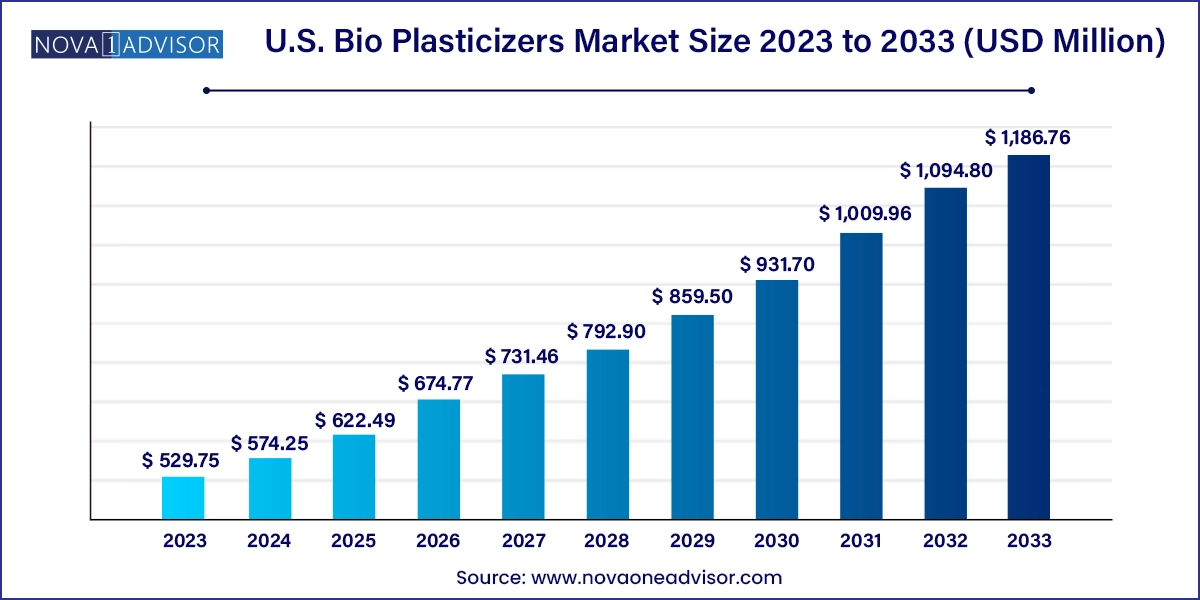
The U.S. bio plasticizers market size was exhibited at USD 529.75 million in 2023 and is projected to hit around USD 1,186.76 million by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 8.4% during the forecast period 2024 to 2033.
The U.S. bio plasticizers market is an evolving and rapidly expanding sector that addresses the growing need for safer, non-toxic, and environmentally sustainable alternatives to conventional plasticizers. Traditionally, plasticizers used to improve flexibility, workability, and durability in polymers, especially PVC were based on phthalates, which have raised health and environmental concerns. Bio plasticizers, derived from renewable sources such as vegetable oils, citrates, and succinic acid, have emerged as a viable and increasingly preferred alternative.
Driven by heightened regulatory scrutiny and consumer awareness about toxic chemical exposure, U.S. manufacturers across industries like packaging, automotive, construction, and consumer goods are transitioning to bio-based plasticizer alternatives. These bio plasticizers are not only biodegradable but also offer comparable or superior performance characteristics in many applications.
The U.S. market benefits from a robust agricultural sector capable of producing the raw materials used in bio plasticizer synthesis, including soybean oil, castor oil, and corn derivatives. In addition, the presence of leading polymer companies and innovation-centric universities and startups provides a fertile ground for research, development, and commercialization of advanced bioplasticizer solutions.
Moreover, state and federal incentives promoting green chemistry, along with bans or limitations on certain phthalates (especially in toys, food packaging, and medical devices), have significantly boosted market momentum. As consumer preferences shift and corporate sustainability initiatives become more aggressive, the demand for bio plasticizers in the U.S. is expected to witness double-digit growth through the coming decade.
Phthalate substitution mandates gaining momentum: Regulatory bans on DEHP, DBP, and BBP are accelerating the adoption of non-toxic bio plasticizers across industries.
Increased R&D in bio-based alternatives: Universities and chemical companies are investing in next-gen plasticizers derived from algae, waste biomass, and fermentation-based succinic acid.
Strong demand in sustainable packaging: FMCG brands are switching to bio plasticizers for flexible packaging to meet circular economy and compostability goals.
Automotive interior green redesigns: EV and automotive OEMs are increasingly opting for bio plasticizers in car interiors and wiring insulation to reduce VOC emissions.
Innovation in dual-function plasticizers: New bio plasticizers are being designed to not only act as flexibilizers but also enhance flame retardancy or UV stability.
Growth of castor oil-based derivatives: Castor oil-based plasticizers are finding increased usage due to their consistent performance and hydrophobic properties.
Circular economy and bioeconomy alignment: Bio plasticizers fit within larger corporate strategies on waste reduction, net-zero targets, and closed-loop manufacturing.
Hybrid plasticizer formulations: There’s a growing trend of using hybrid bio-based plasticizers blended with conventional ones to ease the transition in industrial applications.
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 574.25 Million |
| Market Size by 2033 | USD 1,186.76 Million |
| Growth Rate From 2024 to 2033 | CAGR of 8.4% |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Forecast Period | 2024-2033 |
| Segments Covered | Type, Application |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) | Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Country scope | U.S. |
| Key Companies Profiled | Avient Corporation; Cargill, Incorporated; Dow, Inc.;ACS Technical Products; Emery Olechemicals; Valtris Specialty Chemicals; PolyOne Corporation; Vertellus LLC.; Mayriant Corporation. |
One of the strongest drivers in the U.S. bio plasticizers market is the mounting regulatory pressure against traditional phthalate-based plasticizers due to their classification as endocrine disruptors. The U.S. Consumer Product Safety Commission (CPSC) and the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) have introduced regulations limiting the use of several phthalates in consumer goods, toys, medical devices, and food packaging materials.
