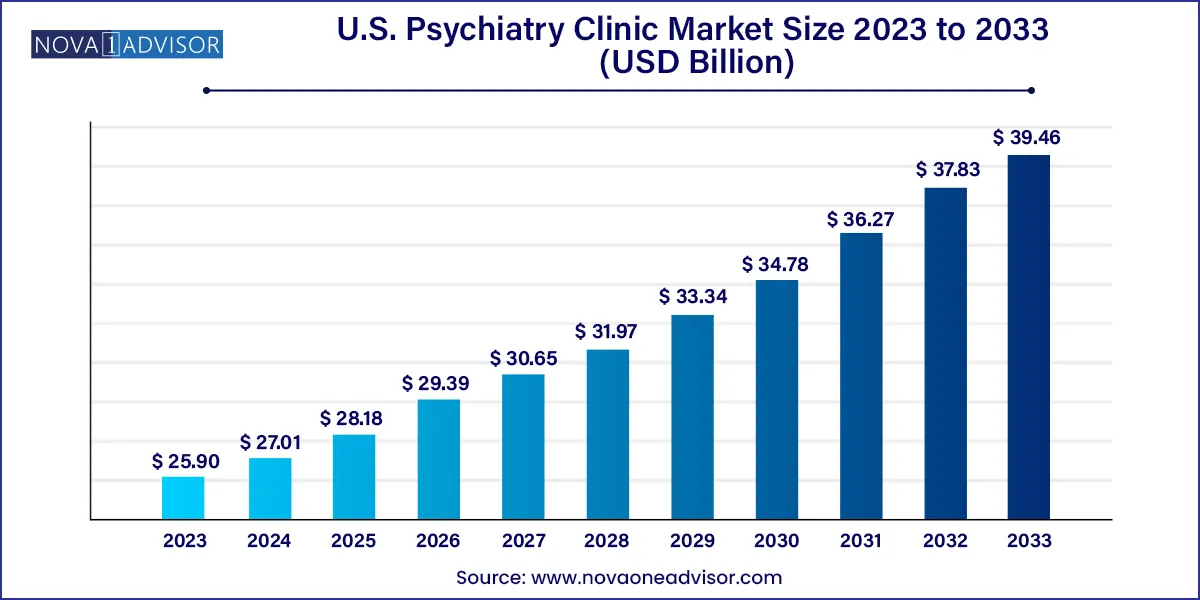
The U.S. psychiatry clinic market size was exhibited at USD 25.90 billion in 2023 and is projected to hit around USD 39.46 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 4.3% during the forecast period 2024 to 2033.
The U.S. Psychiatry Clinic Market has become a cornerstone of the broader mental healthcare system, offering specialized services that diagnose, treat, and manage various psychiatric and behavioral disorders. From major depressive disorder and schizophrenia to anxiety, ADHD, and substance use disorders, psychiatry clinics in the U.S. address a growing need for accessible, quality mental health care across diverse age groups. The market encompasses private outpatient practices, hospital-affiliated clinics, community mental health centers, and telepsychiatry platforms.
Increased mental health awareness, declining stigma, and a surge in insurance coverage have propelled the growth of this market. As of 2025, approximately 1 in 5 U.S. adults live with a mental illness, and many require specialized psychiatric care beyond what primary care physicians can offer. Clinics serve as structured environments where patients can receive medication management, counseling, crisis stabilization, and long-term care planning from board-certified psychiatrists and mental health professionals.
Amid the COVID-19 pandemic and its aftermath, the psychiatric clinic market witnessed a paradigm shift. Remote consultations, digital intake assessments, and online group therapies became not just viable alternatives but also permanent fixtures of mental healthcare delivery. As a result, hybrid models of in-person and virtual care are now prevalent. With policy momentum around mental health parity and employer-provided wellness programs gaining ground, psychiatry clinics are expected to see sustained growth and evolving delivery strategies.
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 27.01 Billion |
| Market Size by 2033 | USD 39.46 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2024 to 2033 | CAGR of 4.3% |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Forecast Period | 2024-2033 |
| Segments Covered | Age Group |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) | Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Regional Scope | U.S. |
| Key Companies Profiled | Universal Health Services; Langley Porter Psychiatric Hospital (LPPH); Bellevue Hospital; Manhattan Psychiatric Center; Menninger Clinic, Tucker Psychiatric Clinic; Acadia Healthcare; UCSF Health; Peninsula Behavioural Health; Mayo Clinic. |
The rising prevalence of mental health disorders across all demographics has become a key driver of the U.S. psychiatry clinic market. According to the National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH), nearly 60 million adults in the U.S. experience mental illness annually. Public discourse around mental well-being, amplified by social media and advocacy campaigns, has destigmatized psychiatric care, encouraging more individuals to seek help earlier.
This trend has created a ripple effect, increasing patient volumes at clinics and spurring new clinic openings, especially in underserved regions. High-profile endorsements from celebrities and athletes, employer-led wellness initiatives, and college mental health programs have all contributed to the growing acceptance and demand for psychiatric services. With earlier intervention and lifelong care models becoming the norm, psychiatry clinics are well-positioned to address both acute episodes and chronic psychiatric needs.
Despite the rising demand, a significant barrier to growth is the nationwide shortage of psychiatrists and trained mental health professionals. Many clinics face long waitlists, particularly in rural areas and low-income urban neighborhoods. The American Psychiatric Association (APA) reports that over 60% of counties in the U.S. have no practicing psychiatrists.
