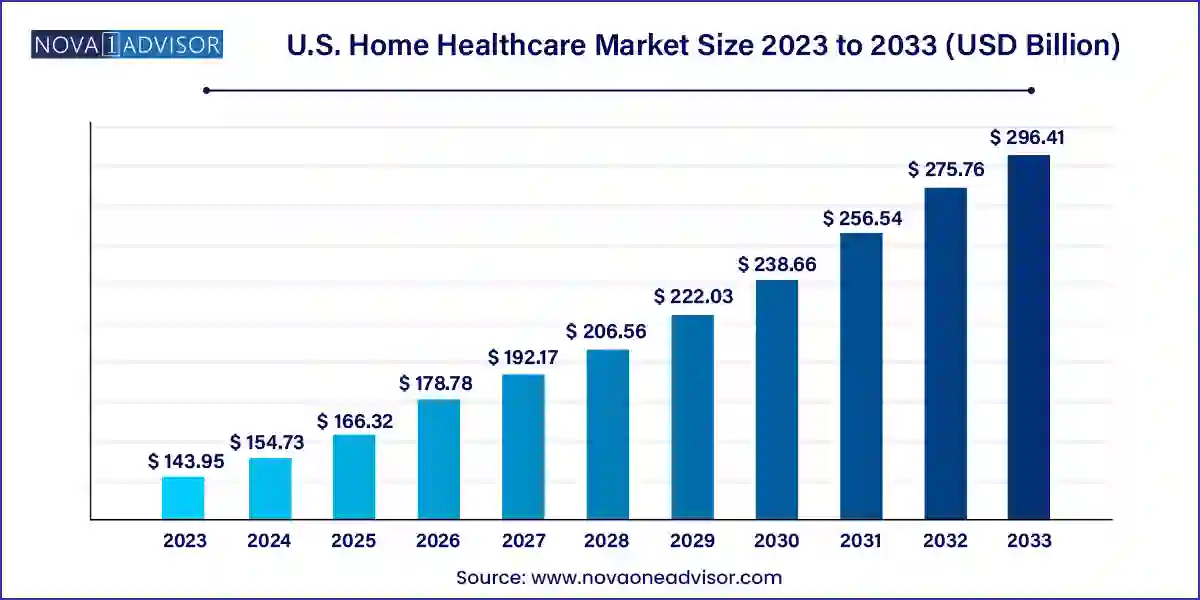
The U.S. home healthcare market size was exhibited at USD 143.95 billion in 2023 and is projected to hit around USD 296.41 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 7.49% during the forecast period 2024 to 2033.
The U.S. Home Healthcare Market represents one of the most rapidly expanding sectors in the broader healthcare industry, driven by demographic shifts, the rise in chronic illnesses, increasing healthcare costs, and a decisive shift toward patient-centric care. Home healthcare encompasses a wide range of medical and non-medical services delivered at a patient's home, including skilled nursing, therapy services, diagnostic support, and durable medical equipment. The goal is to provide quality care in a more convenient, cost-effective, and comfortable setting, especially for elderly patients, individuals with disabilities, and those recovering from surgery or managing chronic conditions.
The United States, with its aging Baby Boomer population and healthcare system increasingly focused on value-based outcomes, is uniquely positioned for a boom in home healthcare services. According to the U.S. Census Bureau, by 2030, nearly 1 in every 5 Americans will be over the age of 65, many of whom will require long-term assistance and frequent clinical monitoring. Simultaneously, the rising burden of chronic diseases such as diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, COPD, and Alzheimer’s has intensified demand for at-home care interventions that reduce hospital admissions and improve quality of life.
Additionally, innovations in remote monitoring, mobile diagnostics, and therapeutic equipment have extended the range of care that can be administered at home. The COVID-19 pandemic further accelerated the shift from facility-based to home-based care, demonstrating the viability and benefits of decentralized healthcare delivery. Government programs like Medicare Advantage have expanded coverage for in-home services, fueling provider expansion and investment in infrastructure. Consequently, the U.S. home healthcare market is expected to experience sustained growth and play a pivotal role in the future of integrated healthcare delivery.
Growth of Hospital-at-Home Programs: Leading health systems are developing comprehensive home hospitalization services to treat acute conditions like pneumonia and heart failure at home.
Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) Integration: Use of connected devices for vitals tracking and real-time alerts is enhancing clinical oversight in home settings.
Rise of AI and Predictive Analytics in Care Coordination: AI tools are being deployed to anticipate patient deterioration and optimize caregiver schedules.
Expansion of Unskilled Home Healthcare Services: Demand for personal care aides and companions is growing alongside medical needs, particularly for dementia and Alzheimer’s patients.
