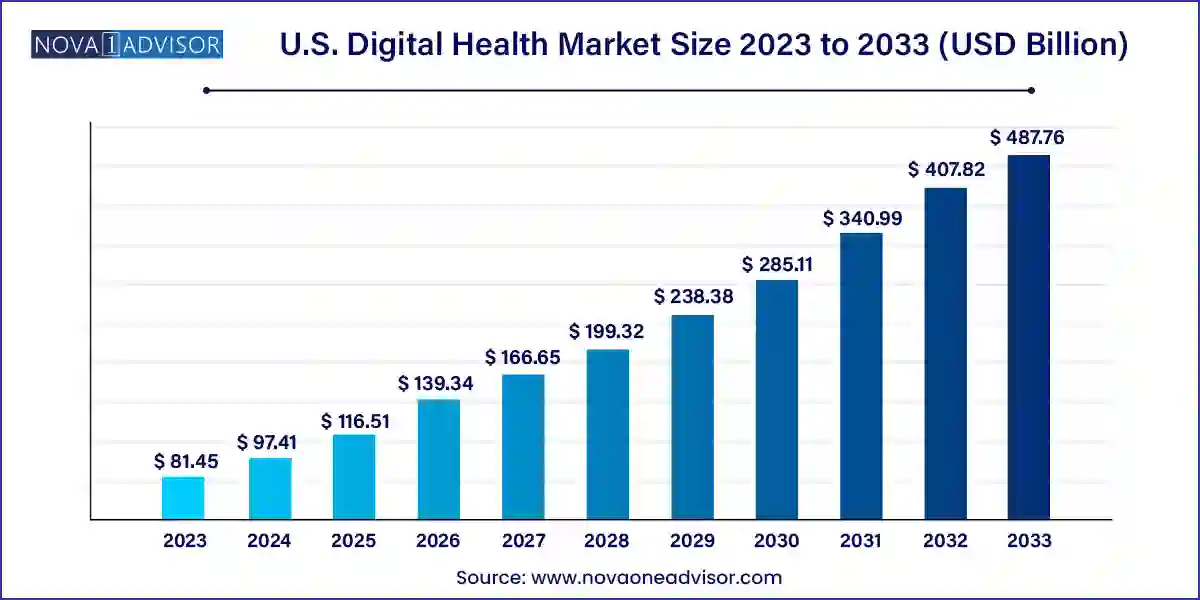
The U.S. digital health market size was exhibited at USD 81.45 billion in 2023 and is projected to hit around USD 487.76 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 19.6% during the forecast period 2024 to 2033.
The U.S. digital health market is experiencing an unprecedented transformation, driven by a confluence of technology innovation, shifting healthcare policies, increasing chronic disease burdens, and rising consumer engagement. At its core, digital health encompasses the use of information and communication technologies (ICT) to deliver healthcare services, manage diseases, improve patient outcomes, and optimize health system efficiency. From telehealth consultations to wearable health monitors, and AI-powered diagnostic tools to digital health records, the U.S. is at the forefront of a healthcare revolution that emphasizes accessibility, personalization, and value-based care.
The COVID-19 pandemic acted as a pivotal catalyst, dramatically accelerating the adoption of digital health tools across hospitals, clinics, and households. Lockdowns and fear of viral transmission forced providers to rethink traditional models and prompted regulators to ease restrictions on telemedicine. This environment fostered rapid innovations and investments in digital platforms, mobile health apps, AI diagnostics, and remote patient monitoring systems. In 2021 alone, digital health startups in the U.S. secured over $29 billion in venture capital funding an indication of market confidence in the sector's long-term viability.
Today, stakeholders from across the healthcare ecosystem patients, providers, payers, tech companies, and government bodies—are investing in digital solutions to improve outcomes, contain costs, and enhance patient satisfaction. The convergence of big data analytics, cloud computing, 5G networks, and Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) is enabling real-time decision-making, remote treatment, and predictive care strategies. As interoperability standards improve and AI-powered tools mature, the U.S. digital health market is poised to redefine the future of healthcare delivery.
