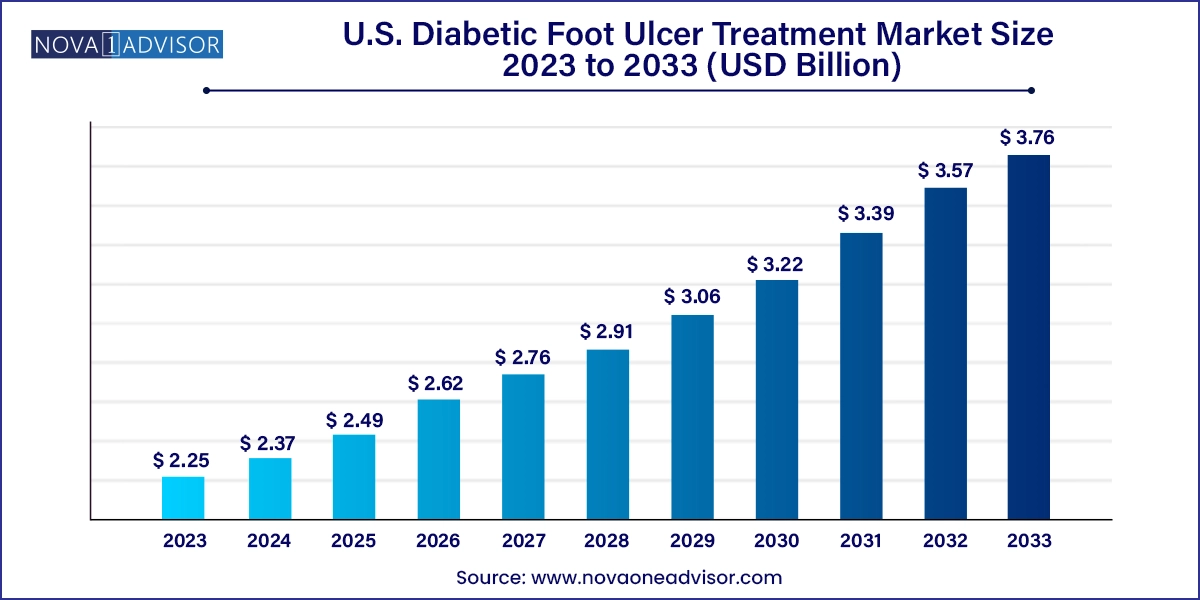
The U.S. diabetic foot ulcer treatment market size was exhibited at USD 2.25 billion in 2023 and is projected to hit around USD 3.76 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 5.27% during the forecast period 2024 to 2033.
The U.S. Diabetic Foot Ulcer (DFU) Treatment Market has become a critical segment of the broader wound care and diabetic healthcare ecosystem. With diabetes continuing to pose a substantial public health burden across the United States, complications such as diabetic foot ulcers remain prevalent and challenging. Diabetic foot ulcers are open sores or wounds that typically occur on the bottom of the foot in diabetic patients. Due to poor glycemic control, neuropathy, and peripheral arterial disease, many patients are prone to chronic wounds that do not heal easily and carry the risk of severe infections and amputations.
An estimated 15% of diabetic patients in the U.S. are expected to develop foot ulcers during their lifetime, and approximately 14–24% of those cases may result in lower limb amputation. As a result, the demand for advanced, multidisciplinary approaches to treatment continues to rise. Hospitals, ambulatory surgical centers, and specialized wound care clinics play a crucial role in managing these patients using a combination of wound dressings, biologics, antibiotic medications, and therapy devices.
What differentiates the U.S. DFU treatment market is its strong infrastructure for innovation, clinical trials, and reimbursement support. The country has been at the forefront of introducing novel biologics, regenerative therapies, and negative pressure wound therapy (NPWT) systems. Public awareness campaigns, early screening protocols, and insurance coverage under Medicare and Medicaid further stimulate market demand and enable broader access to treatment.
Moreover, the market is being driven by an aging population, increasing obesity rates, and lifestyle-related diabetes, particularly among younger demographics. The multidisciplinary nature of DFU treatment, involving endocrinologists, podiatrists, surgeons, and wound care specialists, reinforces the demand for coordinated care solutions. As technologies evolve and patient expectations grow, the U.S. DFU treatment market is poised for significant transformation and sustained growth.
Rise of Biologics in Chronic Wound Management: Skin substitutes and growth factors are gaining traction for their regenerative properties and ability to accelerate healing in complex ulcers.
Adoption of Negative Pressure Wound Therapy (NPWT): NPWT systems are becoming standard care in hospital and home settings, improving wound drainage and promoting granulation.
Expansion of Outpatient and Home-Based Treatment Models: With rising healthcare costs, care is shifting toward ambulatory surgical centers and homecare using portable wound management systems.