Workforce Challenges and Technology-Driven Training: Providers are using virtual simulation tools and mobile apps to train caregivers amid staffing shortages.
Pharmacy and Infusion at Home: Home infusion therapies are gaining traction for antibiotics, chemotherapy, and hydration support.
Policy and Reimbursement Support: CMS and state Medicaid programs are widening reimbursement for in-home services, especially under managed care models.
Smart Home Integration for Safety and Monitoring: Voice-activated assistants, fall detection sensors, and video surveillance are enhancing home care environments.
Consolidation and Strategic Partnerships: Mergers, acquisitions, and collaborations between home care agencies, health systems, and tech providers are reshaping the competitive landscape.
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 154.73 Billion |
| Market Size by 2033 | USD 296.41 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2024 to 2033 | CAGR of 7.49% |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Forecast Period | 2024-2033 |
| Segments Covered | Component |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) | Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Regional Scope | U.S. |
| Key Companies Profiled | McKesson Medical-Surgical, Inc.; NxStage Medical (Fresenius Medical Care); Medline Industries Inc.; Medtronic plc; 3M Healthcare; Baxter International Inc.; B. Braun Melsungen AG; F. Hoffman-La Roche AG; Becton, Dickinson and Company; Kindred Healthcare, LLC; Brookdale Senior Living Inc.; Sunrise Senior Living, LLC; Genesis Healthcare, Inc.; Capital Senior Living Corporation (Sonida Senior Living); Diversicare Healthcare Services, Inc.; Senior Care Center; Atria Senior Living, Inc.; Amedisys, Inc.; Home Instead, Inc. |
One of the most potent drivers of the U.S. home healthcare market is the expanding elderly demographic coupled with an escalating chronic disease burden. Aging is often accompanied by increased vulnerability to illnesses such as diabetes, arthritis, Alzheimer’s, heart failure, and respiratory disorders, many of which require ongoing management rather than episodic treatment. Hospitals are no longer ideal as primary care settings for such long-term, non-acute conditions due to their high cost, infection risks, and capacity limitations.
Home healthcare offers a viable alternative, allowing patients to receive necessary medical services in the comfort of their homes. For instance, a COPD patient can now receive oxygen therapy and remote pulmonary function monitoring without visiting a clinic. Elderly stroke survivors can undergo physiotherapy at home, improving adherence and outcomes. Furthermore, Medicare data suggests that home healthcare services are often less costly and associated with fewer complications than institutional care, thereby aligning with the goals of value-based reimbursement models. This demographic and epidemiological shift is structurally fueling long-term growth in the sector.
Despite growing demand, the home healthcare market in the U.S. faces a persistent constraint in the form of workforce shortages and high turnover rates. Home care requires a broad array of professionals from registered nurses and therapists to home health aides and personal care attendants. However, the supply of qualified personnel has not kept pace with demand, particularly in rural and underserved areas. According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, the need for home health aides is projected to grow 25% between 2021 and 2031, but training pipelines and retention efforts are lagging.
Low wages, high emotional stress, limited career mobility, and irregular work hours contribute to burnout and attrition among caregivers. For instance, home health aides often juggle multiple clients, travel long distances, and receive minimal support for mental health and upskilling. These issues compromise care continuity and patient satisfaction. Providers are increasingly investing in technology and scheduling optimization tools to alleviate staffing gaps, but systemic workforce development remains a pressing challenge for sustainable market expansion.
A key opportunity within the U.S. home healthcare market lies in the scaling of hybrid care models that combine in-person services with digital health technologies. The post-pandemic healthcare paradigm has normalized virtual visits, remote diagnostics, and AI-driven monitoring. These tools are being integrated into traditional home healthcare pathways to increase efficiency, reach, and quality. For example, a physical therapist might conduct the initial evaluation at the patient’s home but follow up through a secure video platform, reducing travel and appointment delays.
Technology also enables continuous engagement. Wearable devices track vitals like blood pressure or glucose levels, while AI algorithms can flag anomalies and notify care teams for early intervention. Platforms like Current Health and DispatchHealth are leveraging logistics, analytics, and telemedicine to provide urgent care at home. Furthermore, payer-provider collaborations are establishing bundled reimbursement for hybrid care pathways. This convergence of hands-on and virtual care is not only cost-effective but also adaptable to evolving patient preferences and clinical complexities.
