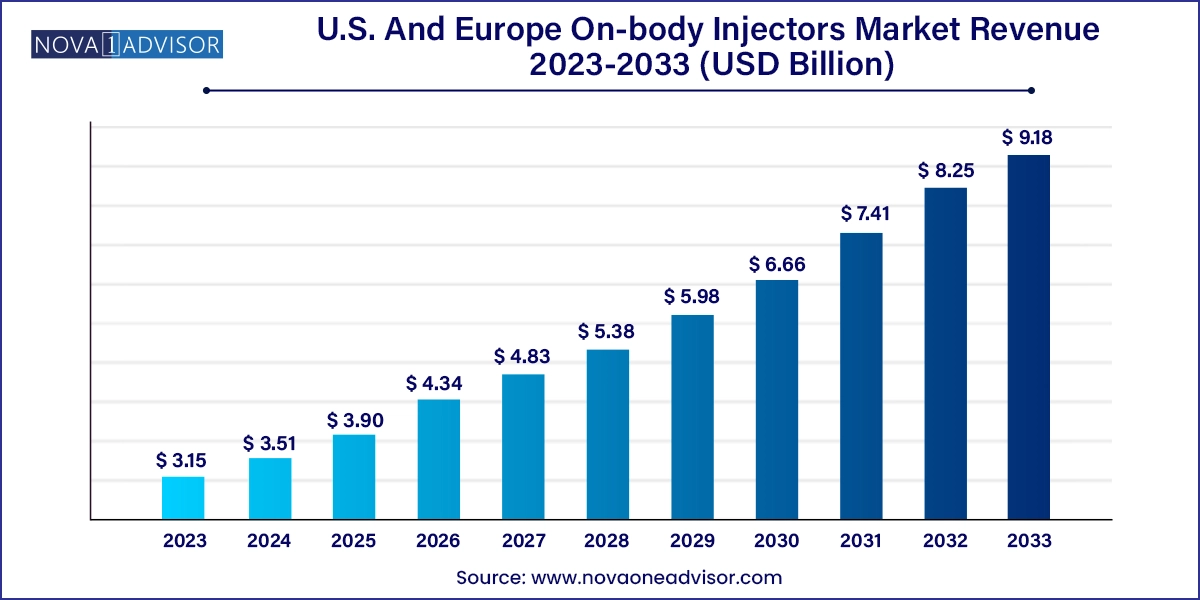
The U.S. and Europe on-body injectors market size was exhibited at USD 3.15 billion in 2023 and is projected to hit around USD 9.18 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 11.29% during the forecast period 2024 to 2033.
The U.S. and Europe On-body Injectors Market has witnessed substantial growth in recent years due to increasing patient demand for advanced, user-friendly drug delivery systems that allow for subcutaneous administration of medications without the need for repeated hospital visits. These wearable injectors, also referred to as patch pumps or large volume injectors, have become a cornerstone in the management of chronic diseases such as cancer, diabetes, and autoimmune disorders.
These devices, which are typically affixed to the patient’s body and programmed to administer medications over a specific period, are revolutionizing drug delivery. Their rising adoption is being fueled by the global shift towards home-based care, the need to reduce healthcare costs, and increasing biologics consumption that requires patient-friendly administration methods. Particularly in the United States and key European countries like Germany, France, and the United Kingdom, there is growing healthcare infrastructure to support such technologies and regulatory incentives promoting patient-centric solutions.
The on-body injector’s ability to administer high-viscosity and high-volume drugs without user intervention enhances patient adherence and convenience. Furthermore, the expanding portfolio of biologic drugs and the focus of pharmaceutical companies on delivering these via wearable devices underpin the upward trajectory of the market.
Shift Towards Home-based and Self-administrable Therapies: Patients prefer drug delivery methods that minimize hospital visits, especially in the post-COVID era.
Integration of Digital Connectivity: Devices are increasingly equipped with Bluetooth and app-based monitoring, allowing remote patient tracking.
Growing Biologics Pipeline: Biologic and biosimilar drugs requiring precise, long-term dosing are boosting demand for wearable injectors.
R&D Focused on Volume and Viscosity Flexibility: Manufacturers are innovating devices that can handle higher drug volumes and viscosities.
Emphasis on Human-Centric Design: Compact, discreet, and easy-to-use designs are being prioritized to improve user compliance.
Partnerships Between Biotech and Device Companies: Co-development models are emerging where drug makers collaborate with device developers early in the product lifecycle.
