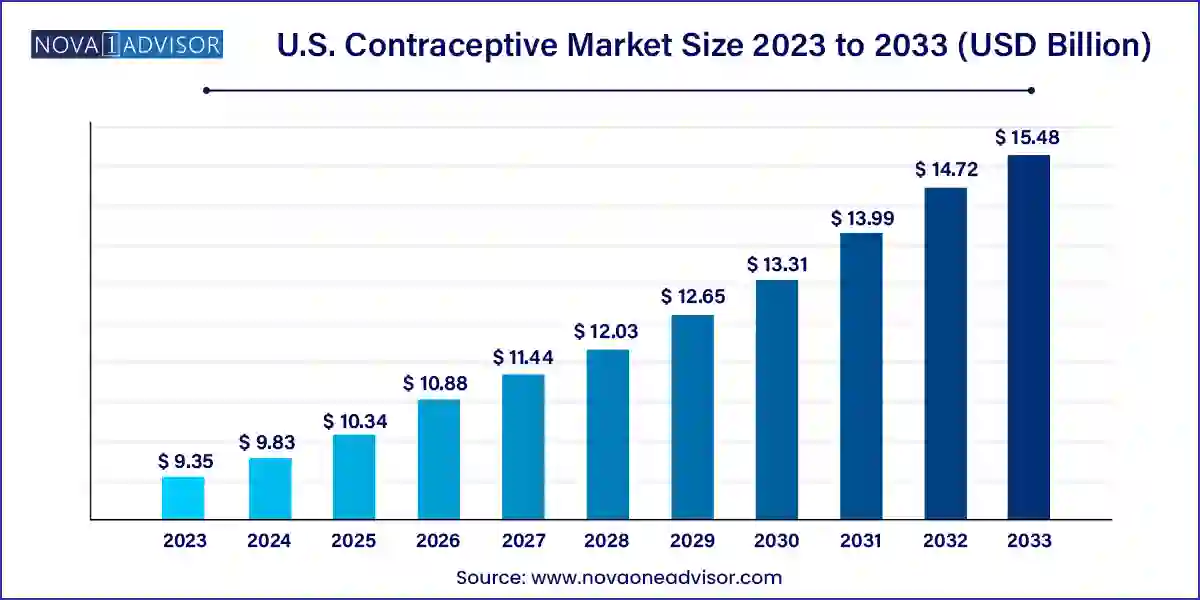
The U.S. contraceptive market size was exhibited at USD 9.35 billion in 2023 and is projected to hit around USD 15.48 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 5.71% during the forecast period 2024 to 2033.
The U.S. contraceptive market is a significant and evolving sector of the broader healthcare and reproductive health landscape. It plays a vital role in empowering individuals, especially women, to exercise control over their reproductive choices. The market comprises a wide array of products including oral contraceptive pills, intrauterine devices (IUDs), condoms, subdermal implants, injectables, vaginal rings, and emerging solutions aimed at improving convenience, efficacy, and accessibility.
As of 2025, the market continues to be shaped by shifting sociopolitical dynamics, technological advancements, changing cultural attitudes towards family planning, and an increasing emphasis on gender-inclusive healthcare. In the U.S., contraception is not merely a private health concern but a matter closely linked to public policy, insurance coverage, women’s rights, and education. The Affordable Care Act (ACA) remains one of the most influential legislative measures affecting the contraceptive landscape by mandating coverage of birth control without copay in most insurance plans.
The U.S. has one of the most diverse contraceptive landscapes globally, reflecting both its heterogeneous population and deeply rooted advocacy for reproductive autonomy. However, it also faces distinct challenges, including disparities in access based on geography, income, race, and insurance status. While states like California and New York offer expansive access and public health initiatives, others have more restrictive policies, especially regarding long-acting reversible contraception (LARC) and emergency contraceptive access.
Evolving consumer preferences, combined with increased public awareness about reproductive rights and a surge in telehealth platforms, are driving innovation and engagement in the market. The rise of digital health startups offering discreet, home-delivered contraceptives and virtual consultations is redefining how individuals interact with contraceptive services, making the sector more dynamic and consumer-driven than ever before.
Growth in long-acting reversible contraceptives (LARCs): Intrauterine devices and subdermal implants are gaining traction for their high efficacy and low maintenance.
Telecontraception expansion: Digital health startups like Nurx and Favor are offering prescription and delivery of birth control pills and emergency contraception through virtual platforms.
Shift towards hormonal IUDs: Hormonal IUDs such as Mirena and Kyleena are being preferred for their additional benefits like reduced menstrual bleeding and cramp relief.
