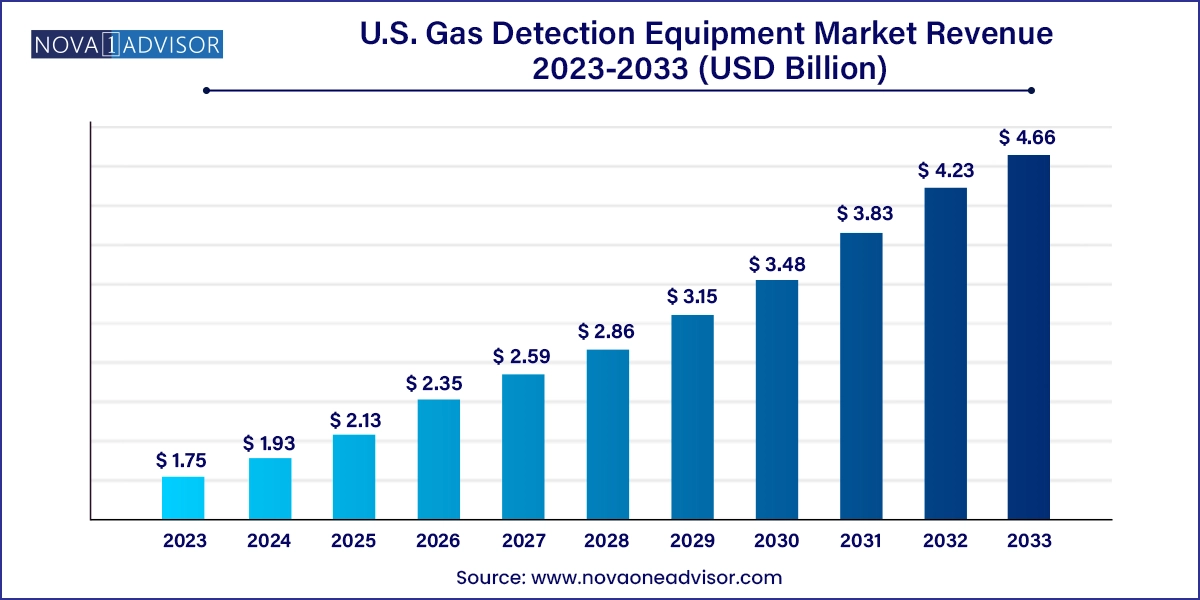
The U.S. gas detection equipment market size was exhibited at USD 1.75 billion in 2023 and is projected to hit around USD 4.66 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 10.3% during the forecast period 2024 to 2033.
The U.S. gas detection equipment market is a critical segment within the nation’s industrial safety ecosystem. These systems are designed to detect the presence of toxic, flammable, or hazardous gases in both enclosed and open environments, triggering alerts and initiating safety responses to protect human life, environmental assets, and infrastructure. Gas detection technologies serve as the first line of defense in high-risk operations across petrochemical facilities, mining operations, confined space entry zones, laboratories, automotive garages, and public buildings.
The increasing industrial footprint, coupled with stringent federal regulations from agencies such as OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration), EPA (Environmental Protection Agency), and NFPA (National Fire Protection Association), continues to reinforce the demand for gas detection systems across the United States. Furthermore, recent incidents of gas leaks, explosions, and industrial accidents have intensified the emphasis on workplace safety and real-time environmental monitoring.
With the convergence of the Internet of Things (IoT), cloud computing, and smart manufacturing initiatives, gas detection equipment in the U.S. is undergoing a paradigm shift from traditional standalone sensors to intelligent, interconnected, and predictive systems. Companies are investing heavily in wearable gas detectors, wireless fixed detection networks, and advanced analytics platforms that not only provide alerts but also enable root-cause analysis, compliance auditing, and preventive maintenance strategies.
Rise of Connected Gas Detection Systems: IoT-enabled detectors offering real-time telemetry and remote monitoring capabilities are gaining adoption in industrial facilities.
Shift Toward Multi-Gas Detection Devices: Portable and fixed units with multi-gas capabilities are in demand to monitor a wider range of gas types simultaneously in dynamic environments.
Adoption of AI and Predictive Maintenance: Predictive analytics using AI help anticipate sensor degradation or detect early gas anomalies before they reach critical thresholds.
Miniaturization of Gas Sensors: Wearable detectors for workers in confined or mobile settings are being deployed for personal safety, especially in construction and oil and gas sectors.
Increasing Focus on Indoor Air Quality Monitoring: Demand is growing for gas detection in commercial buildings and homes due to concerns over CO, VOCs, and radon exposure.
Regulatory Push on Methane Leak Detection: Government programs are enforcing more rigorous leak detection protocols in oil & gas, leading to an increase in laser and infrared-based detectors.
Integration with Building Automation Systems (BAS): Gas detectors are increasingly being integrated into HVAC and security systems in smart buildings and campuses.
Battery-operated and Solar-powered Units for Remote Monitoring: Standalone, low-power detectors with long battery life or solar capabilities are being used in remote and off-grid facilities.
