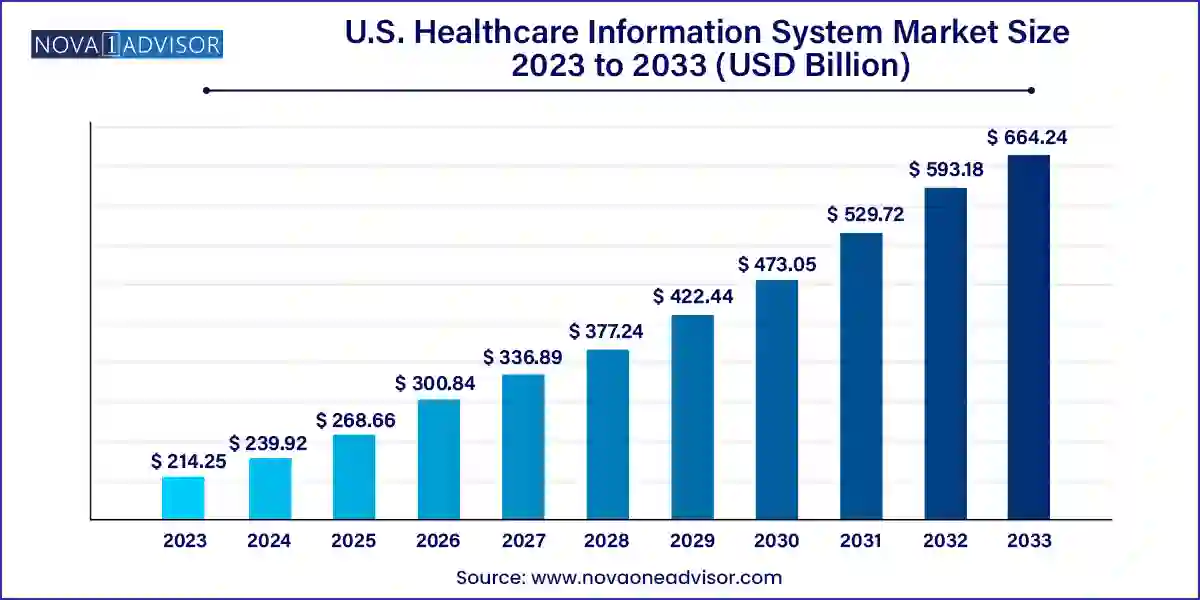
The U.S. healthcare information system market size was exhibited at USD 214.25 billion in 2023 and is projected to hit around USD 664.24 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 11.98% during the forecast period 2024 to 2033.
The U.S. Healthcare Information System (HIS) market is a cornerstone of digital transformation within the country’s healthcare sector. Characterized by rapid innovation, increasing digital literacy, and a pressing need to optimize patient care and streamline clinical workflows, HIS represents a multi-faceted ecosystem. It comprises a suite of integrated software, hardware, and service solutions that enable healthcare providers to manage medical, administrative, financial, and operational data effectively. The transformation from paper-based systems to electronic health records (EHRs) and real-time data analytics platforms has been pivotal to improving the quality, accuracy, and accessibility of healthcare information across the U.S.
Driving this momentum are a confluence of factors, including evolving regulatory frameworks like the Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health (HITECH) Act, ongoing digitalization of hospitals and clinics, and the need for cost containment in an aging and increasingly chronically ill population. With the surge in telemedicine, artificial intelligence (AI), and interoperability mandates, healthcare information systems have evolved from static data repositories into dynamic, intelligent platforms that aid in predictive diagnostics, clinical decision-making, and patient engagement.
In the U.S., market maturity is evident in the widespread use of cloud-based and web-integrated solutions, the consolidation of data ecosystems among health systems, and the emergence of value-based care models. Additionally, healthcare payers and providers are investing in health IT infrastructures to meet Medicare and Medicaid quality standards, avoid penalties, and enhance population health management. The market is expected to continue expanding as digital healthcare becomes embedded in the national strategy to deliver cost-effective, personalized, and accessible care.
Rise in Interoperability Solutions: Increasing demand for seamless integration across EHRs, laboratory systems, and pharmacy automation platforms.
AI and Predictive Analytics Adoption: Growing integration of artificial intelligence in medical imaging, diagnostics, and real-time healthcare monitoring.
Surge in Patient-Centric Platforms: Expansion of patient portals, remote access EHRs, and engagement apps to improve patient experience and compliance.
Cloud-first Deployments: Accelerated migration to cloud-based systems to improve scalability, accessibility, and cybersecurity.
Focus on Cybersecurity and Compliance: Heightened attention to HIPAA compliance, ransomware protection, and zero-trust architectures.
Growth in Telehealth Integration: Merging telehealth platforms with HIS for integrated virtual consultation records and billing.
Expansion of Revenue Cycle Management Tools: Digitization of billing, claims processing, and prior authorization to minimize revenue leakage.