This shift is not only regulatory-driven but also significantly influenced by consumer demand for non-toxic and eco-friendly products. In sectors like baby products, personal care packaging, and interior furnishings, manufacturers are under increasing pressure to prove that their materials are free from harmful additives. Bio plasticizers, derived from food-grade sources like citrates and soybean oil, offer a compelling alternative, making it easier for companies to comply with regulations while meeting market demands.
Despite the clear environmental and regulatory advantages of bio plasticizers, their cost remains a major restraint. Bio plasticizers, especially those derived from niche feedstocks or complex synthesis routes, tend to be more expensive than their petrochemical-based counterparts. This price premium becomes particularly challenging in cost-sensitive industries such as construction and textiles, where high-volume usage is a factor.
Additionally, bio plasticizers may present variability in performance across different applications. For instance, certain bioplasticizers may not offer the same long-term thermal stability or resistance to extraction under harsh environmental conditions. This raises concerns among end-users regarding long-term performance reliability, especially in outdoor applications or medical-grade materials. Without robust standardization and testing frameworks, some manufacturers remain hesitant to make the full transition.
A transformative opportunity in the U.S. bio plasticizers market lies in their growing integration into sustainable packaging. As major brands commit to recyclable, biodegradable, or compostable packaging solutions, the role of non-toxic plasticizers becomes increasingly crucial. In flexible packaging—used extensively for snacks, cosmetics, and pharmaceuticals—plasticizers are key to ensuring sealability, flexibility, and resilience.
Major packaging players like Amcor, Berry Global, and Sealed Air are investing in bio-based solutions to differentiate their offerings. The use of bio plasticizers like epoxidized soybean oil (ESBO) and citrates in flexible films, shrink wraps, and clamshells allows these companies to align with brand mandates for chemical safety and environmental integrity. Given the size and scale of the U.S. packaging industry, the opportunity for bio plasticizers to carve out significant market share in this space is substantial.
Packaging materials represented the largest application segment in the U.S. bio plasticizers market, driven by the country’s high per capita consumption of packaged goods and a significant push toward sustainable packaging. In flexible PVC packaging such as wraps, films, and clamshells bio plasticizers offer a non-toxic alternative to phthalates without compromising flexibility or durability. ESBO and citrate-based plasticizers are widely used in packaging films for perishables, pharmaceuticals, and even stretchable labels. In an era where eco-labeling and plastic reduction have become marketing differentiators, brand owners are prioritizing bioplasticizer-based solutions to align with consumer values.
Automotive & transport applications are growing rapidly as EV manufacturers and OEMs in the U.S. focus on greener supply chains. Bio plasticizers are being used in seat covers, dashboards, underbody coatings, wire insulation, and sound-deadening panels. Ford and Tesla have both shown interest in integrating plant-based materials into their vehicle interiors, where plasticized polymers are essential. Additionally, U.S. Department of Transportation regulations regarding low VOC emissions from interior materials are steering automakers toward bio-based alternatives. This segment also benefits from the durability and thermal stability offered by newer bio plasticizer formulations, supporting adoption in more structurally demanding roles.
Epoxidized Soybean Oil (ESBO) dominates the U.S. bio plasticizers market due to its widespread availability, cost-effectiveness, and functional versatility. As a by-product of the soybean processing industry, ESBO provides a domestic, renewable feedstock that aligns well with U.S. agricultural strengths. ESBO is extensively used in PVC-based products like flooring, cables, and synthetic leathers. Its dual role as a plasticizer and heat stabilizer has made it a preferred choice in applications demanding durability and low toxicity. Products such as vinyl wall coverings and food-grade containers often feature ESBO to meet FDA safety standards.
.webp)
Citrate-based plasticizers particularly triethyl citrate and acetyl tributyl citrate are among the fastest-growing segments due to their applications in pharmaceuticals, personal care, and food-contact materials. These plasticizers, derived from citric acid (a fermentation product), are non-toxic, biodegradable, and compliant with GRAS (Generally Recognized As Safe) status, making them ideal for sensitive applications. Their usage is growing rapidly in bio-based polymers like PLA (polylactic acid), which are used in compostable trays, lids, and cutlery. As consumer demand for clean-label products continues to rise, citrate plasticizers are gaining favor in cosmetics packaging and hygienic film applications.
The U.S. bio plasticizers market is shaped by a confluence of environmental legislation, consumer demand, industrial capability, and raw material availability. States like California, New York, and Washington have introduced stricter controls on phthalates and other hazardous additives in consumer goods, thus boosting regional demand for safer alternatives like bio plasticizers.
The U.S. also benefits from a strong agricultural sector that supports the production of raw materials like soybean oil, corn, and castor seeds. This localized feedstock availability reduces the carbon footprint of production and ensures supply chain resilience. Moreover, collaborations between universities (e.g., MIT, UC Berkeley) and startups are accelerating the commercialization of innovative bioplastics and their associated plasticizers.
Industrial hubs in the Midwest and Southeast are seeing growing investments in green chemistry and polymer processing facilities. Government programs like the BioPreferred Program and various USDA and DOE grants for biobased materials further support R&D and manufacturing scale-up. These macroeconomic and policy drivers collectively enhance the attractiveness and scalability of bio plasticizers in the U.S. context.
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2033. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the U.S. bio plasticizers market
Type
Application