Increasing Integration of AI and Remote Monitoring: Digital platforms that track wound progression using AI-enhanced imaging and wearable devices are emerging.
Focus on Personalized and Precision Wound Care: Tailored treatment plans based on ulcer etiology, patient profile, and microbiology are replacing one-size-fits-all approaches.
Growth in Multidisciplinary Wound Care Centers: Comprehensive wound care centers offering podiatry, vascular surgery, endocrinology, and dermatology under one roof are expanding.
Public-Private Partnerships for Diabetic Care Awareness: Government and private sectors are increasingly collaborating to promote early detection, education, and foot screening.
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 2.37 Billion |
| Market Size by 2033 | USD 3.76 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2024 to 2033 | CAGR of 5.27% |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Forecast Period | 2024-2033 |
| Segments Covered | Treatment, Ulcer Type, End-use |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) | Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Country scope | U.S. |
| Key Companies Profiled | ConvaTec Group Plc; 3M Health Care; Coloplast Corp.; Smith & Nephew Plc.; B Braun Melsungen AG; Medline Industries, LP; Molnlycke Health Care AB; Medtronic Plc |
The increasing prevalence of diabetes and obesity in the United States is the most significant driver propelling the DFU treatment market. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), over 37 million Americans have diabetes, and approximately 96 million are prediabetic. Obesity, a key risk factor for type 2 diabetes, continues to affect over 40% of adults in the country. These conditions directly contribute to the development of diabetic neuropathy, peripheral vascular disease, and consequently, foot ulcers.
Furthermore, as the population ages, age-related physiological changes exacerbate the risk of ulcer formation and poor healing. Diabetic foot ulcers lead to frequent hospitalizations, increased healthcare spending, and a marked decrease in quality of life. In response, healthcare providers are increasingly implementing preventative foot care programs, early intervention protocols, and sophisticated wound care strategies thus driving steady demand for DFU treatment products and services.
A key restraint in the U.S. DFU treatment market is the high cost associated with advanced wound care therapies, including biologics, NPWT systems, and combination treatment plans. Biologics, such as growth factors and skin grafts, often come with a premium price due to complex manufacturing and regulatory hurdles. While these solutions can reduce healing time and prevent complications, their high upfront costs can be a barrier for providers and patients, especially where reimbursement coverage is limited.
Smaller clinics, uninsured populations, and those with high deductibles may face difficulty accessing the most effective DFU treatments. Although insurance systems like Medicare cover certain therapies, inconsistencies in coverage and pre-authorization requirements can delay care. The cost disparity between traditional wound dressings and advanced therapies remains a challenge in achieving universal access and optimizing patient outcomes.
The rapid expansion of home-based wound care and telemedicine platforms presents a significant opportunity for the U.S. DFU treatment market. Amid healthcare system strains and the push toward value-based care, homecare has emerged as a cost-effective and patient-friendly solution for managing chronic wounds, including diabetic foot ulcers. Portable NPWT devices, remote wound monitoring software, and at-home dressing kits are enabling high-quality treatment beyond the hospital setting.
Telewound services are also gaining popularity, especially among elderly patients or those in rural areas. These platforms allow clinicians to remotely assess wound healing progress using images and digital wound measurement tools. In combination with mobile nursing services, these technologies can reduce hospital readmissions, improve patient adherence, and lower overall treatment costs. As reimbursement models increasingly support homecare delivery, companies offering smart wound devices and virtual care platforms are well-positioned for growth.
Wound care dressings dominate the DFU treatment segment, being the frontline modality for managing ulcers of varying severity. Foam dressings, hydrofiber, alginates, and hydrocolloids are extensively used for moisture balance, exudate control, and wound protection. Surgical dressings and hydrogels are often employed post-debridement or surgical intervention. Foam and hydrocolloid dressings, in particular, are favored for their ability to absorb exudate while promoting a moist healing environment.
However, biologics are the fastest-growing treatment segment, driven by their efficacy in managing complex and chronic ulcers. Products such as growth factors (e.g., recombinant human platelet-derived growth factor) and bioengineered skin substitutes have demonstrated promising results in difficult-to-heal wounds. Biologics are being increasingly adopted in tertiary care and wound care centers, often as adjuncts to standard dressing protocols. The growth in clinical evidence, FDA approvals, and inclusion in clinical guidelines further supports their rapid adoption.
Neuropathic ulcers are the most prevalent and therefore dominate the ulcer type segment in the U.S. These ulcers arise due to peripheral nerve damage, common in long-standing diabetics, resulting in loss of sensation in the feet. Because patients cannot feel pain, injuries go unnoticed and progress to open wounds. Neuropathic ulcers are typically located on weight-bearing areas like the heel or ball of the foot and are often managed using offloading devices, wound dressings, and debridement.