Laboratory Informatics Expansion: Increase in laboratory workflow automation with advanced LIMS (Laboratory Information Management Systems).
Personalized Medicine and Genomic Data Integration: HIS evolving to accommodate genomic data for precision treatment planning.
Mobile-first Strategies: Increasing development of mobile interfaces for clinical staff and remote monitoring applications.
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 239.92 Billion |
| Market Size by 2033 | USD 664.24 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2024 to 2033 | CAGR of 11.98% |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Forecast Period | 2024-2033 |
| Segments Covered | Application, Deployment, Component, End-use |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) | Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Regional Scope | U.S. |
| Key Companies Profiled | Cerner Corporation; Athenahealth Inc.; Change Healthcare Inc.; GE Healthcare; IBM; Oracle Corporation; Dell Technologies Inc.; Philips Healthcare; Optum; Infor; Epic Systems Corporation; Allscripts Healthcare Solutions Inc.; Conduent Inc.; Cognizant Technology Solutions Corporation; eClinicalWorks LLC |
A primary driver of the U.S. healthcare information system market is the ongoing digital transformation fueled by federal mandates, financial incentives, and the shift to value-based care models. Initiatives such as the HITECH Act and MACRA (Medicare Access and CHIP Reauthorization Act) have incentivized providers to adopt EHRs, embrace quality-based reimbursement, and invest in interoperability.
Moreover, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) continues to advance regulatory frameworks that prioritize data exchange, patient access to health records, and transparency in care outcomes. As a result, hospitals and physician groups across the country are implementing HIS solutions to comply with these requirements, prevent penalties, and qualify for performance-based bonuses. Additionally, consumer expectations for digital access, along with pandemic-induced demand for telehealth and virtual monitoring, have further amplified the necessity for sophisticated, integrated HIS platforms.
Despite significant strides in digitalization, the healthcare information system market in the U.S. faces ongoing challenges related to data fragmentation and interoperability. The healthcare ecosystem includes a multitude of proprietary EHR systems, laboratory software, imaging platforms, and pharmacy databases—many of which operate in silos and are incompatible with each other.
This lack of seamless data flow between systems impedes efficient care coordination, leading to duplicated tests, medication errors, and delays in diagnosis. While interoperability standards like HL7 and FHIR (Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources) have been introduced, their inconsistent implementation and lack of standardization across vendors continue to pose barriers. Additionally, system upgrades and integration projects are often resource-intensive and time-consuming, especially for smaller clinics and rural hospitals with limited IT budgets.
A rapidly emerging opportunity in the U.S. healthcare information system market is the integration of predictive analytics and population health management (PHM) into existing workflows. As healthcare shifts from a reactive to a proactive model, providers are increasingly seeking tools that help identify at-risk populations, monitor chronic disease progression, and prevent avoidable hospitalizations.
HIS platforms that incorporate AI-driven analytics, real-time health data, and socio-economic indicators can enable care teams to personalize interventions and improve outcomes. For instance, predictive models can analyze EHR data to identify patients at high risk of readmission or those needing preventive screenings. Integrated PHM modules can also provide dashboards for accountable care organizations (ACOs) to track performance metrics across patient groups. Vendors offering scalable, secure, and user-friendly analytics platforms are well-positioned to capitalize on this growing demand.
Hospital Information Systems (HIS) dominated the application segment, primarily due to their central role in integrating various facets of hospital operations—from patient administration and clinical documentation to imaging, diagnostics, and billing. Within HIS, Electronic Health Records (EHR) and Electronic Medical Records (EMR) are the most widely adopted components. EHRs provide a longitudinal view of a patient’s health data, allowing for comprehensive diagnosis, care planning, and inter-department communication. The federal EHR incentive programs and Meaningful Use criteria have played a significant role in ensuring near-universal adoption across hospitals.
The fastest-growing application is Population Health Management (PHM), as healthcare organizations prioritize preventive care and chronic disease management. PHM solutions utilize aggregated patient data to identify health trends across populations, manage resource allocation, and drive public health initiatives. For example, during the COVID-19 pandemic, PHM platforms were instrumental in vaccine distribution, hotspot identification, and tracking comorbidities. In the post-pandemic environment, PHM remains crucial for managing diabetes, hypertension, and mental health outcomes on a broader scale.
Web-based deployment models dominated the U.S. market, especially among mid-sized hospitals and outpatient clinics. These models strike a balance between functionality and cost-efficiency, offering browser-accessible interfaces without the complexity of full-scale cloud migration. Many healthcare providers still rely on web-based solutions for EHR access, scheduling, and billing, particularly when facing bandwidth or cybersecurity constraints.
Cloud-based solutions are the fastest-growing segment, driven by scalability, real-time access, and lower infrastructure costs. Major health systems are increasingly migrating to cloud-first models to support remote care, data analytics, and disaster recovery. Companies like Epic and Cerner are offering hybrid cloud solutions to ease the transition for large hospitals. Cloud HIS platforms also simplify collaboration across different care settings, from urgent care clinics to rehabilitation centers.