Telehealth Mainstreaming: Virtual consultations are becoming an integral part of primary care and specialty services, supported by favorable reimbursement policies and patient convenience.
Integration of AI and Machine Learning: Clinical decision support, image diagnostics, and personalized treatment recommendations are being enhanced through AI algorithms.
Wearables as Preventive Health Tools: Fitness trackers, heart rate monitors, and sleep sensors are evolving from lifestyle accessories into medical-grade diagnostic tools.
Digital Therapeutics (DTx) Emergence: Evidence-based software interventions are gaining FDA approval for managing chronic conditions like diabetes and depression.
Expansion of Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM): Medicare’s inclusion of RPM services and the proliferation of connected devices are boosting home-based care.
Growth in Mental Health Apps: The U.S. is witnessing a surge in demand for mental wellness platforms, offering therapy, meditation, and self-care tools via apps.
Healthcare Consumerism: Patients are increasingly acting as healthcare consumers, demanding transparency, convenience, and control over their medical data.
Cybersecurity Focus: With data breaches on the rise, healthcare institutions are investing heavily in securing digital infrastructures and patient information.
Rise of Digital Biomarkers: Passive data from wearables and smartphones is being analyzed to detect early disease signals and monitor treatment response.
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 97.41 Billion |
| Market Size by 2033 | USD 487.76 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2024 to 2033 | CAGR of 19.6% |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Forecast Period | 2024-2033 |
| Segments Covered | Technology, Component, Application, End-use |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) | Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Regional Scope | U.S. |
| Key Companies Profiled | Apple Inc.; AT&T; Airstrip Technologies; Allscripts; Google Inc.; Orange; Qualcomm Technologies, Inc.; Softserve; MQure; Samsung Electronics Co. Ltd.; Telefonica S.A.; Vodafone Group; Cerner Corp.; McKesson Corp.; Epic Systems Corp.; NextGen Healthcare, Inc; Greenway Health LLC; CureMD Healthcare; HIMS; Computer Programs and Systems, Inc; Vocera Communications; IBM Corp.; Siemens Healthcare GmbH; Cisco Systems, Inc. |
One of the most compelling drivers propelling the U.S. digital health market is the rising incidence of chronic diseases, coupled with an aging population. According to the CDC, six in ten Americans live with at least one chronic condition, such as heart disease, cancer, diabetes, or respiratory illness. Managing these diseases requires continuous monitoring, regular follow-ups, medication adherence, and lifestyle modifications needs that digital health platforms are uniquely positioned to meet.
For instance, diabetes patients can now use continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) linked to mobile apps, enabling real-time blood sugar tracking and remote adjustments by healthcare providers. Similarly, cardiac patients are using wearable ECG patches that detect arrhythmias and send alerts to care teams. These solutions not only enhance patient safety but also reduce hospital readmissions and enable proactive interventions. With the U.S. population over 65 expected to reach 80 million by 2040, digital health tools will become indispensable in delivering cost-effective, high-quality care to the elderly while alleviating the strain on healthcare infrastructure.
While digital health solutions offer immense potential, their effectiveness is often constrained by poor interoperability and fragmented data systems. Many digital tools operate in silos, lacking the ability to share data seamlessly with other platforms, electronic health records (EHRs), or provider networks. This leads to duplication, data loss, and inefficiencies in care coordination. For example, a remote monitoring device might collect vital signs but fail to synchronize with the patient’s EHR, making it invisible to treating physicians.
Furthermore, different vendors use varied data standards, architectures, and APIs, complicating integration efforts. The absence of uniform policies around health data sharing adds to the problem, leaving patients with incomplete health records spread across multiple apps and providers. Although initiatives like HL7 FHIR (Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources) are gaining traction, widespread adoption remains a work in progress. Without robust interoperability, the full value of digital health investments may remain unrealized.