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 1.93 Billion |
| Market Size by 2033 | USD 4.66 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2024 to 2033 | CAGR of 10.3% |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Forecast Period | 2024-2033 |
| Segments Covered | Product, Technology, End-use |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) | Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Country scope | U.S. |
| Key Companies Profiled | ABB; Airtest Technologies, Inc.; Teledyne Technologies Inc.; Fluke Corp.; General Electric Company; Honeywell International Inc.; Lynred; Opgal Optronics Industries Ltd.; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.; Siemens; Sensata Technologies |
A primary driver propelling the U.S. gas detection equipment market is the strengthening regulatory environment focused on occupational safety, environmental protection, and risk mitigation. Agencies such as OSHA and EPA have outlined stringent guidelines for permissible exposure limits (PELs) and mandated the presence of safety equipment in various industrial and public environments.
For instance, OSHA requires continuous monitoring in confined spaces and exposure-prone zones where toxic gases like hydrogen sulfide (H₂S), carbon monoxide (CO), methane (CH₄), or ammonia may be present. Furthermore, the EPA’s Greenhouse Gas Reporting Program (GHGRP) and Methane Emissions Reduction Action Plan are accelerating demand for real-time gas leak detection and quantification systems, especially in oil and gas operations.
Compliance with these mandates not only ensures worker and environmental safety but also minimizes legal liabilities, operational downtime, and insurance premiums. This has led companies across sectors—energy, manufacturing, healthcare, and even agriculture—to implement modern gas detection strategies that exceed minimum regulatory standards.
While gas detection technology has advanced significantly in recent years, a notable restraint for its widespread adoption remains the high upfront cost of installation, calibration, and integration—especially in legacy infrastructures. Fixed detection systems, particularly in large facilities, require comprehensive mapping, sensor placement, control panel setup, and network connectivity, which can involve significant capital expenditures.
Moreover, gas detection systems require regular maintenance and recalibration to ensure accurate performance. The cost of replacement sensors, technician visits, and downtime during recalibration adds to the operational expenditure. Small businesses, in particular, may struggle to justify the ROI if gas exposure risks are perceived to be low. Also, some sectors face challenges in retaining trained personnel to manage and interpret detector readings, especially when multi-gas or AI-enabled devices are used.
A compelling opportunity in the U.S. gas detection equipment market lies in the rapid expansion of smart infrastructure and renewable energy ecosystems. Smart buildings, urban surveillance systems, and connected campuses are integrating gas detection with HVAC, security, and energy management systems to ensure not just safety but also environmental quality and sustainability.
Similarly, renewable energy plants—such as hydrogen generation, biogas, and battery storage facilities—pose unique gas emission and leak detection challenges. For example, hydrogen requires highly sensitive, fast-response detectors due to its flammability and diffusion properties. This creates new application opportunities for advanced semiconductor and laser-based gas detectors tailored to clean energy applications.
Government investments through the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act (IIJA) and incentives under the Inflation Reduction Act are further encouraging developers to include gas detection solutions in next-generation infrastructure planning, especially in transportation, public utilities, and clean tech projects.
Fixed gas detectors dominate the U.S. market, particularly in large-scale industrial environments such as oil refineries, chemical plants, manufacturing facilities, and power stations. These systems are permanently installed and connected to centralized control units that can trigger alarms, ventilation, or shutdown procedures when hazardous gas levels are detected. Their advantage lies in continuous, automated monitoring and integration with broader facility safety systems. Fixed detectors are also preferred for compliance with occupational safety regulations that mandate round-the-clock gas monitoring in high-risk zones.
