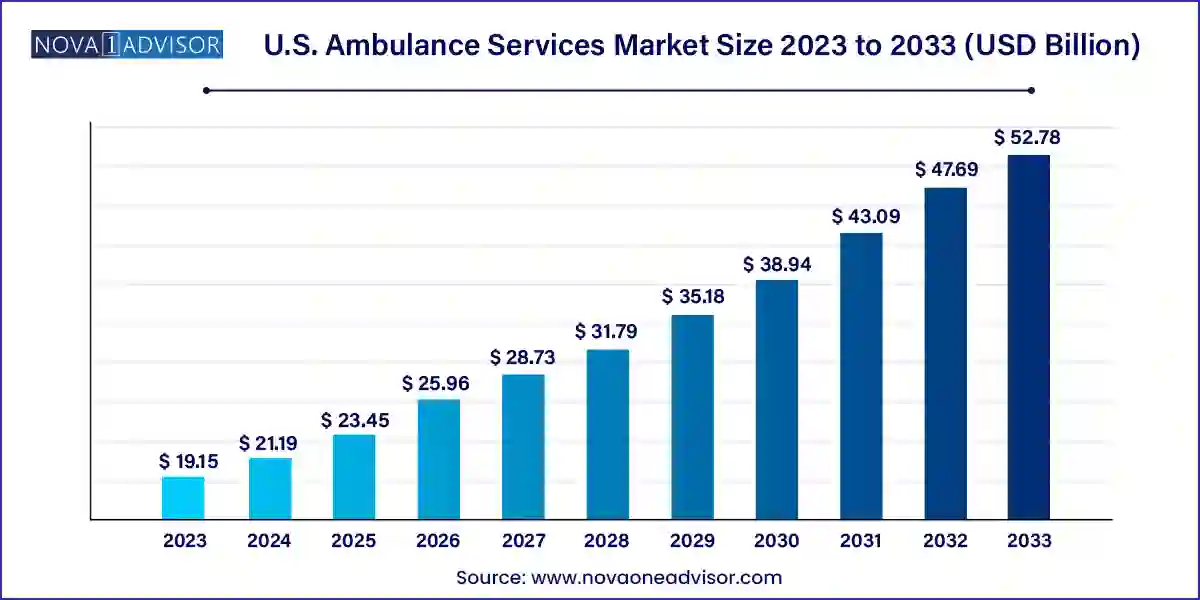
The U.S. ambulance services market size was exhibited at USD 19.15 billion in 2023 and is projected to hit around USD 52.78 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 10.67% during the forecast period 2024 to 2033.
The U.S. ambulance services market serves as a vital cornerstone in the country’s emergency medical infrastructure, providing life-saving transportation, critical care support, and rapid mobilization for millions of patients each year. These services encompass a wide spectrum of transport options ranging from ground ambulances for road-based emergency care to air and water ambulances designed to navigate complex terrains or provide swift access to advanced medical centers. The growing complexity of healthcare needs, coupled with an aging population and increasing incidence of chronic diseases and trauma cases, has significantly amplified the demand for timely, efficient ambulance services in the United States.
Ambulance services operate under both public and private models, with a notable presence of third-party service providers like Global Medical Response (GMR), American Medical Response (AMR), and Acadian Ambulance Service dominating large metropolitan and rural service areas. While traditionally centered around emergency care, the role of ambulance services has expanded to include non-emergency transport for patients requiring scheduled medical visits, long-term care transfers, and post-discharge follow-ups. These functions are crucial in reducing hospital readmissions and supporting integrated care delivery.
Furthermore, advancements in onboard medical equipment ranging from mobile telemetry and ventilator support to AI-powered triage systems have enhanced the scope of pre-hospital care provided by ambulance teams. Legislative shifts such as the Emergency Triage, Treat, and Transport (ET3) Model initiated by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) are promoting more value-based, flexible approaches to emergency response. As the healthcare landscape evolves toward patient-centered, coordinated care, ambulance services are poised to play a central role in bridging the gap between communities and health facilities.
Rising use of non-emergency ambulance transport for chronic care patients and elderly populations.
Growing investments in air ambulance fleets to serve rural and inaccessible areas with limited hospital infrastructure.
Integration of advanced life support (ALS) systems in both ground and air ambulance vehicles.
Expansion of mobile health capabilities through telemedicine-equipped ambulances.
Adoption of GPS tracking, route optimization, and AI-based dispatch systems to reduce response times.
Growth of public-private partnerships (PPPs) to expand ambulance coverage in underserved communities.
Reimbursement reforms under the ET3 Model allowing for transport to alternative care sites and tele-triage.