Neuro-ischemic ulcers are the fastest-growing category, reflecting a rise in patients with mixed pathology—those who have both neuropathy and ischemia. These ulcers are more complex to treat due to compromised blood flow and nerve damage. Advanced therapies, including biologics, NPWT, and vascular interventions, are often required. As the diabetic population ages and cardiovascular comorbidities rise, the incidence of neuro-ischemic ulcers is expected to increase, boosting demand for multidisciplinary and advanced care solutions.
Hospitals represent the largest end-use segment, as many DFU cases require surgical debridement, infection control, or inpatient management. Hospitals also have the infrastructure to offer integrated care through multidisciplinary wound teams, vascular surgeons, endocrinologists, and infectious disease specialists. They are typically the first point of contact for patients with severe or infected ulcers and play a central role in initiating long-term care plans.
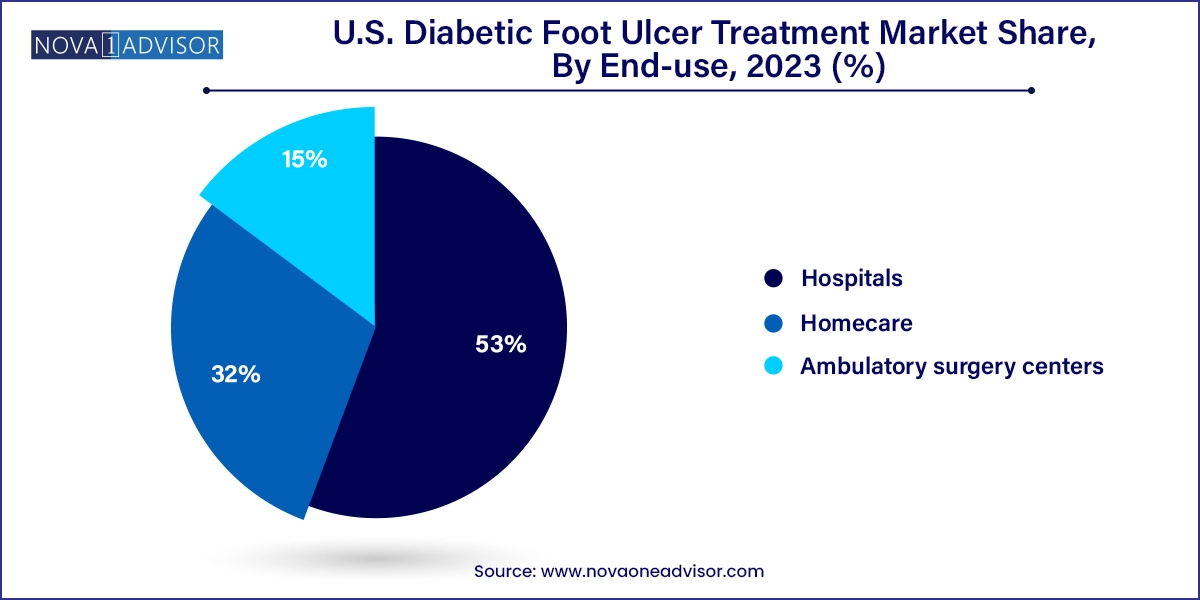
Homecare is the fastest-growing end-use setting, supported by the increasing deployment of mobile wound care services, visiting nurses, and portable NPWT devices. Many diabetic patients require long-term wound management and prefer to be treated in the comfort of their homes. As digital health tools and remote monitoring technologies improve, homecare services are gaining traction for stable DFU cases and follow-up wound care. This shift also aligns with payer preferences for cost-effective care pathways and reduced hospital readmissions.
In the United States, the diabetic foot ulcer treatment landscape is shaped by a highly developed healthcare system, active reimbursement support, and access to innovative therapies. Leading hospitals and wound care centers in states like California, Texas, Florida, and New York offer comprehensive DFU management, including hyperbaric oxygen therapy, skin substitutes, and limb salvage surgeries.
Medicare, Medicaid, and private insurers provide partial or full coverage for advanced treatments, though coverage may vary by state and provider. The U.S. also boasts a robust ecosystem of clinical research and medical device innovation, fostering continuous improvement in wound care technologies. National organizations such as the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the Wound Healing Society actively promote guidelines and continuing education programs for clinicians.
Furthermore, the U.S. government has increased funding for diabetes awareness and prevention, which indirectly supports DFU management by promoting early diagnosis and foot screening programs. Retail pharmacy chains, urgent care centers, and home health agencies are also entering the wound care space, improving accessibility across diverse demographics.
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2033. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the U.S. diabetic foot ulcer treatment market
Treatment
Ulcer Type
End-use