Rising male involvement in contraception: Awareness campaigns are gradually increasing male participation, boosting demand for male condoms and new male contraceptive trials.
Innovation in non-hormonal solutions: Companies are exploring non-hormonal contraceptive options to meet the needs of individuals avoiding synthetic hormones.
Over-the-counter (OTC) accessibility: FDA approval for OTC contraceptive pills like Opill (approved in July 2023) is poised to change the accessibility landscape.
Contraceptive equity legislation: Several states are introducing bills to eliminate barriers to birth control, such as pharmacist-prescribed contraception and multi-month dispensing.
Increased demand among Gen Z: Younger populations are showing preference for privacy-friendly, low-commitment solutions like condoms and rings.
Private sector investment in women’s health tech: Venture capital funding into FemTech, especially focused on contraceptive innovation, has surged in the past three years.
Concerns about reproductive autonomy post-Roe v. Wade overturning: Legal restrictions on abortion in certain states have heightened interest in preventive contraceptive measures.
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 9.83 Billion |
| Market Size by 2033 | USD 15.48 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2024 to 2033 | CAGR of 5.17% |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Forecast Period | 2024-2033 |
| Segments Covered | Product |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) | Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Regional Scope | U.S. |
| Key Companies Profiled | Church & Dwight Co. Inc.; Reckitt Benckiser Group Plc; Veru, Inc.; Organon Group Of Companies; Pfizer, Inc.; Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd.; The Cooper Companies, Inc.; Mayer Laboratories, Inc.; Agile Therapeutics; TherapeuticsmMD, Inc.; Bayer Ag; Afaxys, Inc.; Mithra Pharmaceuticals; Abbvie |
A major driver fueling growth in the U.S. contraceptive market is the increasing demand for long-acting reversible contraceptives (LARCs), particularly IUDs and subdermal implants. LARCs offer significant advantages over short-term methods—they provide high efficacy, extended protection (ranging from 3 to 10 years), and eliminate user error, which is a common issue with pills and condoms. As a result, both healthcare professionals and public health campaigns advocate for their use, especially among young adults and postpartum women.
Programs like the Colorado Family Planning Initiative (CFPI) demonstrated remarkable success by offering free or low-cost LARCs, leading to a significant reduction in unintended pregnancies and abortion rates among teens and low-income women. The rising popularity of hormonal IUDs like Mirena, Skyla, and Liletta highlights consumer interest in methods that double as therapeutic tools for conditions like endometriosis and heavy menstrual bleeding. LARCs are also increasingly preferred in clinical settings for their cost-effectiveness and minimal need for follow-up.
Despite a broad range of contraceptive options, access remains a significant barrier for many Americans due to geographic, socioeconomic, and racial disparities. In rural and underserved communities, there is a documented shortage of clinics that offer a full suite of contraceptive services, particularly LARCs which require specialized insertion and removal by trained professionals. Additionally, lower-income individuals may still face financial obstacles despite ACA mandates, due to lapses in insurance coverage or administrative barriers.
Social stigma, religious beliefs, and misinformation also play a role in suppressing contraceptive usage in certain communities. Some states have implemented policies that allow pharmacists or healthcare institutions to opt out of providing contraception based on religious objections. The lack of comprehensive sex education in several states further exacerbates the problem, leading to lower awareness and understanding of available contraceptive methods. These combined factors hinder the equitable expansion of the market.
A significant growth opportunity for the U.S. contraceptive market lies in the recent regulatory shift allowing certain birth control pills to be sold over the counter. In July 2023, the FDA approved Perrigo’s Opill, making it the first daily oral contraceptive available without a prescription. This landmark decision has the potential to transform access for millions of people, especially those without insurance or those facing barriers to visiting a healthcare provider.
OTC availability of pills is expected to boost sales volumes, improve adherence, and address gaps in access among youth, underserved populations, and rural residents. The market is likely to see the emergence of new players focused on branding, affordability, and distribution. Moreover, retail pharmacies and e-commerce platforms stand to gain from the shift, potentially forming partnerships with pharmaceutical companies to promote accessibility. This move is anticipated to not only expand the user base but also normalize contraceptive use through visibility and convenience.
Oral contraceptive pills remain the most widely used contraceptive product in the U.S., primarily due to their long-standing familiarity, ease of use, and effectiveness when taken consistently. Pills are especially popular among women in their 20s and 30s, with many beginning usage in their late teens. Their relatively low cost and availability via telehealth services have reinforced their market dominance. Moreover, the emergence of combination pills with fewer side effects and the availability of pills with added therapeutic benefits (e.g., acne management or PMS relief) further elevate their appeal.