This shortage is further compounded by clinician burnout, administrative burdens, and reimbursement disparities, leading to high turnover rates. Clinics often struggle to recruit and retain board-certified psychiatrists, particularly those specializing in child and adolescent psychiatry. While telepsychiatry has helped bridge access gaps, it does not fully substitute the need for physical clinic infrastructure and local provider presence. Without scalable workforce solutions, the market risks bottlenecks in care delivery and diminished outcomes.
An emerging opportunity in the U.S. psychiatry clinic market is the integration of psychiatric services into primary care and workplace environments. Collaborative care models wherein psychiatrists work closely with primary care providers, psychologists, and care coordinators are being adopted to address complex patient needs efficiently. This model improves early diagnosis, treatment adherence, and long-term outcomes.
Furthermore, as employers recognize the productivity costs associated with untreated mental health conditions, many are contracting with psychiatry clinics to offer on-site or virtual counseling, psychiatric evaluations, and stress management programs. Employers are also subsidizing mental health care as part of employee benefits. These trends enable clinics to expand beyond traditional outpatient settings and embed themselves into the daily lives of patients, creating broader care touchpoints and new revenue streams.
Adult psychiatric services dominate the U.S. psychiatry clinic market, accounting for the highest volume of outpatient visits. Adults often present with a spectrum of conditions including anxiety, depression, bipolar disorder, PTSD, and substance use disorders. With mental health increasingly linked to workplace performance, relationships, and chronic disease management, demand for adult psychiatric evaluations and medication management has escalated. Clinics cater to this segment with tailored treatment plans, group therapy options, and ongoing care coordination. Furthermore, veterans, first responders, and trauma survivors often require long-term psychiatric oversight, creating stable demand.
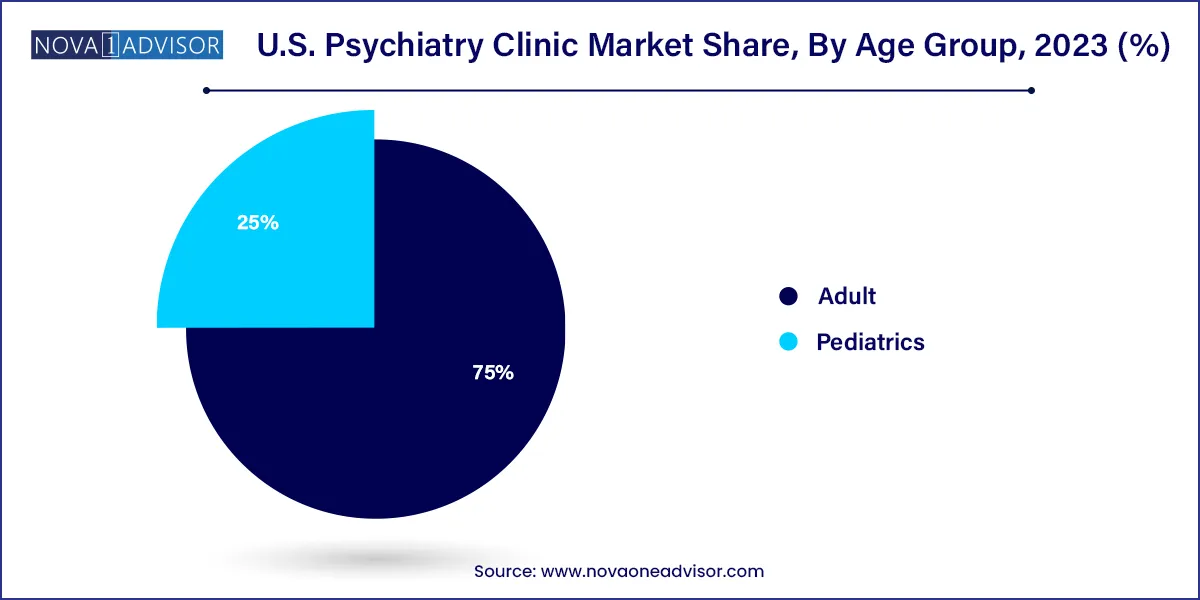
Pediatric psychiatric services are among the fastest-growing segments, spurred by increasing recognition of mental health issues in children and adolescents. Disorders such as ADHD, autism spectrum disorders, eating disorders, and school-related anxiety are now being diagnosed earlier. The COVID-19 pandemic further exacerbated stress and isolation among youth, triggering a surge in clinic visits and crisis interventions. Clinics are responding with child psychiatrists, behavioral therapists, and school-based outreach programs. The integration of family-based therapy and parental education further supports the holistic management of pediatric psychiatric conditions, driving growth in this segment.
The U.S. psychiatry clinic landscape is shaped by healthcare access disparities, reimbursement frameworks, and evolving public policy. States such as California, New York, Texas, and Florida lead in the number of practicing psychiatrists and specialty clinics, while rural states face severe shortages. Federally Qualified Health Centers (FQHCs), community mental health centers, and academic hospitals play a key role in serving low-income populations.
Policy measures such as the Mental Health Parity and Addiction Equity Act (MHPAEA) and increased funding for behavioral health services through Medicaid and the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA) have expanded the scope of reimbursable psychiatric care. Moreover, the growing adoption of digital health platforms has enabled interstate telepsychiatry under relaxed licensure agreements. As mental health becomes a bipartisan legislative priority, the U.S. market is likely to experience continued investment, workforce development, and infrastructure expansion.
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2023 to 2033. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the U.S. psychiatry clinic market.
Age-Group