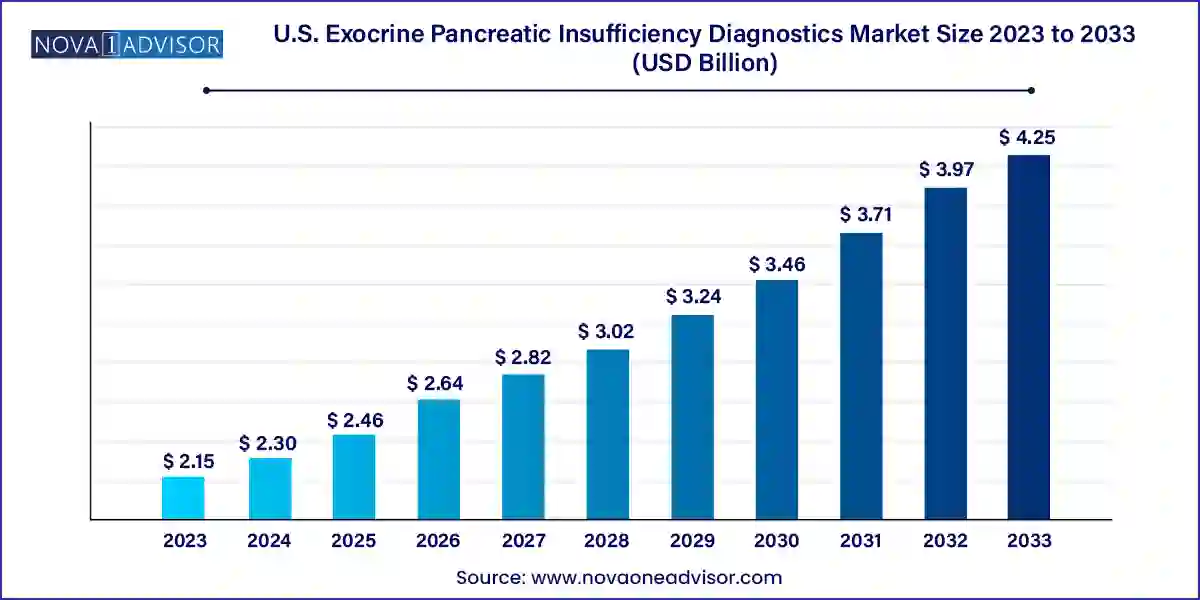
The U.S. exocrine pancreatic insufficiency diagnostics market size was exhibited at USD 2.15 billion in 2023 and is projected to hit around USD 4.25 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 7.05% during the forecast period 2024 to 2033.
Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency (EPI) is a clinical condition characterized by the pancreas’s inability to produce sufficient digestive enzymes, impairing the proper digestion and absorption of nutrients. The condition is often a consequence of chronic pancreatitis, cystic fibrosis, pancreatic cancer, or surgical resection of the pancreas. Given the rising prevalence of such underlying conditions, the diagnostic need for EPI is becoming increasingly significant across the United States.
In the U.S., the EPI diagnostics market has gained momentum due to a shift towards early disease identification, rising awareness about pancreatic disorders, and advancements in diagnostic technologies. The aging population, lifestyle factors contributing to gastrointestinal and metabolic diseases, and an increase in genetic disorders like cystic fibrosis contribute to a higher incidence of EPI. This surge is prompting healthcare systems to integrate more precise and non-invasive diagnostic approaches.
Moreover, the healthcare industry’s growing inclination toward value-based care, with an emphasis on early detection and prevention, is enhancing the importance of diagnostic tools. EPI, being a condition with symptoms that mimic other gastrointestinal diseases such as IBS or celiac disease, often goes undiagnosed or misdiagnosed. Thus, the push for more specific, sensitive, and rapid diagnostic tests is strong.
The U.S. EPI diagnostics market is being bolstered by both public and private sector efforts. Government agencies like the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK) are supporting research and public health campaigns. Concurrently, companies are investing in innovative diagnostics, from biomarker testing to advanced imaging technologies, to gain competitive advantage and market share.
As of 2025, the U.S. EPI diagnostics market continues to evolve with emerging technologies, integrated diagnostics platforms, and point-of-care testing strategies. This growth trajectory is expected to sustain well into the next decade as early detection and personalized medicine become central to gastrointestinal healthcare.
Integration of AI in Imaging Diagnostics: Advanced AI-powered tools are increasingly used to enhance the accuracy of imaging diagnostics like MRI and CT scans for pancreatic abnormalities.
Growing Use of Non-invasive Stool-Based Tests: Fecal elastase testing is becoming more common due to its ease of use, patient compliance, and accurate diagnostic capability.