However, the fastest-growing category within pills is over-the-counter oral contraceptives, a market segment that is in its nascent stage but holds immense potential. The recent approval of Opill has paved the way for more brands to follow suit, potentially triggering a shift from prescription-based access to retail-focused models. Retail chains such as Walgreens, CVS, and Walmart are likely to expand shelf space for OTC pills, while online platforms may compete with delivery and subscription-based models to increase market penetration.
Among intrauterine devices, hormonal IUDs dominate the market due to their dual benefits of contraception and therapeutic relief. These devices, including Mirena and Kyleena, release small doses of progestin, which thicken cervical mucus and suppress ovulation. Their efficacy rate exceeds 99%, and they offer additional health benefits such as reducing menstrual cramps and regulating bleeding an added advantage for users dealing with heavy periods or endometriosis.
Conversely, nonhormonal IUDs, such as Paragard, are gaining traction among hormone-averse consumers. These devices rely on copper to create a spermicidal environment and offer long-term protection without altering natural hormone levels. With increasing awareness about hormone-free health solutions, the nonhormonal IUD segment is expected to grow rapidly, especially among individuals with contraindications to hormonal contraceptives or preferences for natural options.
Male condoms hold the largest share within the condom segment due to their widespread availability, affordability, and dual protection against pregnancy and sexually transmitted infections (STIs). They are particularly popular among young adults and casual partners, as they require no prescription and are easy to use. The presence of well-known brands like Trojan, Durex, and LifeStyles ensures strong market visibility, while new variants such as ultra-thin, textured, and flavored condoms continue to attract consumer interest.
Female condoms, although historically underutilized, are now one of the fastest-growing subsegments. Increased education and advocacy for female-controlled contraception have driven growth. Public health programs in underserved communities and investments in improved product design (e.g., the FC2 Female Condom) are enhancing user experience and acceptance. Furthermore, they provide a discreet option for women in environments where male participation in contraception may be limited or culturally discouraged.
Subdermal implants such as Nexplanon are gaining steady adoption for their efficacy and long-term reliability (up to 3 years). These are especially favored by women seeking a "set-and-forget" solution. Healthcare providers often recommend implants to adolescents and postpartum women. Despite requiring minor surgical procedures for insertion and removal, their convenience and effectiveness are driving their popularity, particularly within the LARC category.
Vaginal rings like NuvaRing and Annovera are gaining popularity due to their user-controlled mechanism and lower systemic hormone exposure compared to pills. Rings are discreet, require monthly or yearly replacement depending on the brand, and appeal to users seeking alternatives to daily regimens. This product category is seeing increasing adoption among urban, college-educated demographics who are comfortable with inserting and managing devices themselves.
Injectables like Depo-Provera remain a crucial contraceptive option for individuals seeking mid-range, reversible contraception that does not require daily adherence. With a dosing interval of once every three months, injectables strike a balance between convenience and medical oversight. They are especially popular in clinics serving low-income and minority populations due to subsidy programs and public health campaigns.
Growth in this segment is further supported by school-based health centers and mobile clinics, particularly in states with strong reproductive health programs. While concerns about delayed fertility return and bone density remain, improvements in formulation and counseling have alleviated some user hesitance.
The U.S. contraceptive market reflects a patchwork of state policies, insurance models, and public health initiatives that influence access and utilization. States like California, New York, Oregon, and Massachusetts lead in contraceptive access due to proactive legislation supporting pharmacist-prescribed contraception, expanded Medicaid coverage, and public education campaigns. In contrast, states with more conservative governance structures may restrict funding or impose additional requirements for contraception access.
Urban centers tend to see higher adoption of newer and premium contraceptive products, while rural areas often rely on federally qualified health centers (FQHCs) and Title X clinics. Telehealth platforms are bridging some of these divides by offering discreet consultations and delivery services nationwide. Moreover, the post-Roe environment has led many residents in restrictive states to stock up on emergency contraception and long-term methods, highlighting how judicial and political shifts continue to affect the contraceptive landscape in the U.S.
July 2023: The U.S. FDA approved Opill, the first over-the-counter birth control pill, marking a significant milestone in reproductive health access.
October 2023: Nurx launched a partnership with Uber Health to offer same-day delivery of emergency contraception in select cities.
January 2024: Bayer AG announced a $100 million investment in its Missouri facility to expand production of Mirena and Kyleena IUDs for the North American market.
March 2024: Twentyeight Health, a telecontraception startup, secured Series B funding to expand into underserved states with limited brick-and-mortar clinics.
February 2025: Perrigo began mass retail distribution of Opill, including placement in major pharmacy chains and e-commerce platforms.
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2033. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the U.S. contraceptive market
Product