An exciting opportunity within the U.S. digital health market lies in leveraging big data analytics for personalized and predictive healthcare. With millions of patients generating vast volumes of health-related data through wearables, apps, clinical records, and genomics, healthcare providers now have unprecedented insights into individual and population health. By applying machine learning models to this data, clinicians can predict disease onset, tailor treatments to genetic profiles, and identify at-risk patients before symptoms emerge.
For instance, startups are developing predictive analytics platforms that flag early signs of sepsis, heart failure, or diabetic complications using EHR data. Personalized cancer care is also becoming a reality, with genomic sequencing and real-world evidence guiding treatment decisions. Pharmaceutical companies are employing AI-driven platforms to monitor patient adherence and optimize clinical trial recruitment. As regulatory frameworks evolve and data privacy safeguards strengthen, big data promises to transform reactive care into proactive, customized health management.
Telehealth dominated the U.S. digital health market by technology, particularly through video consultations and remote medication management. The pandemic-induced boom in virtual care solidified telehealth as a primary mode of care delivery. Tele-consultations enabled patients to access specialists without geographic barriers, improving outcomes and reducing costs. Remote medication management solutions allowed providers to track adherence, renew prescriptions, and send reminders. Activity monitoring and LTC (long-term care) solutions helped caregivers remotely oversee elderly or chronic patients. According to surveys, over 70% of patients who tried telehealth during the pandemic are willing to continue using it as part of routine care.
mHealth is the fastest-growing technology segment, driven by the proliferation of smartphones, smartwatches, and mobile apps. This category includes wearables like Fitbit, Apple Watch, and Whoop that monitor vital signs, sleep, and fitness metrics. Chronic disease management apps ranging from diabetes to mental health are enabling patients to self-monitor and engage with care providers digitally. Notably, mental health apps have surged in popularity, offering AI-driven therapy, guided meditations, and community support. mHealth’s appeal lies in its convenience, affordability, and potential to deliver personalized care on demand.
Services dominated the digital health market in terms of component share, fueled by the rising demand for remote monitoring and diagnosis services. These include chronic disease management, independent aging solutions, and post-acute care services. Providers offer subscription-based or reimbursement-supported services that ensure continuity of care. Diagnosis services such as tele-radiology and AI-based image interpretation are also scaling rapidly. Services offer a human interface to technology, ensuring that digital tools translate into real-world outcomes.
Software is witnessing the fastest growth, particularly in areas like EHR, mHealth apps, and healthcare analytics. With cloud computing and SaaS models, hospitals and clinics are rapidly adopting digital health platforms to streamline workflows, ensure regulatory compliance, and improve patient engagement. Health analytics tools are enabling population-level insights and performance benchmarking, crucial for accountable care organizations (ACOs) and Medicare Advantage plans.
Cardiovascular diseases held the largest application share, given the high mortality and monitoring needs associated with cardiac conditions. Remote ECG monitoring, blood pressure apps, and heart rate trackers are helping patients and physicians manage risks more effectively. Many cardiac rehab programs have shifted to digital formats, improving accessibility and adherence.
Diabetes is the fastest-growing application, largely due to the advancement of CGMs, insulin management apps, and connected glucometers. These tools empower patients with real-time data and allow providers to make timely adjustments. In 2024, companies like Dexcom and Abbott launched integrated diabetes management ecosystems combining devices, apps, and clinician portals, signaling the evolution of end-to-end digital care for diabetes.
Providers dominated the digital health market end-use segment, as hospitals, health systems, and physician networks are the primary users of telehealth, EHR, and analytics tools. Clinical decision-making, remote diagnosis, and patient engagement tools are being adopted to improve efficiency, comply with CMS guidelines, and reduce readmissions.