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 3.51 Billion |
| Market Size by 2033 | USD 9.18 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2024 to 2033 | CAGR of 11.29% |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Forecast Period | 2024-2033 |
| Segments Covered | Technology, Application, End use, Region |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) | Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Country scope | U.S. |
| Key Companies Profiled | West Pharmaceutical Services, Inc.; BD; Stevanato Group; Enable Injections; Nemera; Debiotech SA; AbbVie, Inc.; Coherus BioSciences, Inc; Gerresheimer AG; E3D Elcam Drug Delivery Devices |
One of the primary drivers for the U.S. and Europe On-body Injectors Market is the increasing prevalence of chronic conditions, notably cancer and diabetes. According to the American Cancer Society, nearly 2 million new cancer cases were projected in the U.S. alone for 2024, many of which require continuous and precise drug administration. Similarly, diabetes affects over 38 million people in the United States, as reported by the CDC, with insulin delivery remaining a cornerstone of treatment.
On-body injectors provide a more consistent and controlled delivery of medications, improving outcomes and minimizing complications. These devices allow patients to remain active and mobile, which is particularly valuable for individuals undergoing long-term therapy. In Europe, aging populations and increasing sedentary lifestyles further elevate the incidence of chronic disease, making the need for scalable, wearable solutions ever more critical.
Despite their benefits, on-body injectors come with significant manufacturing complexity. Incorporating advanced sensors, connectivity, programming, and drug containment in a single compact device elevates development costs. Additionally, these devices must comply with rigorous safety and biocompatibility regulations, requiring extensive clinical trials and approvals that further increase costs and extend timelines.
This high cost barrier makes it difficult for smaller companies to enter the market and limits affordability in publicly funded healthcare systems, particularly in parts of Europe. Moreover, manufacturers must ensure the compatibility of their devices with specific drug formulations, leading to extensive customization and individualized testing.
There is a substantial opportunity in the development of next-generation on-body injectors that incorporate digital health technologies. These include devices with real-time monitoring capabilities, adherence tracking, automated alerts, and integration with electronic health records. As personalized medicine gains traction, wearable injectors can be programmed to administer customized doses based on individual metabolism, drug tolerance, or disease progression.
Companies that capitalize on these innovations stand to gain a competitive edge. For instance, developing AI-enabled injectors or devices that adapt based on user feedback and biometric readings could greatly enhance user satisfaction and therapy compliance. Regulatory bodies in both the U.S. and Europe are beginning to support such innovations through fast-track approvals and digital health initiatives.
Spring-based injectors dominated the technology segment due to their cost-effectiveness and ease of manufacturing. These devices rely on a mechanical spring to deliver the drug into the patient’s body, making them highly reliable and straightforward for patient use. Particularly in diabetes and autoimmune treatment, where patients self-administer regularly, the predictability and simplicity of spring-based systems are appreciated. Furthermore, these devices require minimal electronic integration, making them suitable for patients who prefer analog solutions or have limited access to digital tools.
However, motor-driven injectors are emerging as the fastest-growing segment due to their precision and programmability. These devices allow for better control over drug flow rates, making them ideal for high-viscosity drugs used in oncology and chronic autoimmune therapies. Additionally, motor-driven injectors are better suited for integration with connectivity features, enabling patients and clinicians to monitor therapy compliance and performance. This capability is becoming especially important in clinical trials and post-market surveillance in regulated markets like the U.S. and EU.
Oncology held the largest share in the application segment owing to the rising use of biologics and monoclonal antibodies for cancer treatment. Many of these medications require slow, high-volume administration over extended periods, a function well-served by on-body injectors. With the global cancer burden increasing and therapies becoming more personalized and biologic-intensive, on-body injectors offer a practical and patient-centric alternative to infusion centers. Particularly in outpatient cancer care models in the U.S., these devices are being adopted to streamline treatment regimens.
Diabetes is anticipated to grow at the highest rate within the forecast period. With the global diabetes epidemic showing no signs of slowing, patients are increasingly turning to advanced delivery mechanisms to manage their condition effectively. Innovations like automated basal insulin delivery and integration with continuous glucose monitors are further supporting adoption. Companies are also developing on-body injectors specifically tailored for insulin and GLP-1 receptor agonists, targeting both Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes populations in both urban and rural settings.
Hospitals and clinics were the dominant end users due to the initial administration, training, and supervision required for the adoption of on-body injectors. In oncology and cardiovascular applications, these healthcare settings serve as the first point of care, where patients receive instruction and initial administration before transitioning to home-based use. Furthermore, healthcare providers benefit from data collected by connected devices for real-time monitoring, which can be integrated into hospital electronic systems.
