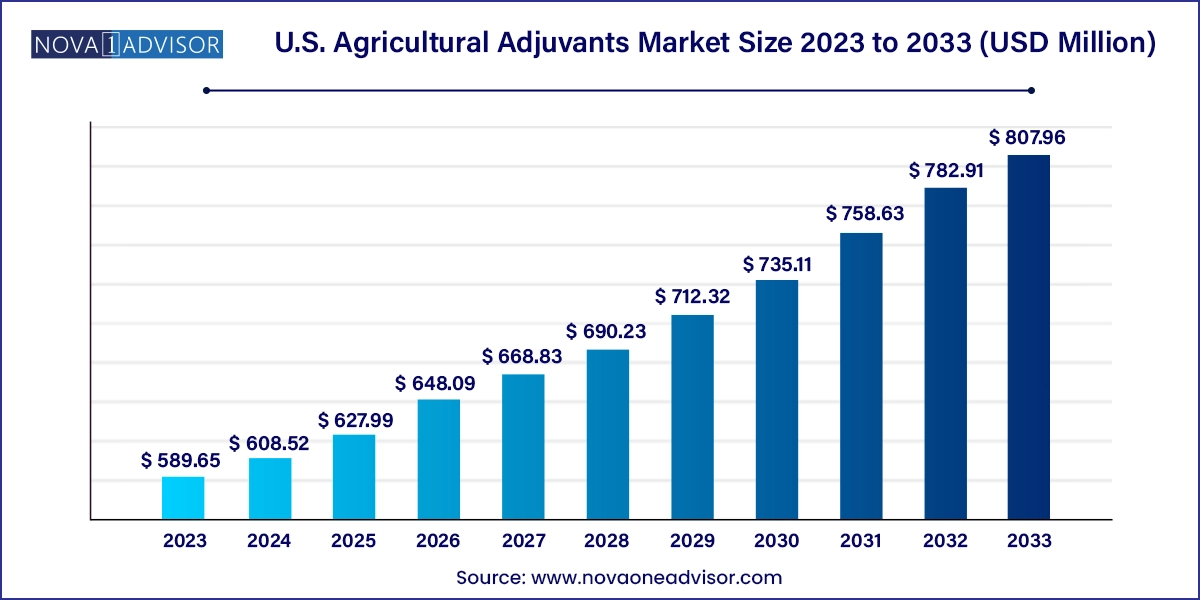
The U.S. agricultural adjuvants market size was exhibited at USD 589.65 million in 2023 and is projected to hit around USD 807.96 million by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 3.2% during the forecast period 2024 to 2033.
The U.S. agricultural adjuvants market represents a vital subset of the nation’s broader agricultural inputs industry. Agricultural adjuvants, which are added to crop protection products such as herbicides, insecticides, and fungicides, enhance their effectiveness by improving spreading, sticking, penetration, and compatibility. In a country like the United States where agriculture is both economically and socially foundational adjuvants play a critical role in increasing crop yields, reducing environmental impact, and optimizing input costs for farmers.
The market's growth trajectory is aligned with trends in precision agriculture, sustainable farming practices, and the increasing need to address pest and disease outbreaks effectively. The U.S. has been at the forefront of adopting integrated pest management (IPM) systems, where the synergy between pesticides and adjuvants becomes particularly important. Moreover, ongoing concerns about herbicide resistance and the environmental safety of agrochemicals have prompted a shift toward advanced formulations supported by efficient adjuvants.
As the agricultural industry contends with growing demand for food, fluctuations in climatic conditions, and evolving regulatory pressures, agricultural adjuvants offer a powerful solution to improve the efficacy of agrochemicals, reduce the volume of active ingredients, and ensure optimal coverage and absorption. This blend of agronomic and economic value positions adjuvants as an indispensable element of modern U.S. agriculture.
Surge in demand for precision agriculture tools: Adjuvants are becoming crucial in precision spraying technologies, ensuring uniform application and improved efficacy in targeted areas.
Rising use of oil-based adjuvants: These are gaining traction in the U.S. due to their superior penetration properties and better retention, especially in systemic herbicides.
Environmental sustainability and reduced pesticide runoff: The focus on reducing agrochemical runoff into water bodies has pushed the adoption of drift control and buffering agents.
Custom blends by manufacturers: Companies are developing tailor-made adjuvant solutions for specific agrochemical products to enhance compatibility and reduce antagonism.
Shift toward biocompatible and biodegradable adjuvants: There is an increasing preference for adjuvants derived from renewable sources that are eco-friendly and compliant with regulatory norms.
Integration with drone-based spraying systems: Adjuvants that reduce droplet size variation and promote better spread are seeing rising adoption in UAV-based applications.