Rise in Home Sample Collection Services: Many diagnostic companies are offering home testing kits and sample pickup services, increasing accessibility and convenience for patients.
Collaborative Research and Academic Partnerships: Institutions like Johns Hopkins University and Mayo Clinic are partnering with diagnostics companies to develop novel assays and validate pancreatic function biomarkers.
Adoption of Multiplex Testing Platforms: Platforms that simultaneously detect multiple biomarkers are gaining traction, helping distinguish EPI from other gastrointestinal diseases.
Increased Focus on Pediatric EPI Diagnosis: There’s growing awareness of EPI in children with cystic fibrosis, prompting innovations in pediatric diagnostic methods.
Telemedicine Integration in GI Diagnostics: Diagnostic consultations and test result interpretations via telemedicine are becoming mainstream post-COVID, including for EPI evaluations.
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 2.30 Billion |
| Market Size by 2033 | USD 4.25 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2024 to 2033 | CAGR of 7.05% |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Forecast Period | 2024-2033 |
| Segments Covered | Diagnostic Method, End-use |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) | Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Regional Scope | U.S. |
| Key Companies Profiled | ChiRhoClin; Certest Biotec; ScheBo Biotech AG; Immundiagnostik AG; Laboratory Corporation of America Holdings; Boster Biological Technology; ALPCO Diagnostics; Quest Diagnostics Incorporated; DiaSorin S.p.A.; ARUP Laboratories; Alpha Laboratories; Verisana Laboratories |
A critical driver for the U.S. EPI diagnostics market is the increasing prevalence of underlying conditions such as chronic pancreatitis and cystic fibrosis. Chronic pancreatitis, often caused by alcohol abuse, autoimmune diseases, or genetic mutations, leads to progressive pancreatic damage, significantly elevating the risk of EPI. Additionally, cystic fibrosis a genetic disorder impacting over 30,000 individuals in the U.S. almost invariably results in EPI due to obstructed pancreatic enzyme flow.
These chronic conditions are being increasingly diagnosed owing to better awareness and enhanced healthcare access. As treatment guidelines recommend routine EPI screening for such patients, the demand for effective diagnostics is on the rise. Diagnostic laboratories, hospitals, and specialists are incorporating EPI testing as a routine protocol in managing such diseases, thereby fueling market expansion.
One significant restraint in the market is the overlapping symptomology of EPI with other gastrointestinal disorders such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), celiac disease, and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Diarrhea, weight loss, bloating, and malnutrition hallmarks of EPI are not exclusive to the condition, often leading to misdiagnosis or delayed diagnosis.
This diagnostic ambiguity results in either excessive or unnecessary testing, complicating the patient pathway and increasing healthcare costs. It also undermines the trust in current diagnostics, especially when test results are not definitive. Additionally, the lack of widespread physician awareness regarding updated diagnostic protocols contributes to underutilization of dedicated EPI testing platforms, limiting market growth.
The development and commercialization of novel biomarker-based tests represent a strong opportunity within the U.S. EPI diagnostics market. Emerging research highlights that specific biomarkers in blood or stool can accurately reflect early pancreatic dysfunction before full-blown EPI sets in. These tests can offer higher sensitivity, particularly in detecting early-stage enzyme deficiency or mild-to-moderate EPI cases.
Companies and academic centers are investing in R&D to identify panels of biomarkers that could allow for rapid, point-of-care diagnostics. For example, measuring serum levels of trypsinogen or stool-based microRNAs is showing promise. If clinically validated, such tests could revolutionize screening protocols, allowing earlier intervention, reducing disease burden, and improving quality of life for at-risk populations such as those with diabetes or pancreatic resection.
Laboratory tests dominated the U.S. EPI diagnostics market, due to their wide adoption, cost-effectiveness, and relative ease of implementation in clinical workflows. Stool elastase tests are particularly prevalent because they are non-invasive and provide a reliable measure of pancreatic enzyme output. These tests are frequently used in hospital and outpatient settings to assess enzyme deficiency in patients presenting with chronic gastrointestinal symptoms. Additionally, blood tests that measure fat-soluble vitamin levels or specific enzyme markers continue to play a supporting role in comprehensive diagnostic workups. Laboratories are increasingly integrating automated systems to reduce turnaround time, enhancing their appeal.
