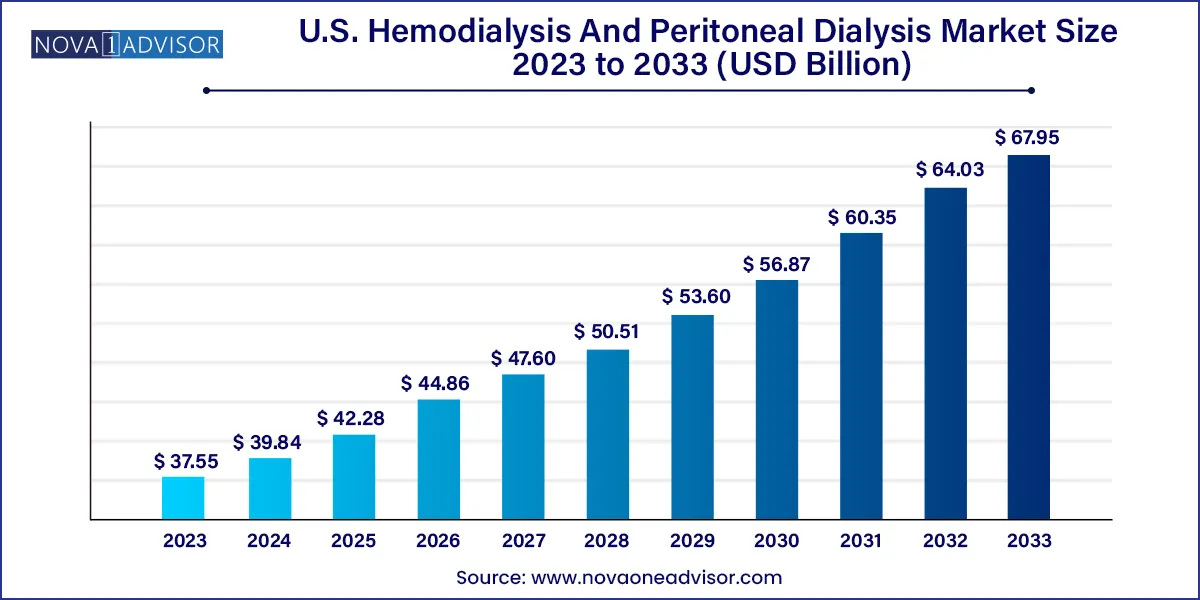
The U.S. hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis market size was exhibited at USD 37.55 billion in 2023 and is projected to hit around USD 67.95 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 6.11% during the forecast period 2024 to 2033.
The U.S. hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis market forms a vital part of the country’s renal care infrastructure, addressing the growing burden of end-stage renal disease (ESRD) and chronic kidney disease (CKD). With over 37 million Americans suffering from CKD, and more than 750,000 living with ESRD, the demand for dialysis has reached historic highs. Dialysis serves as a life-sustaining therapy, compensating for the kidney's inability to remove waste and excess fluid from the body. The market encompasses various treatment modalities, including in-center hemodialysis, home-based dialysis, and peritoneal dialysis, along with associated machines, consumables, and support services.
The increasing incidence of diabetes and hypertension the two leading causes of kidney failure in the U.S. has significantly driven demand for renal replacement therapies. Additionally, a paradigm shift toward value-based care and home-based modalities is reshaping how dialysis is delivered and reimbursed. Innovations in dialysis machines, wearable technologies, and connected health platforms are further redefining patient management by offering real-time data tracking, improved portability, and enhanced quality of life.
Government programs such as Medicare ESRD coverage and the Kidney Care Choices (KCC) model from CMS are fueling adoption by promoting home dialysis and incentivizing outcomes-based treatments. With the market projected to grow steadily, stakeholders are increasingly focused on balancing clinical efficacy, patient comfort, and economic sustainability.
Rising preference for home-based dialysis, especially peritoneal dialysis (PD)
Technological advancements in dialysis machines and portable equipment
CMS incentives for home dialysis under the KCC model
Integration of remote patient monitoring and digital health tools
Consolidation and partnerships among dialysis service providers
Emergence of artificial kidneys and wearable dialysis prototypes
Emphasis on patient education and self-management tools
Development of biocompatible dialyzers and improved membranes
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 39.84 Billion |
| Market Size by 2033 | USD 67.95 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2024 to 2033 | CAGR of 6.11% |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Forecast Period | 2024-2033 |
| Segments Covered | Product, Type, End-use |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) | Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Regional Scope | U.S. |
| Key Companies Profiled | Baxter, B; Braun Melsungen AG; Fresenius Medical Care AG; Medtronic; Asahi Kasei Medical Co., Ltd.; Nipro Corp; DaVita; BD; Nikkiso Co., Ltd.; Cantel Medical |
A key driver of the U.S. dialysis market is the rising prevalence of end-stage renal disease, primarily driven by an aging population and an increase in comorbid conditions such as diabetes and hypertension. According to the United States Renal Data System (USRDS), the number of ESRD patients receiving dialysis is growing at a steady pace, with over 70% of new ESRD patients beginning with hemodialysis. The sheer scale of this population necessitates ongoing expansion and innovation within the dialysis ecosystem.
To support this growing demand, government-backed programs such as Medicare provide coverage for most dialysis-related services. More recently, CMS has introduced the Kidney Care Choices (KCC) model to encourage earlier detection, improved care coordination, and greater utilization of home dialysis. These initiatives are driving investment and innovation in at-home technologies, expanding access and improving outcomes.
While home dialysis offers many advantages, including cost savings, flexibility, and improved quality of life, several barriers hinder widespread adoption. First, there is a significant need for infrastructure upgrades and specialized training for both patients and caregivers. Home dialysis, particularly peritoneal dialysis (PD), requires sterile environments, reliable water systems, and adequate space features not available in every household.
