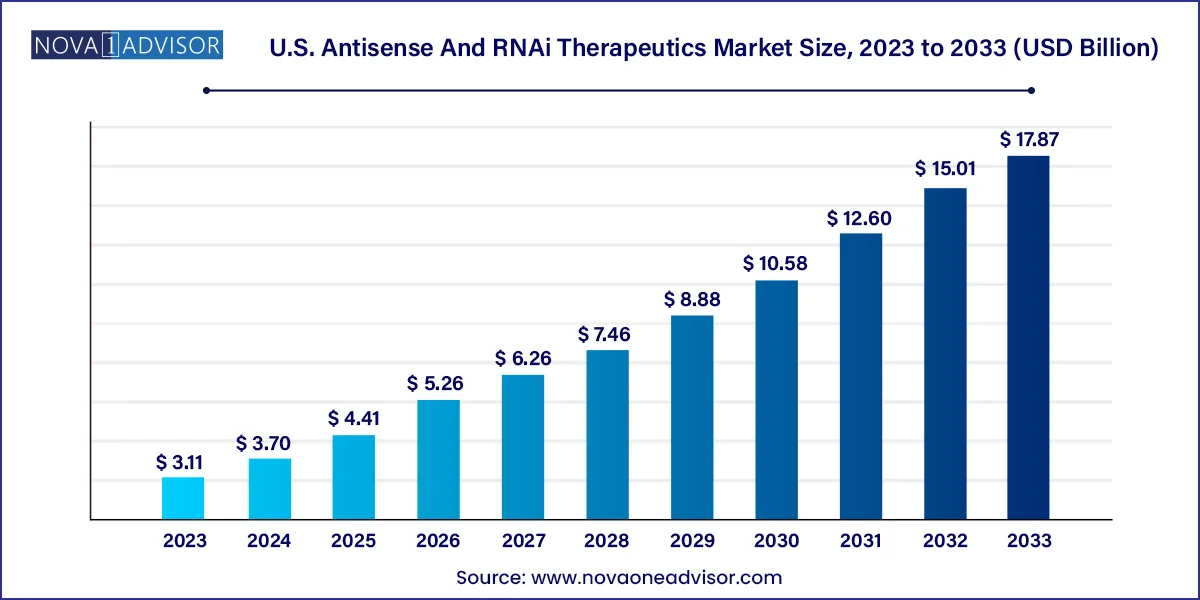
The U.S. antisense and RNAi therapeutics market size was valued at USD 3.11 billion in 2023 and is projected to surpass around USD 17.87 billion by 2033, registering a CAGR of 19.11% over the forecast period of 2024 to 2033.
The U.S. antisense and RNA interference (RNAi) therapeutics market is undergoing a transformative phase, fueled by the convergence of genomics, drug delivery innovation, and personalized medicine. These nucleic acid-based therapies have emerged as powerful tools for modulating gene expression, targeting previously undruggable genetic conditions, and developing ultra-precise treatments for complex disorders such as neurodegenerative, ocular, and cardiometabolic diseases.
Antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs) and RNA interference agents (including small interfering RNA or siRNA molecules) operate by silencing specific messenger RNA (mRNA) sequences, effectively halting the production of pathogenic proteins at the genetic level. Unlike traditional small molecule drugs, these therapies address the root cause of genetic disorders rather than just treating the symptoms.
In the United States, favorable regulatory frameworks, rising investments from both public institutions and private pharmaceutical firms, and successful clinical outcomes have accelerated market expansion. FDA approvals of therapies like Spinraza (nusinersen) for spinal muscular atrophy, Onpattro (patisiran) for hereditary ATTR amyloidosis, and Givlaari (givosiran) for acute hepatic porphyria have proven the therapeutic viability of this drug class.
With over 50 antisense and RNAi candidates in clinical development across therapeutic areas, and an increasing emphasis on rare and genetic disease drug development, the U.S. market stands at the forefront of this new paradigm in molecular medicine. Advanced delivery platforms, improved chemical modifications, and a surge in biotech partnerships are shaping a robust pipeline and a promising commercial outlook.
Rise in FDA Approvals for RNA-based Drugs: Regulatory momentum is growing as more RNAi and antisense drugs reach the market with breakthrough or orphan designations.