Increased research in nanotechnology-based adjuvants: Innovations in nanoemulsions and encapsulation are emerging as next-gen solutions in adjuvant formulation.
Focus on combating herbicide resistance: Adjuvants are increasingly employed in resistance management strategies to enhance the efficacy of alternate chemistries.
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 608.52 Million |
| Market Size by 2033 | USD 807.96 Million |
| Growth Rate From 2024 to 2033 | CAGR of 3.2% |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Forecast Period | 2024-2033 |
| Segments Covered | Product, Application, Crop type |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) | Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Country scope | U.S. |
| Key Companies Profiled | BASF SE, Dow Inc., Nufarm Limited, Helena Agri Enterprises, Huntsman Corporation, Corda International Plc., Evonik Industries AG, Stepan Company, Wilbur-Ellis Company LLC |
One of the principal drivers propelling the U.S. agricultural adjuvants market is the continuous need to enhance crop productivity amidst a backdrop of limited arable land and fluctuating climatic conditions. With the increasing global population and rising domestic food demand, U.S. farmers are under pressure to optimize crop yields per unit area. Agricultural adjuvants contribute significantly by ensuring that herbicides, insecticides, and fungicides deliver maximum effectiveness.
For instance, surfactants help in breaking the surface tension on plant leaves, ensuring better contact and uptake of crop protection agents. Oil-based adjuvants facilitate deeper penetration of active ingredients into plant tissues, especially in tough-to-control weeds. These performance-enhancing features not only lead to better pest and disease control but also result in lower repeat application rates, thus reducing input costs and environmental burden.
A significant restraint to the growth of the U.S. agricultural adjuvants market is the complex and often stringent regulatory framework surrounding agrochemicals. Adjuvants, although not directly classified as pesticides, are often regulated in a similar fashion by agencies like the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). Manufacturers must navigate extensive compliance procedures for product registration, environmental safety, and toxicity testing.
This regulatory burden can delay product launches, increase R&D costs, and pose barriers for smaller players or startups seeking entry into the market. For example, if an adjuvant is found to interfere with the efficacy or safety profile of a pesticide product, it could result in legal or commercial liabilities. As public scrutiny of chemical use in agriculture intensifies, the need for exhaustive testing and transparency in adjuvant formulation is only growing—thereby restraining rapid innovation and adoption.
As consumer demand for organic produce rises and farmers explore sustainable farming alternatives, a significant opportunity is emerging in the development and deployment of bio-based and organic-compliant adjuvants. These products are formulated using plant-derived oils, natural surfactants, and biodegradable agents, aligning well with the principles of organic agriculture.
U.S. farmers, especially those serving high-end and export-oriented markets, are increasingly seeking adjuvants that are certified for use in organic farming systems. Companies that can cater to this demand by offering OMRI (Organic Materials Review Institute)-listed or USDA-approved formulations are likely to gain a strong foothold. Additionally, these adjuvants find applications in bio-pesticides, which are becoming mainstream as the agriculture industry moves away from synthetic chemical reliance.
Activator adjuvants held the dominant share in the U.S. agricultural adjuvants market due to their widespread utility in improving the efficacy of a broad range of crop protection products. These include surfactants and oil-based adjuvants. Surfactants are particularly favored for herbicide applications, where they assist in reducing surface tension and improving adhesion on leaf surfaces. Non-ionic surfactants (NIS) are extensively used in combination with glyphosate to improve performance against tough weeds. Oil-based adjuvants, including methylated seed oils and crop oil concentrates, have witnessed strong demand in Midwest states, where systemic herbicides are commonly applied to row crops such as corn and soybean.
Utility adjuvants are the fastest-growing category due to the increasing complexity of tank mixes and the necessity to maintain chemical stability and environmental safety. Drift control agents are gaining ground in states like California, where pesticide drift is a legal and environmental concern. Water conditioning agents are also in high demand in regions with hard water issues, such as Texas and parts of the Great Plains. These adjuvants ensure that hard water cations do not neutralize the efficacy of herbicides like glyphosate or 2,4-D. Compatibility agents and buffering agents are becoming essential tools in precision agriculture applications, particularly for custom blends and advanced tank mixes.
Herbicides remain the largest application area for agricultural adjuvants in the U.S., driven by the country’s reliance on broad-acre crops like corn, soybeans, and wheat, which are heavily impacted by weed pressure. The rise of herbicide-resistant weed species such as Amaranthus palmeri (Palmer amaranth) has necessitated the use of more effective spray solutions that include adjuvants for increased penetration and absorption. Adjuvants are routinely used in glyphosate, dicamba, and glufosinate-based formulations to boost efficiency and manage resistance.