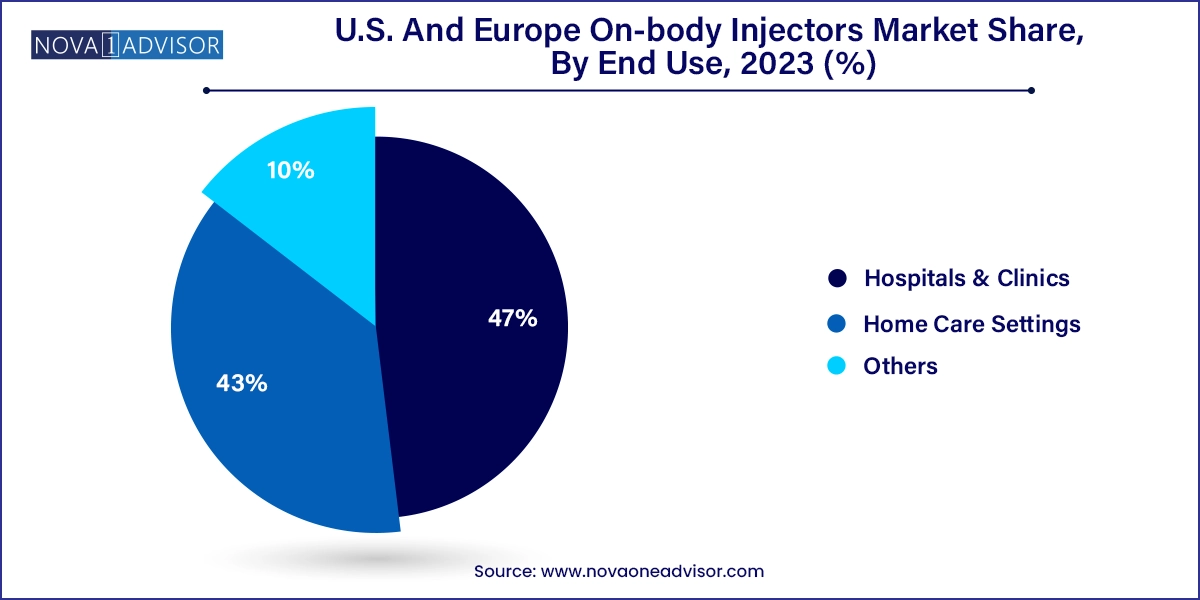
Home care settings are the fastest-growing end-use segment, reflecting the broader industry shift toward decentralized care. With healthcare systems in the U.S. and Europe facing staffing shortages and budget constraints, there’s a strong incentive to move stable patients out of hospitals and into self-managed care models. On-body injectors enable this transition seamlessly by offering safe, accurate, and comfortable drug delivery options. The growth of home health services and telemedicine further accelerates this trend, making home care not only viable but preferred by many patients.
The U.S. market is driven by high chronic disease burden, strong healthcare reimbursement policies, and a robust ecosystem for digital health. FDA initiatives such as the Digital Health Innovation Action Plan and growing support for patient-centered drug delivery systems enhance market growth. Numerous clinical trials and product rollouts, including Amgen’s Onpro® kit for Neulasta® delivery, have established the commercial viability of on-body injectors in the U.S.
In Europe, countries like Germany and France are pioneering the adoption of on-body injectors, particularly in their public healthcare systems. Efforts to reduce hospital admissions and improve outpatient drug administration are key enablers. The European Medicines Agency (EMA) has shown increasing openness to digital health tools, encouraging innovation. Moreover, EU initiatives supporting medical device innovation, such as Horizon Europe, create favorable conditions for market expansion.
January 2025: Becton, Dickinson and Company (BD) announced FDA clearance for its new on-body injector platform designed for viscous biologics, marking a significant advancement in wearable drug delivery for high-volume formulations.
December 2024: Amgen revealed the expansion of its Neulasta® Onpro® delivery kit distribution across European oncology centers following increased post-chemotherapy demand.
October 2024: Ypsomed collaborated with a U.S.-based pharmaceutical firm to develop a customized wearable injector compatible with their pipeline monoclonal antibody therapy.
August 2024: West Pharmaceutical Services launched the SmartDose® Gen III platform in Europe, integrating Bluetooth connectivity and automated adherence tracking.
June 2024: Enable Injections closed a $215 million funding round to accelerate the development of its enFuse® platform targeting both insulin and oncology applications.
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2033. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the U.S. and Europe on-body injectors market
Technology
Application
End Use
Regional