Services dominated the U.S. home healthcare market by component, as patient care is inherently dependent on hands-on medical and non-medical support provided in home settings. Skilled nursing care, physical therapy, palliative care, and physician visits constitute the core of clinical home health services. These are often supplemented by nutrition counseling and wound care. Additionally, unskilled services such as grooming, meal preparation, companionship, and household chores are vital for maintaining a patient’s overall wellbeing. Elderly individuals with mobility issues or cognitive impairments rely heavily on these unskilled services. The combination of skilled and non-skilled services ensures a holistic approach to health and wellness.
Equipment is the fastest-growing segment, propelled by innovations in portable therapeutic and diagnostic devices. The increasing availability of compact, user-friendly medical equipment for home use—ranging from IV pumps to sleep apnea monitors is transforming chronic care management. Home dialysis equipment and insulin delivery systems are especially crucial for patients with end-stage renal disease and diabetes, respectively. Diagnostic equipment such as multi-parameter monitors, pregnancy test kits, and ECG Holter monitors allow for periodic assessment without clinic visits. As tech-enabled self-monitoring gains popularity, the demand for home-compatible, interoperable devices is rising exponentially.
Therapeutic equipment dominated the equipment category, with home respiratory devices, dialysis machines, and insulin delivery systems seeing the highest adoption. Patients with COPD or post-COVID lung conditions increasingly require oxygen concentrators and nebulizers at home. Home dialysis machines are helping kidney disease patients avoid frequent visits to dialysis centers. Insulin delivery systems, including pumps and smart pens, empower diabetes patients to maintain better glucose control under remote supervision. These devices are often integrated with RPM tools to ensure medication adherence and reduce complications.
Diagnostic equipment is witnessing the fastest growth, as proactive health monitoring becomes central to chronic disease prevention and early diagnosis. BP monitors, blood glucose meters, and portable ECG devices have become commonplace in homes, thanks to consumer awareness and payer encouragement. The trend is also driven by direct-to-consumer models, where companies like Withings and Omron offer diagnostic kits that sync with mobile apps. Sleep monitoring systems and fertility test kits are increasingly being used for niche conditions, expanding the market footprint beyond traditional disease monitoring.
Skilled home healthcare services dominate the service segment, as they involve direct medical care typically provided by licensed professionals. Nursing care is essential for post-surgical patients, wound management, medication administration, and chronic disease monitoring. Therapy services—physical, occupational, and speech—are crucial for recovery and rehabilitation. Hospice and palliative care services are also gaining momentum as more patients prefer to spend their final days at home rather than in a hospital. Physician-led home visits are increasing, particularly for high-risk, frail elderly patients.
Unskilled home healthcare services are growing fastest, spurred by the aging population’s need for assistance with daily living activities. These include bathing, dressing, light housekeeping, companionship, and transportation. As dementia and Alzheimer’s prevalence increases, demand for trained personal care aides has surged. Many families are opting for live-in aides or scheduled visits to support seniors aging in place. States are increasingly offering Medicaid waivers that cover such services, thereby expanding access to non-clinical home care for low-income households.
The U.S. home healthcare market is shaped by its unique demographic, policy, and technological landscape. Federal initiatives such as the Home Health Value-Based Purchasing (HHVBP) Model and Medicare Advantage expansions are reinforcing the shift toward at-home care. State-specific programs, including waiver initiatives and managed long-term services and supports (MLTSS), are helping local agencies scale operations. Urban hubs are seeing increased investment in tech-enabled home care startups, while rural regions face provider shortages and logistical challenges.
Healthcare systems like Mount Sinai, Geisinger, and Kaiser Permanente have launched home-based acute care programs that blend in-home services with telehealth, analytics, and emergency response tools. The U.S. is also witnessing growing private equity interest in consolidating home health agencies. Moreover, partnerships between payers and providers are creating new care pathways that bundle home health into integrated delivery networks. With rising cost pressures and patient preferences converging toward home-based solutions, the U.S. market is well-positioned for continued evolution and expansion.
March 2025 – Humana Inc. announced the acquisition of Kindred at Home's remaining stake, completing its transition into a fully integrated home health business, focusing on chronic care and Medicare Advantage populations.
February 2025 – Amedisys Inc. launched a new remote patient monitoring service, incorporating AI algorithms to flag early warning signs for cardiac and pulmonary patients.
January 2025 – LHC Group partnered with Epic Systems to integrate its home health documentation into major hospital EHRs, streamlining cross-continuum care coordination.
November 2024 – BAYADA Home Health Care rolled out a new mobile app for caregiver scheduling and patient updates, enhancing operational transparency and client satisfaction.
October 2024 – Best Buy Health expanded its home health technology line with fall detection sensors and 24/7 response services, targeting elderly individuals living alone.
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2033. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the U.S. home healthcare market
Component