Software and Systems dominated the component category, reflecting the central role of platforms such as EHRs, laboratory information systems (LIS), pharmacy automation software, and billing modules. These systems provide the foundational framework for digital healthcare operations, with frequent upgrades and updates to meet compliance and usability standards. Advanced software features like AI algorithms, NLP tools, and blockchain are being integrated to elevate functionality and security.
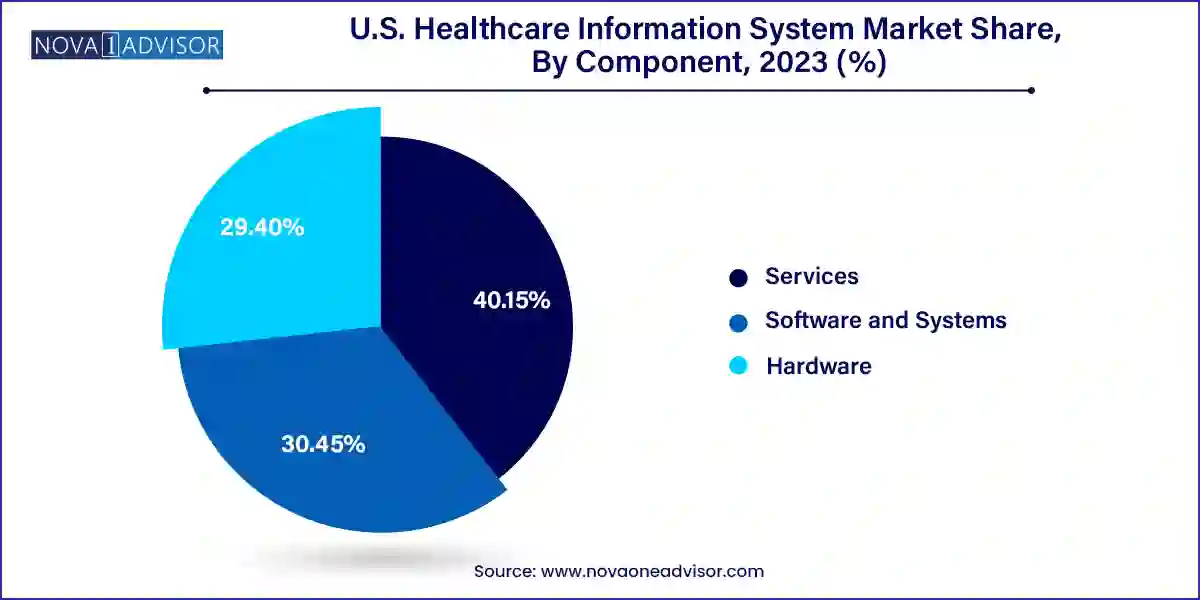
The fastest-growing component is Services, encompassing system integration, consulting, data migration, and technical support. As healthcare organizations embrace complex digital transformations, the need for expert guidance in implementing, customizing, and optimizing HIS has grown significantly. Managed services are especially in demand among smaller institutions that lack dedicated IT departments. Companies offering bundled service packages alongside software licenses are gaining a competitive edge.
Hospitals remain the largest end-users of healthcare information systems, accounting for a significant share due to the volume and diversity of their digital requirements. From emergency departments to radiology units, hospitals rely on HIS for coordinated care delivery, efficient documentation, and performance measurement. Moreover, accreditation standards, Medicare compliance, and integration with public health databases necessitate sophisticated HIS platforms in hospital settings.
The fastest-growing end-users are Diagnostic Centers, driven by the surge in outpatient diagnostic services, including imaging and laboratory tests. These centers are investing in radiology information systems (RIS), laboratory information management systems (LIMS), and cloud-based PACS to improve turnaround times and enable teleradiology. Integration with hospital and physician EHR systems ensures seamless data sharing, improving diagnostic accuracy and patient outcomes.
The U.S. stands at the forefront of the global healthcare information system industry, both in terms of technological advancement and regulatory leadership. The federal government’s commitment to digital healthcare infrastructure, through agencies like the Office of the National Coordinator for Health Information Technology (ONC), has established a strong policy foundation for HIS growth. Programs like TEFCA (Trusted Exchange Framework and Common Agreement) promote secure, nationwide health data exchange, further fueling market development.
Leading health systems in states such as California, Massachusetts, and New York have made substantial investments in HIS platforms that support AI-based diagnostics, mobile care delivery, and population health monitoring. Community hospitals and rural health centers are also receiving federal grants and support through the Health Resources and Services Administration (HRSA) to upgrade their IT capabilities. As a result, HIS penetration continues to rise, with broader public-private partnerships shaping the next phase of digital health in the U.S.
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2033. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the U.S. healthcare information system market
Application
Deployment
Component
End-use