Fungicides represent the fastest-growing application segment, especially in high-value specialty crops such as grapes, strawberries, and almonds. Adjuvants used in fungicide applications improve canopy penetration, reduce runoff, and enhance contact retention on waxy surfaces. In states like California and Florida, where humid conditions promote fungal diseases, adjuvants help optimize the performance of preventive and curative fungicide sprays. Additionally, drone-based spraying of fungicides is increasingly incorporating adjuvants to ensure even distribution and optimal droplet size.
Cereals & grains are the dominant crop type using agricultural adjuvants in the U.S., largely due to the vast acreage under corn and wheat cultivation. These crops are extensively treated with herbicides, where surfactants and oil-based adjuvants are used to maximize foliar uptake and systemic action. States like Iowa, Illinois, and Nebraska have high penetration rates of adjuvant use in row cropping systems, where early weed control is crucial to ensure yield optimization.
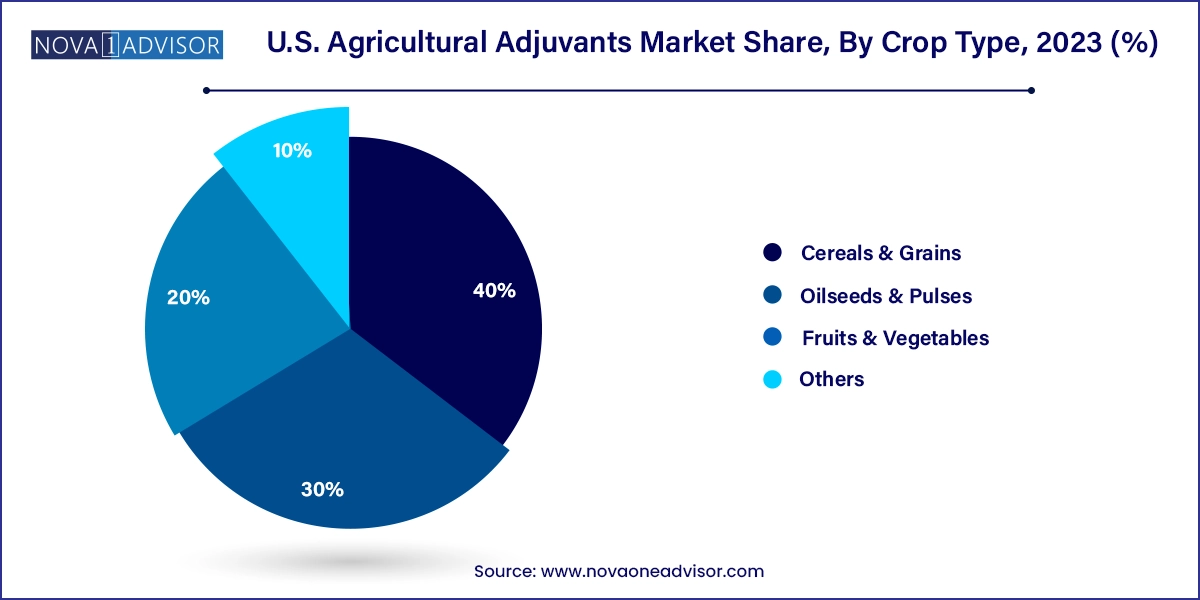
Fruits & vegetables are witnessing the fastest adoption of advanced adjuvant technologies due to their high market value and strict quality requirements. In the western U.S., especially in California’s Central Valley, vineyards and orchards use buffering agents and drift control adjuvants to protect nearby sensitive crops. Vegetable growers in Florida and Arizona are leveraging compatibility agents for multi-product tank mixes to manage a wide spectrum of pests and diseases in shorter crop cycles. This segment’s growth is also propelled by export-oriented growers who need maximum crop quality and reduced pesticide residues.
The U.S. agricultural adjuvants market is significantly influenced by regional agronomic practices, climatic diversity, and the scale of agricultural operations. In the Midwest, the demand for surfactants and oil-based adjuvants is high due to the dominance of corn and soybean cultivation, which requires extensive herbicide use. In the Southeast, where insect and fungal pressures are higher, adjuvants are more frequently used with insecticides and fungicides in fruits and vegetables.
States like California are leading in the adoption of environmentally compliant adjuvants, including drift control and biodegradable agents, due to stringent state-level regulations. Texas and Kansas see increasing use of water conditioning agents, particularly where high levels of calcium and magnesium in irrigation water reduce pesticide performance. Washington and Oregon, home to high-value tree fruits and vineyards, are experiencing a rising demand for adjuvants that support disease control while maintaining export quality standards.
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2033. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the U.S. agricultural adjuvants market
Product
Application
Crop Type