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 21.19 Billion |
| Market Size by 2033 | USD 52.78 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2024 to 2033 | CAGR of 10.67% |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Forecast Period | 2024-2033 |
| Segments Covered | Transport Vehicle, Emergency Services, Equipment |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) | Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Regional Scope | U.S. |
| Key Companies Profiled | Babcock International Group PLC; Acadian Ambulance Service; American Air Ambulance; PHI Air Medical; Express Air Medical Transport, LLC; Air Medical Group Holdings, Inc. (Amgh); Falck A/S; American Medical Response; Rural/Metro Corporation; Medstar |
One of the foremost drivers of the U.S. ambulance services market is the increasing incidence of emergency medical situations, largely attributed to an aging population and rising prevalence of chronic diseases. According to the U.S. Census Bureau, by 2030, more than 20% of the U.S. population will be aged 65 or older. This demographic shift is closely tied to higher incidences of cardiovascular disorders, respiratory illnesses, diabetes, and stroke all of which are common triggers for emergency medical transport.
Older adults are more likely to require rapid intervention during acute episodes, often necessitating both emergency and non-emergency ambulance transport. Additionally, comorbidities in this age group often require inter-facility transfers to specialized treatment centers. As a result, the demand for Basic Life Support (BLS) and Advanced Life Support (ALS) equipped ambulances is rising. The expansion of long-term care centers and home health programs has also increased the need for scheduled medical transport for the elderly, further driving market growth.
Despite increasing demand, the U.S. ambulance services market faces significant financial challenges stemming from high operational costs and uneven reimbursement models. Operating an ambulance service involves substantial expenditures—fuel, insurance, medical equipment, maintenance, and certified personnel, especially paramedics and emergency medical technicians (EMTs). For air ambulance services, costs escalate significantly due to aircraft procurement, aviation safety compliance, and onboard intensive care equipment.
Moreover, ambulance services often face hurdles with insurance reimbursements. While Medicare, Medicaid, and private insurers offer coverage for ambulance transport, reimbursement levels may not fully reflect operational expenses especially in non-emergency transport scenarios or when transporting uninsured patients. Surprise billing controversies and regulatory scrutiny have further complicated billing practices in recent years. This financial unpredictability can undermine service continuity and limit expansion efforts, particularly for rural and community-based providers.
A transformative opportunity for ambulance service providers in the U.S. lies in embracing technological innovation and aligning with the CMS Emergency Triage, Treat, and Transport (ET3) Model. This initiative, launched to promote value-based care in emergency services, allows ambulance providers to deliver treatment at the scene, facilitate telemedicine consultations, or transport patients to urgent care centers instead of emergency rooms, where appropriate. These changes open up new revenue channels while reducing emergency department overcrowding and healthcare costs.
Technology plays a critical role in enabling these models. Telehealth-equipped ambulances, digital patient monitoring, real-time vitals transmission, and AI-assisted triage tools are empowering EMS teams to make informed care decisions on the go. Companies investing in digital dispatch platforms, predictive routing, and electronic medical records (EMRs) integrated into ambulances are positioned to offer high-efficiency services with better clinical outcomes. These capabilities can reshape emergency care workflows, positioning ambulance providers as dynamic mobile health units within the broader continuum of care.
Ground ambulances dominate the U.S. ambulance services market, accounting for the majority of all emergency and non-emergency medical transportation. Their ubiquity across cities, towns, and rural roads makes them the first responders in nearly every medical emergency scenario. Ground ambulances are typically classified into ALS and BLS configurations, with ALS vehicles equipped to handle cardiac monitoring, medication delivery, and airway support. Local fire departments, hospital systems, and private providers such as AMR and Paramedics Plus operate extensive ground fleets supported by trained EMTs and paramedics.
Air ambulances represent the fastest-growing vehicle segment, driven by the need for rapid transport from remote or trauma-prone areas to tertiary care centers. These include both rotor-wing (helicopter) and fixed-wing (airplane) transport. Leading players like Air Methods, REVA Air, and Global Medical Response have invested heavily in expanding their fleets and operational coverage. In April 2024, Global Medical Response launched a new air medical base in Arizona, signaling increased demand for aerial critical care capabilities. As trauma care and stroke centers become more centralized, air transport becomes essential for timely patient access, supporting this segment's growth.
Emergency services form the largest segment, as they cater to acute medical events such as heart attacks, injuries, strokes, respiratory distress, and other life-threatening conditions. Emergency services require rapid response, high clinical expertise, and full-service medical capabilities onboard. They are tightly regulated and often coordinated with 911 dispatch systems. Public fire departments and large EMS contractors are the primary operators in this space, with urban markets accounting for the highest call volumes.