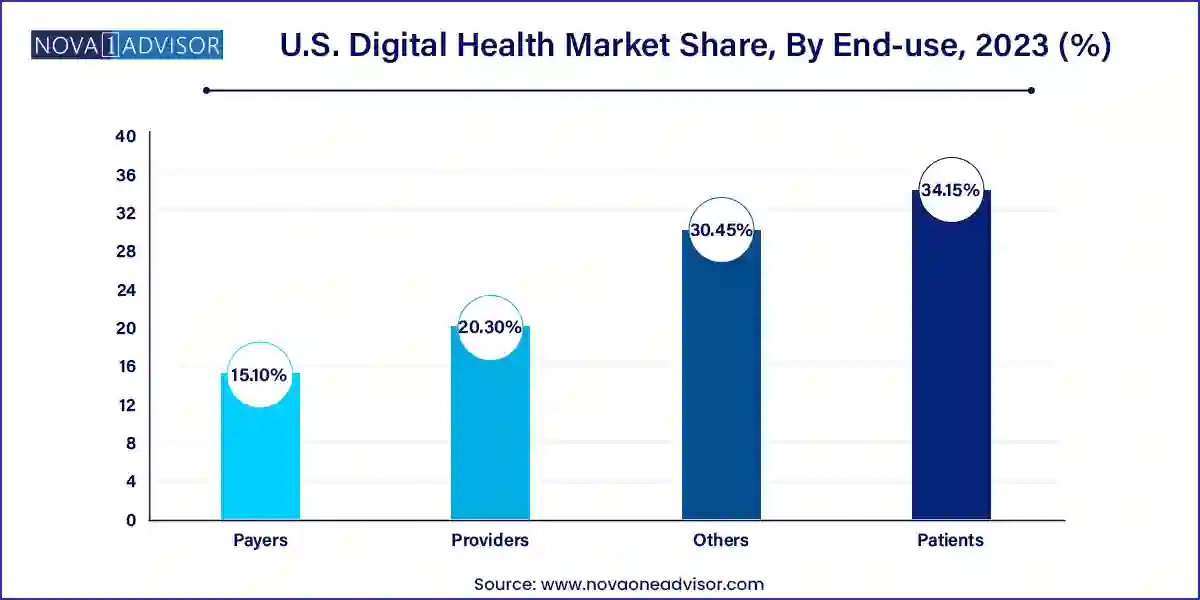
Patients represent the fastest-growing user group, as health consumerism accelerates. Individuals are increasingly using fitness apps, personal health records, sleep trackers, and mental wellness apps to manage their health proactively. Direct-to-consumer platforms are bypassing traditional healthcare intermediaries, offering on-demand consultations, genetic testing, and medication delivery.
The United States has emerged as the global leader in digital health adoption, innovation, and investment. Federal policies such as the 21st Century Cures Act, CMS telehealth reimbursement, and the Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health (HITECH) Act have laid a strong foundation for digital transformation. Private sector innovation, supported by venture capital and public-private partnerships, continues to drive growth across all segments.
States like California, New York, and Texas are implementing telehealth parity laws, fostering reimbursement equity and expanding care access. Medicaid and Medicare Advantage plans now support digital interventions, from RPM to chronic care apps. National interoperability initiatives like TEFCA (Trusted Exchange Framework and Common Agreement) aim to unify disparate health data systems. The U.S. is also home to a vibrant digital health startup ecosystem, with hubs in Silicon Valley, Boston, and Chicago producing cutting-edge solutions.
March 2025 – Teladoc Health launched a new AI-powered virtual primary care platform designed for health systems, integrating chronic care, mental health, and general consultations.
January 2025 – Apple expanded its HealthKit ecosystem with sleep apnea monitoring and fertility planning features, enhancing its footprint in women’s health and diagnostics.
December 2024 – Google Health introduced a generative AI tool for clinical documentation, aiming to reduce EHR burden and improve physician satisfaction.
November 2024 – Epic Systems and Microsoft Azure deepened their partnership to expand cloud-based EHR access across U.S. hospitals, improving scalability and security.
October 2024 – Fitbit (Google-owned) announced a clinical-grade version of its wearable with FDA-cleared ECG and atrial fibrillation detection.
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2033. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the U.S. digital health market
Technology
Component
Application
End-use