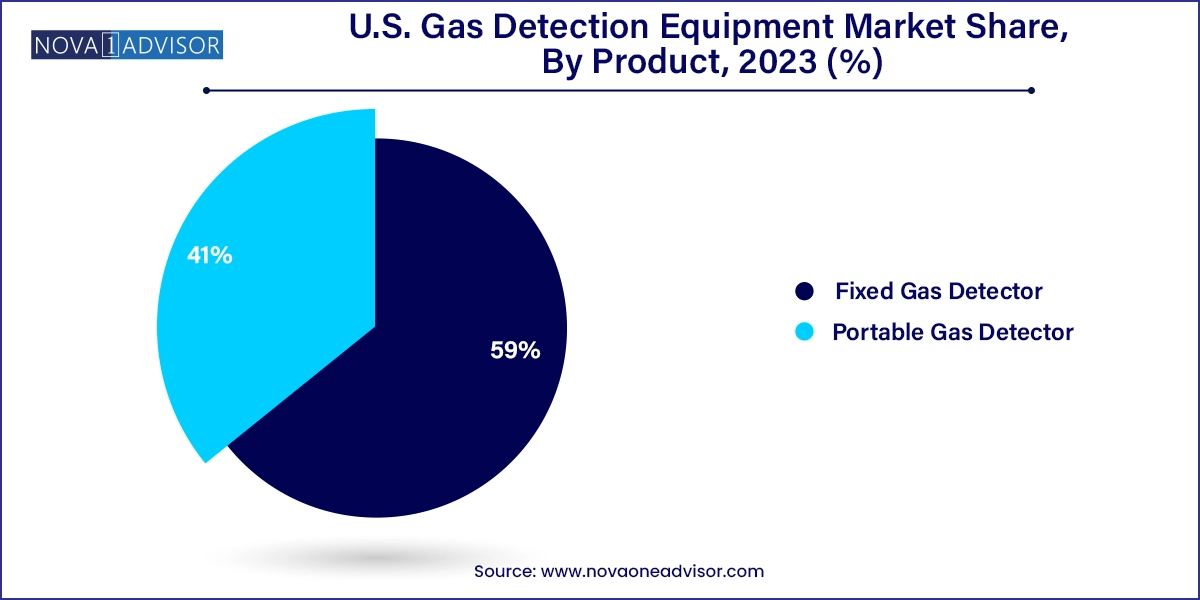
Portable gas detectors are growing at a faster rate, thanks to their flexibility, compact size, and ability to protect mobile workers operating in confined spaces, construction zones, or during emergency responses. These battery-operated devices are now capable of detecting multiple gases, logging data, and communicating wirelessly with central monitoring software. Firefighters, first responders, maintenance crews, and inspection teams rely heavily on portable detectors, especially in scenarios where environmental conditions change rapidly. Miniaturization and ruggedization are making these tools indispensable across sectors from mining to agriculture.
The industrial segment dominates the U.S. gas detection market, reflecting the critical need to protect worker health and ensure plant safety in environments where toxic or combustible gases are routinely handled. Industries such as petrochemicals, steel manufacturing, food processing, and pulp & paper rely on both fixed and portable systems to comply with OSHA, ANSI, and local environmental codes. The scale of operations, high density of processes, and explosion risks necessitate multi-tiered gas detection strategies involving real-time monitoring and automation.
The building automation & domestic appliances segment is witnessing rapid growth, largely due to increasing public awareness and legislative action focused on indoor air quality (IAQ). Gas detectors are now routinely installed in residential buildings, apartment complexes, commercial kitchens, and HVAC systems to detect CO, radon, and refrigerant gases. Smart home integration has made gas detection systems user-friendly, enabling remote monitoring through smartphones and integration with voice assistants. States like California and New York are already enforcing building codes that include gas detection infrastructure in new developments.
Infrared (IR) technology leads the technology segment, particularly in detecting hydrocarbon gases such as methane, propane, and ethylene in oil & gas, petrochemical, and HVAC applications. IR detectors are reliable, stable, and suitable for continuous monitoring in explosive atmospheres. They are also less susceptible to sensor poisoning and offer longer operational life, which makes them a preferred choice for fixed installations.
Laser-based gas detection is the fastest-growing technology, especially for applications involving remote sensing, pipeline leak detection, and fence-line monitoring. Tunable diode laser absorption spectroscopy (TDLAS) is gaining traction due to its high selectivity, sensitivity, and speed. Recent U.S. policies targeting methane emissions have pushed companies to deploy laser-based solutions across upstream and midstream oil & gas operations. Furthermore, drones equipped with laser sensors are being used to inspect inaccessible or dangerous locations safely.
The U.S. is a global leader in gas detection equipment demand and innovation, backed by a robust industrial landscape, proactive regulatory bodies, and a strong base of original equipment manufacturers (OEMs). The country’s shale gas revolution, widespread industrial base, and increasing climate accountability have led to greater investments in gas safety systems. States like Texas, Louisiana, California, and Pennsylvania represent high-demand hubs due to their concentration of oil, chemical, and energy assets.
Additionally, the U.S. is at the forefront of integrating gas detection into broader environmental, health, and safety (EHS) strategies. Federal support through the Clean Air Act, Methane Emissions Reduction Program, and the National Emissions Inventory creates a policy environment that promotes continuous investment in advanced detection equipment. The rise of smart cities and environmental justice initiatives in underserved communities is also expanding the market scope beyond industrial zones to urban, domestic, and public infrastructure sectors.
April 2024 – MSA Safety introduced its ALTAIR io™ 4 gas detector in the U.S. market, featuring real-time cloud connectivity, self-check diagnostics, and an integrated safety dashboard for industrial users.
February 2024 – Honeywell announced a partnership with a major U.S. oil & gas operator to deploy fixed IR gas detectors equipped with AI-driven anomaly detection across upstream assets in Texas.
January 2024 – Emerson Electric launched a new laser-based gas leak detection solution integrated with autonomous drones for pipeline inspection, aimed at the midstream energy sector.
November 2024 – Teledyne Gas & Flame Detection unveiled its GD10P IR gas detector series optimized for ammonia detection in food processing and HVAC sectors.
September 2024 – Thermo Fisher Scientific introduced an AI-powered portable gas chromatograph for emergency responders and hazmat teams, capable of identifying complex gas mixtures in under 5 minutes.
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2033. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the U.S. gas detection equipment market
Product
Technology
End-use