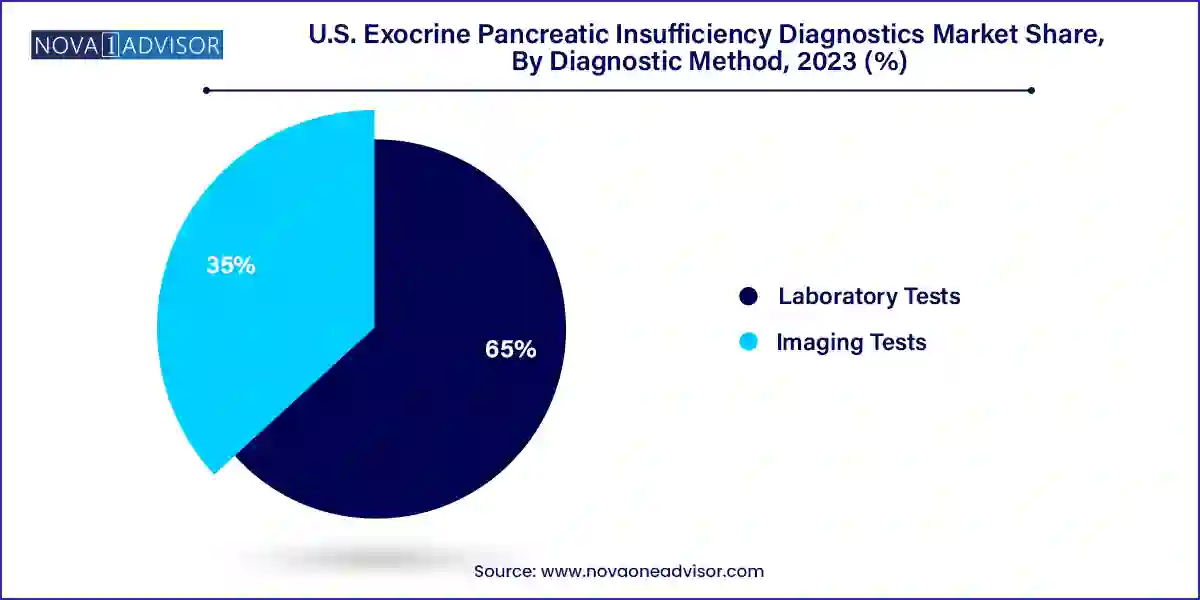
The fastest-growing segment, however, is imaging tests, particularly CT scans and MRI. These modalities are gaining traction for their ability to provide anatomical insights into pancreatic abnormalities that may underlie EPI. CT imaging is particularly valuable in identifying structural damage due to chronic pancreatitis or pancreatic tumors. Meanwhile, endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) for pancreatic function tests is emerging as a highly accurate albeit specialized diagnostic method. As the integration of AI and 3D imaging continues to enhance resolution and diagnostic precision, imaging tests are expected to witness robust growth. Furthermore, as awareness increases among gastroenterologists and radiologists, their usage in routine diagnostic pathways is anticipated to rise significantly.
Hospitals and clinics were the leading end-use segment in the U.S. EPI diagnostics market, accounting for the majority share due to their comprehensive diagnostic infrastructure and availability of multi-disciplinary expertise. Hospitals typically serve as referral centers for complex cases of pancreatic disorders, facilitating access to advanced imaging equipment, specialized laboratories, and gastroenterology specialists. The increasing number of hospital-based outpatient clinics has also improved patient access to EPI diagnostics, particularly in urban areas. Furthermore, reimbursement policies are often more favorable in hospital settings, encouraging patients to opt for tests within these facilities.
Diagnostic laboratories are expected to be the fastest-growing segment over the forecast period. Independent and chain diagnostic labs have expanded their service offerings to include comprehensive pancreatic function panels, driven by increasing test volumes and growing physician referrals. Their ability to offer specialized, high-throughput testing at competitive costs makes them attractive to both clinicians and insurance providers. Moreover, strategic partnerships between diagnostic laboratories and biotechnology companies are driving innovation in EPI-related assays. Some labs are also incorporating telehealth-enabled diagnostic consultations, broadening their reach to underserved or remote regions.
The U.S. market for EPI diagnostics is uniquely positioned due to its robust healthcare ecosystem, high disease burden, and progressive reimbursement framework. The country sees a significant number of EPI cases annually, particularly among older adults and those with comorbidities like diabetes or pancreatic malignancies. States with a higher prevalence of chronic diseases—such as Florida, Texas, and California tend to account for a disproportionate share of diagnostic testing volumes.
Academic medical centers and specialized gastroenterology clinics in cities like Boston, Chicago, and New York are at the forefront of EPI research and diagnostics. These institutions not only provide testing services but also participate in clinical trials aimed at developing next-generation diagnostic assays. Meanwhile, suburban and rural hospitals are beginning to integrate more advanced diagnostic protocols, supported by mobile imaging units and centralized testing hubs. Insurance coverage, including through Medicare and Medicaid, plays a significant role in making diagnostics accessible, particularly for seniors and low-income populations. Overall, the country remains a lucrative and evolving landscape for EPI diagnostics.
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2033. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the U.S. exocrine pancreatic insufficiency diagnostics market
Diagnostic Method
End-use