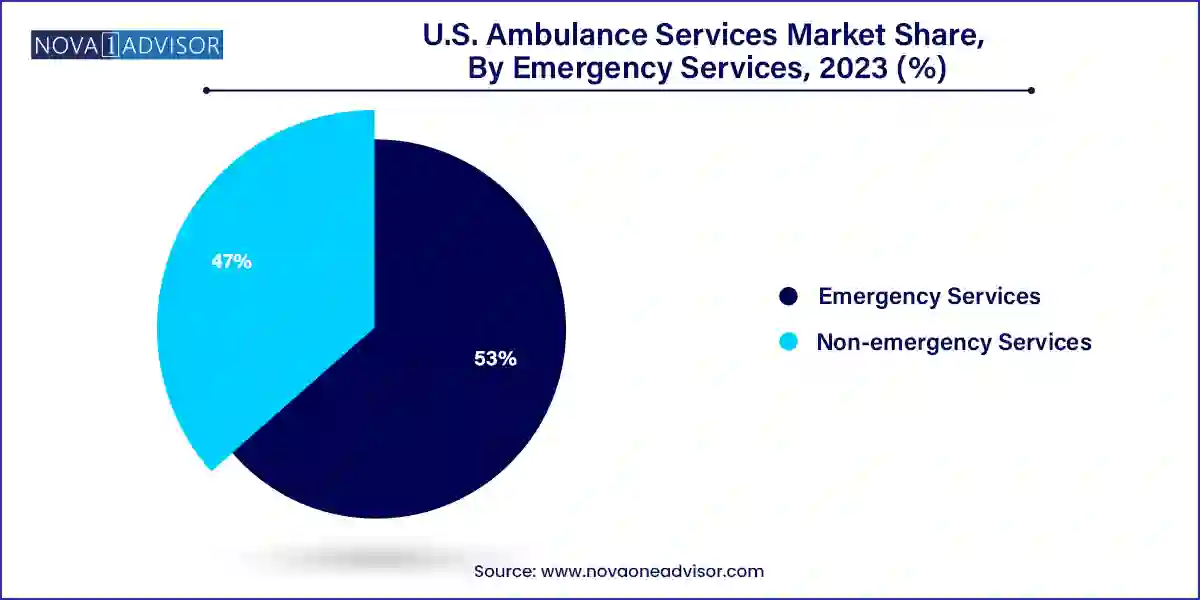
Non-emergency services are the fastest-growing, fueled by increasing demand for patient transport to dialysis centers, rehab clinics, nursing homes, and medical appointments. This segment plays a vital role in ensuring continuity of care for patients with mobility constraints or complex needs. Non-emergency medical transportation (NEMT) providers such as Ambulnz and Modivcare are expanding rapidly, often working under contracts with Medicaid or commercial health plans. The segment is increasingly leveraging app-based scheduling, subscription models, and AI dispatching to improve efficiency and lower costs.
Advanced Life Support (ALS) ambulances dominate in terms of value, given their extensive medical equipment, certified paramedics, and higher per-transport charges. ALS ambulances handle high-acuity cases, including trauma resuscitation, cardiac events, and respiratory crises. These vehicles are outfitted with defibrillators, IV infusion systems, cardiac monitors, and emergency drug kits. Large-scale hospital systems and metropolitan EMS providers predominantly deploy ALS ambulances, especially in regions with a high volume of critical care transport.
Basic Life Support (BLS) services are growing faster, particularly in rural and suburban areas where medical emergencies are less frequent but patient mobility is still a challenge. BLS ambulances cater to stable patients who require monitoring, assistance with mobility, or low-risk transport between facilities. Staffing and equipment requirements are lower, making BLS more cost-effective for long-distance or scheduled transfers. Many healthcare systems are strategically expanding BLS fleets to optimize resource allocation and cost management.
The United States represents the most developed and structured ambulance services market globally. With an estimated 240 million EMS calls annually, the country has one of the most active emergency response systems in the world. Ambulance services in the U.S. are delivered through a combination of municipal fire departments, private contractors, hospital-based EMS, and volunteer squads. Regulations vary across states, but the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) and CMS provide foundational guidelines for medical equipment, personnel training, and reimbursement protocols.
Rising healthcare costs, demographic shifts, and legislative efforts like the No Surprises Act and ET3 Model are reshaping how ambulance services are funded and delivered. Hospital consolidation and the growth of accountable care organizations (ACOs) are encouraging integrated EMS strategies to reduce readmissions and improve pre-hospital care coordination. Urban regions have access to advanced, multi-tiered EMS systems, while rural areas face challenges with staffing and funding—prompting state-level investments in air medical bases and telemedicine-enabled ambulance units.
April 2024 – Global Medical Response (GMR) launched a new helicopter base in Arizona to expand air ambulance coverage in remote areas and reduce rural transport delays.
March 2024 – Ambulnz, a subsidiary of DocGo, announced the deployment of AI-driven dispatch optimization software to reduce EMS response times and enhance fleet efficiency across New York and California.
February 2024 – REVA Air Ambulance signed a partnership with several academic medical centers to provide long-distance air critical care transport for transplant and cardiac patients.
January 2024 – Acadian Ambulance Service opened a simulation training facility in Texas, aimed at improving paramedic response in mass casualty scenarios and disaster preparedness.
December 2023 – Falck USA expanded its non-emergency services in Florida and Nevada, adding 100+ vehicles equipped for wheelchair and stretcher transport under Medicare Advantage contracts.
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2033. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the U.S. ambulance services market
Transport Vehicle
Emergency Services
Equipment