Strategic Collaborations and Licensing Deals: Large pharma companies are partnering with biotech firms to co-develop and commercialize RNA-targeting therapeutics.
Advancements in Delivery Technologies: Lipid nanoparticles (LNPs), GalNAc conjugates, and intrathecal formulations are enhancing drug delivery efficiency.
Shift Toward Rare and Orphan Diseases: The market is increasingly focusing on ultra-rare and genetic disorders with high unmet clinical needs.
Use of AI in Target Selection and Molecule Design: Machine learning platforms are improving the precision of target identification and oligonucleotide optimization.
Increasing Interest in CNS Disorders: ASOs and RNAi agents are being developed for neurological diseases like Huntington’s and ALS using intrathecal administration.
Patient-Specific Therapies (N-of-1 Trials): Customized antisense therapies tailored to individual patients are emerging, especially for ultra-rare genetic mutations.
Expansion of Manufacturing Capabilities: CDMOs and biotech firms are investing in scalable nucleic acid synthesis and formulation technologies.
Regulatory Support for Accelerated Programs: The FDA is facilitating rapid development through Fast Track, Breakthrough Therapy, and RMAT designations.
Growing Integration of RNAi in Combination Therapies: RNAi-based drugs are being studied alongside conventional therapies to enhance efficacy.
| Report Attribute | Details |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 3.70 Billion |
| Market Size by 2033 | USD 17.87 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2024 to 2033 | CAGR of 19.11% |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Forecast Period | 2024 to 2033 |
| Segments Covered | Technology, application, route of administration |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) | Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Report Coverage | Revenue forecast, company ranking, competitive landscape, growth factors, and trends |
| Key Companies Profiled | Sarepta Therapeutics, Inc; Ionis Pharmaceuticals, Inc; Benitec Biopharma, Inc; Arbutus Biopharma; Alnylam Pharmaceuticals, Inc.; Microsynth AG; Aragen Bioscience Moderna; Nutcracker Therapeutics;Deep Genomics |
Subcutaneous injections dominate the market, particularly in commercially available therapies like Givlaari and Tegsedi. This route provides ease of administration, better patient adherence, and is suitable for drugs targeting the liver and systemic circulation. Subcutaneous delivery also aligns with chronic disease management, where regular self-administration is preferred over hospital-based infusions.
Intrathecal injections are the fastest-growing route, especially in CNS applications. Drugs like Spinraza are administered directly into the cerebrospinal fluid to bypass the blood-brain barrier and reach the spinal cord and brain tissue. With more CNS-targeted programs entering trials, demand for intrathecal formulations is expected to increase rapidly, along with innovations in injection devices and patient monitoring protocols.
RNA interference (RNAi) technology dominates the U.S. market, particularly due to its success in hepatocyte-targeted therapies using siRNA molecules and GalNAc-conjugation. Products like Onpattro and Givlaari, both FDA-approved, illustrate how RNAi can effectively silence specific genes associated with genetic liver disorders. RNAi therapies offer a strong safety profile and sustained silencing effects, making them attractive for chronic conditions.
In contrast, antisense RNA is the fastest-growing segment, largely driven by its flexibility in treating a broader range of conditions, including CNS and ocular diseases. ASOs are easier to design and modify, can be used to alter splicing, and often do not require complex delivery carriers. Their ability to be injected intrathecally has also enabled breakthroughs in neurodegenerative disease trials. The development of customized ASOs in “N-of-1” trials (e.g., Milasen for Batten disease) further highlights the agility of this approach in targeting ultra-rare conditions.
Genetic disorders are the dominant application area, reflecting the natural fit between gene-targeting therapies and inherited conditions. Many approved and late-stage drugs target diseases like spinal muscular atrophy, familial hypercholesterolemia, and ATTR amyloidosis. These disorders typically have well-understood molecular causes, making them ideal for RNA-based therapeutic intervention.