Moreover, patients often express concerns about self-managing complex medical procedures without professional supervision. This reluctance is compounded by socioeconomic disparities, lower health literacy, and regional inconsistencies in support services. For providers, the transition to home-based care involves investments in telehealth systems, training modules, and support staff, which can be resource-intensive. Until these structural issues are addressed, in-center hemodialysis is likely to remain dominant.
One of the most promising opportunities in the U.S. dialysis market is the development and commercialization of wearable and portable dialysis solutions. These innovations aim to enhance mobility, reduce treatment times, and improve patient lifestyle. The wearable artificial kidney (WAK) prototype, for example, has demonstrated success in preliminary trials by allowing continuous dialysis without being tethered to a dialysis chair or machine.
Companies are also exploring compact home hemodialysis systems that require minimal setup and maintenance. These technologies appeal to working-age patients and active seniors who desire independence and reduced hospital visits. As regulatory frameworks evolve to support these innovations, and private insurers begin to recognize their long-term benefits, the market for portable dialysis is expected to accelerate significantly.
Hemodialysis dominates the U.S. dialysis market, with conventional in-center treatment accounting for the largest share. This is due to the long-established clinical protocols, extensive infrastructure, and Medicare coverage favoring facility-based treatments. Conventional hemodialysis involves thrice-weekly sessions in a clinical setting and is the standard for managing ESRD across the U.S. Despite the rising interest in home modalities, the in-center model remains predominant because of its clinical oversight and logistical simplicity.
Nocturnal and short daily hemodialysis are gaining popularity, particularly among patients seeking flexibility and improved outcomes. These modalities allow for extended or more frequent dialysis sessions, often at home, which more closely mimic natural kidney function. Clinical evidence supports their benefits in terms of fluid management, blood pressure control, and reduced cardiovascular risks. As telemonitoring and training programs improve, these subsegments are expected to grow faster than traditional approaches.
Peritoneal dialysis (PD) is the fastest-growing dialysis modality, fueled by CMS incentives and increased awareness of home-based care. Among PD options, Automated Peritoneal Dialysis (APD) is gaining traction due to its ease of use, especially during nighttime. APD uses cycler machines to perform multiple exchanges while the patient sleeps, allowing for normal daytime activities. On the other hand, Continuous Ambulatory Peritoneal Dialysis (CAPD) remains preferred by patients seeking manual control and schedule flexibility. While PD still represents a smaller share compared to hemodialysis, its annual growth rate is outpacing other modalities.
Devices represent the largest product segment, driven by the demand for dialysis machines, dialyzers, and water treatment systems. Dialysis machines have become more advanced with user-friendly interfaces, remote connectivity, and safety features. The development of wearable machines and smart interfaces has further expanded the scope of this segment. Water treatment systems are indispensable for in-center hemodialysis, maintaining the quality and safety of dialysate solutions.
Consumables are a rapidly expanding segment, particularly due to their recurring usage in every dialysis session. Products like dialysate concentrates, bloodlines, catheters, and filters are essential for both peritoneal and hemodialysis. Innovations in biocompatible and antimicrobial materials are improving patient outcomes and reducing infection rates. As the patient pool grows, demand for high-quality, single-use consumables will continue to rise.
Services, including maintenance, training, and home support programs, are becoming increasingly important. As home-based dialysis gains momentum, the role of service providers in education, remote monitoring, and equipment maintenance is expanding. These value-added services are crucial for ensuring treatment continuity and patient confidence.
Hospital-based dialysis centers dominate the market, as they offer comprehensive renal care, multidisciplinary supervision, and access to emergency services. Most newly diagnosed ESRD patients start their treatment in hospital-based settings due to the need for vascular access creation and medical stabilization. These facilities often have affiliations with nephrology specialists and access to surgical services, making them ideal for patients with complex comorbidities.

Home-based dialysis is the fastest-growing end-use segment, propelled by government incentives, cost advantages, and patient preference for convenience. Home modalities reduce travel burdens, lower exposure to hospital-acquired infections, and empower patients through self-care. With advancements in remote monitoring, compact machines, and teleconsultation services, the home-based segment is attracting significant attention from both private providers and policymakers.
In the United States, dialysis care is undergoing a transformation driven by policy reforms, demographic changes, and technology adoption. The Medicare ESRD program, which covers more than 80% of dialysis patients, provides a strong financial backbone for market growth. CMS's focus on transitioning 80% of new ESRD patients to home dialysis or transplants by 2025 has created a wave of investment in home-based technologies and service models.
Major healthcare providers, including Fresenius Medical Care and DaVita, are expanding their home dialysis training programs and partnering with tech firms to introduce connected care solutions. Simultaneously, startups and medtech firms are innovating around wearable and miniaturized dialysis devices to suit outpatient needs. The U.S. also leads in clinical trials for artificial kidneys and biocompatible membranes, signaling a future of more personalized and efficient renal care.
In April 2025, Outset Medical launched a portable hemodialysis machine designed for both clinic and home settings, enhancing flexibility for ESRD patients.
In February 2025, Fresenius Medical Care announced a $150 million investment to expand its U.S. home dialysis infrastructure.
In January 2025, DaVita Inc. unveiled a partnership with a digital health firm to offer real-time remote monitoring for peritoneal dialysis patients.
In November 2024, Quanta Dialysis Technologies received FDA clearance for its SC+ home hemodialysis system.
In August 2024, NxStage Medical (a Fresenius company) began pilot testing a next-gen compact dialysis device for nocturnal use.
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2033. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the U.S. hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis market
Type
Product
End-use