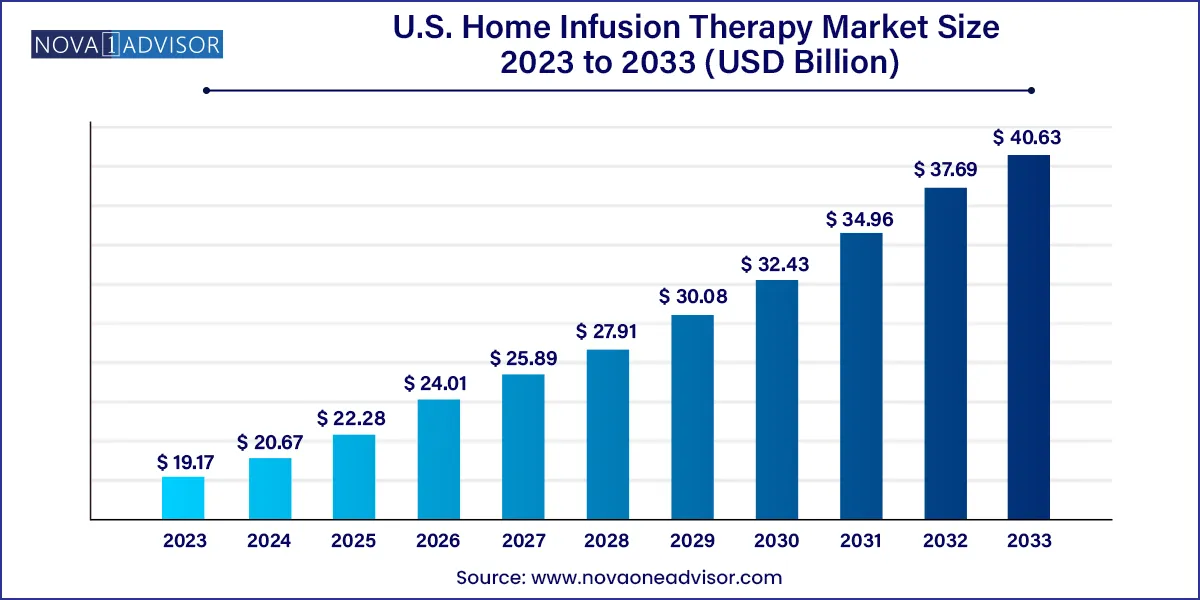
The U.S. home infusion therapy market size was valued at USD 19.17 billion in 2023 and is projected to surpass around USD 40.63 billion by 2033, registering a CAGR of 7.8% over the forecast period of 2024 to 2033.
The U.S. Home Infusion Therapy Market has emerged as a transformative segment within the broader healthcare landscape, reshaping how complex treatments are delivered. Home infusion therapy involves the administration of medications through intravenous (IV) or subcutaneous routes in a home setting. As the healthcare system pivots toward value-based care, patient convenience, and cost efficiency, home infusion therapy is gaining traction for treating chronic conditions, managing pain, and delivering post-surgical care outside of hospital environments.
The market is being shaped by factors such as an aging population, rising prevalence of chronic diseases, advancements in infusion devices, and patient preference for home-based services. Traditional hospital-based infusions come with significant infrastructure costs and higher risks of hospital-acquired infections. In contrast, administering therapies like antibiotics, chemotherapy, hydration, and parenteral nutrition at home can significantly reduce costs and improve patient satisfaction.
The shift is also driven by payers, including Medicare Advantage and private insurers, who are pushing for reduced inpatient care utilization and supporting alternate site care models. The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated this shift, demonstrating the feasibility and safety of remote, professional healthcare. As home health agencies, specialty pharmacies, and infusion providers expand their service portfolios, the U.S. home infusion therapy market is poised for long-term, sustainable growth.
Shift Toward Value-Based and Remote Care Models: Increasing pressure to reduce hospital readmissions and costs is leading to greater support for at-home infusion.
Rising Adoption of Wearable and Smart Infusion Pumps: Portable, user-friendly devices are making self-administration safer and more accurate.
Growing Popularity of Specialty Pharmaceuticals: High-cost drugs for rare and chronic conditions are being infused at home to increase adherence and reduce institutional load.
Expansion of Services for Cancer, Diabetes, and Autoimmune Conditions: Home infusion is expanding beyond anti-infectives and hydration to more complex therapies.
Evolving Reimbursement Structures: CMS and private payers are implementing policies that support home-based infusion over hospital-administered therapy.
Partnerships Between Hospitals and Home Health Providers: Collaboration between acute care institutions and post-acute infusion specialists is on the rise.