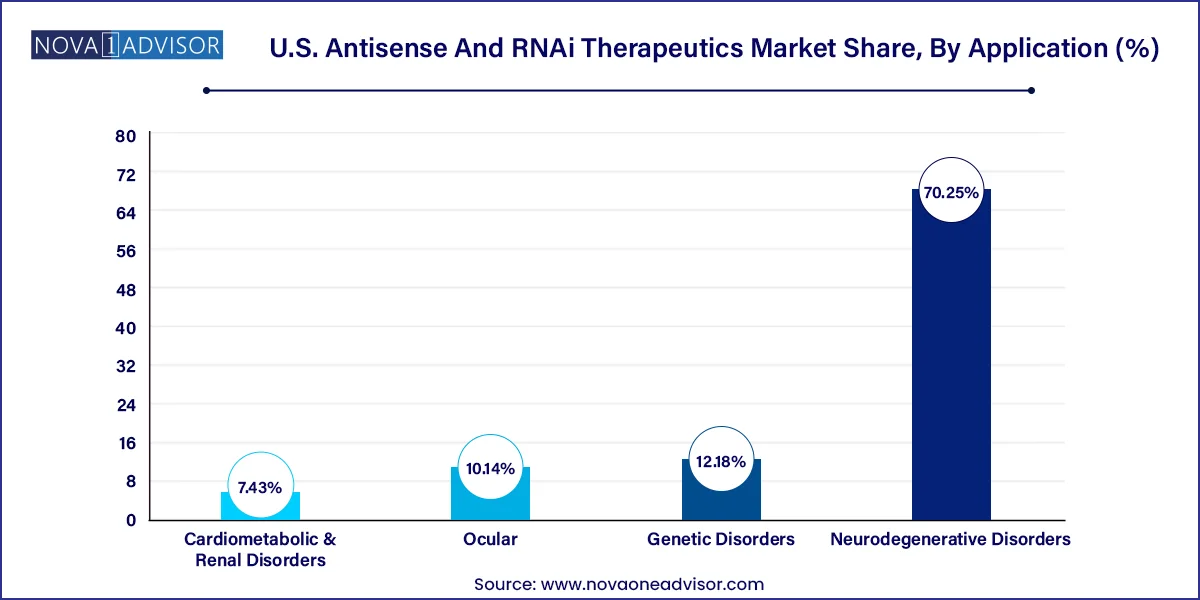
Neurodegenerative disorders represent the fastest-growing application, driven by increasing prevalence and the lack of disease-modifying therapies. Companies are investing heavily in ASOs and RNAi candidates for conditions such as Alzheimer’s, Huntington’s, and ALS. The use of CNS-specific administration techniques and biomarkers is accelerating clinical development. Successful trials in this domain could lead to a dramatic expansion of the market scope.
The United States holds a leading position in the global antisense and RNAi therapeutics market, driven by its dominant biotech sector, robust funding ecosystem, and innovation-friendly regulatory environment. The FDA has played a critical role in enabling rapid development of RNA-based therapies through initiatives like Orphan Drug Designation, Breakthrough Therapy Designation, and Accelerated Approvals.
Academic institutions such as Harvard, MIT, and Stanford are at the forefront of RNA biology research, often collaborating with biotech firms on translational efforts. U.S.-based companies like Alnylam Pharmaceuticals, Ionis Pharmaceuticals, Arrowhead, and Wave Life Sciences are global pioneers in the RNA therapeutics space.
Moreover, the country’s large patient population, sophisticated diagnostic infrastructure, and willingness to adopt personalized medicine approaches make it an ideal launchpad for RNA-targeting drugs. Venture capital investment in RNA therapeutics reached record levels in 2024, reflecting continued investor confidence and commercial potential.
March 2025: Alnylam Pharmaceuticals announced positive Phase 3 results for vutrisiran, an RNAi therapeutic targeting ATTR amyloidosis, with plans to file for FDA approval by Q3 2025.
February 2025: Ionis Pharmaceuticals entered a strategic collaboration with Roche to co-develop an antisense therapy for Huntington’s disease, following encouraging early-phase data.
January 2025: The FDA granted Fast Track designation to Arrowhead Pharmaceuticals’ RNAi candidate for alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency (AATD), signaling strong regulatory support.
December 2024: Wave Life Sciences published preclinical data demonstrating enhanced allele-specific knockdown in Huntington’s disease using stereopure ASOs.
November 2024: Silence Therapeutics established a U.S. headquarters in Cambridge, MA, to accelerate clinical development and regulatory engagement for its siRNA portfolio.
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2033. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the U.S. Antisense And RNAi Therapeutics market.
By Technology
By Application
By Route of Administration