Telehealth Integration in Infusion Monitoring: Remote monitoring and virtual consultation tools are being embedded into infusion therapy protocols.
| Report Attribute | Details |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 20.67 Billion |
| Market Size by 2033 | USD 40.63 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2024 to 2033 | CAGR of 7.8% |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Forecast Period | 2024 to 2033 |
| Segments Covered | Product, application |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) | Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Report Coverage | Revenue forecast, company ranking, competitive landscape, growth factors, and trends |
| Key Companies Profiled | B. Braun Melsungen; Baxter International; Caesarea Medical Electronics Ltd.; CareFusion; Fresenius Kabi; ICU Medical; JMS CO., LTD.; Smiths Medical, Inc.; Terumo Corporation; Coram LLC; Option Care Enterprises, Inc.; BioScrip, Inc.; BriovaRx Infusion Services; Paragon Healthcare |
One of the most critical drivers for the U.S. home infusion therapy market is the increasing burden of chronic diseases, particularly conditions like diabetes, cancer, autoimmune disorders, and infections requiring long-term or recurrent IV treatment. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), 6 in 10 U.S. adults have a chronic disease, and 4 in 10 have two or more. These conditions often necessitate frequent medication, hydration, or nutritional support that traditionally required extended hospital stays or frequent clinic visits.
Home infusion therapy provides a safer and more cost-effective solution by allowing these patients to receive treatment in the comfort of their own homes. For example, patients with Crohn’s disease or rheumatoid arthritis who receive biologic therapies via infusion can do so with the supervision of trained nurses, reducing stress and potential exposure to infections. Moreover, parenteral nutrition for cancer patients experiencing gastrointestinal complications is now widely administered at home with precision and safety, improving their quality of life.
While the home infusion therapy market is expanding, it also faces challenges, particularly in the form of regulatory oversight and patient safety. Home-based administration of high-risk therapies such as chemotherapy or specialty biologics necessitates strict adherence to protocols, skilled nursing, and meticulous monitoring. Variations in state-level regulations, differing licensure requirements, and inconsistent payer reimbursement pose barriers to market standardization.
Moreover, the risk of catheter-related bloodstream infections, drug errors, and complications from poor aseptic technique can deter some healthcare providers and insurers from full-scale adoption. Ensuring that patients and caregivers are properly trained to handle complex devices such as volumetric pumps or patient-controlled analgesia systems adds further layers of complexity. These concerns demand comprehensive training, monitoring, and robust support systems, which may increase provider costs and complexity.
An area of immense opportunity is the technological innovation in infusion devices. Modern home infusion is no longer reliant on bulky IV stands and manual flow rate adjustments. Companies are introducing compact, wearable infusion pumps, smart devices with Bluetooth connectivity, and programmable infusion systems that allow for precise medication delivery, real-time alerts, and remote supervision by healthcare providers.
For instance, wearable elastomeric pumps are enabling cancer patients to receive continuous chemotherapy without being tethered to a clinical setting. Similarly, insulin pumps with closed-loop systems now provide continuous glucose monitoring and automatic basal rate adjustments for diabetic patients. These devices enhance compliance, reduce error rates, and improve outcomes. With ongoing investment in digital health, AI-powered infusion platforms, and mobile integration, infusion therapy is becoming more efficient, intelligent, and patient-centric especially important in the U.S., where patient empowerment and convenience are top priorities.
Infusion pumps dominate the product segment, as they are essential for the controlled delivery of medications, nutrients, and fluids. Among these, volumetric pumps are widely used in hydration therapy and parenteral nutrition due to their ability to deliver large volumes of fluids with accuracy. Meanwhile, syringe pumps and PCA pumps are gaining importance in pain management and palliative care. Infusion pumps have become more compact, programmable, and intelligent, enabling administration of complex therapies such as antibiotics, antivirals, and chemotherapy agents at home. Providers and manufacturers are also incorporating safety features like occlusion alarms, dose tracking, and connectivity with electronic health records.
Needleless connectors are the fastest-growing sub-segment, reflecting a strong industry-wide push toward infection control and ease of administration. These devices help reduce the risk of bloodstream infections, which are a significant concern in home IV therapy. Needleless connectors are especially critical for immunocompromised patients, such as those undergoing chemotherapy or long-term antibiotic therapy. Their usage is also increasing in pediatric and geriatric care, where minimizing pain and complications is a priority. Regulatory support from the FDA and CDC for needleless systems has further fueled market expansion.
Anti-infective therapy dominates the application segment, historically representing the bulk of home infusion cases. Patients requiring long-term treatment for conditions like osteomyelitis, cellulitis, or septicemia often complete their IV antibiotic regimens at home once stabilized. Home-based anti-infective infusion not only reduces hospital stays but also enables faster recovery and lower exposure to nosocomial infections. Antibiotics like vancomycin, ceftriaxone, and meropenem are among the most frequently administered drugs via infusion in this setting.
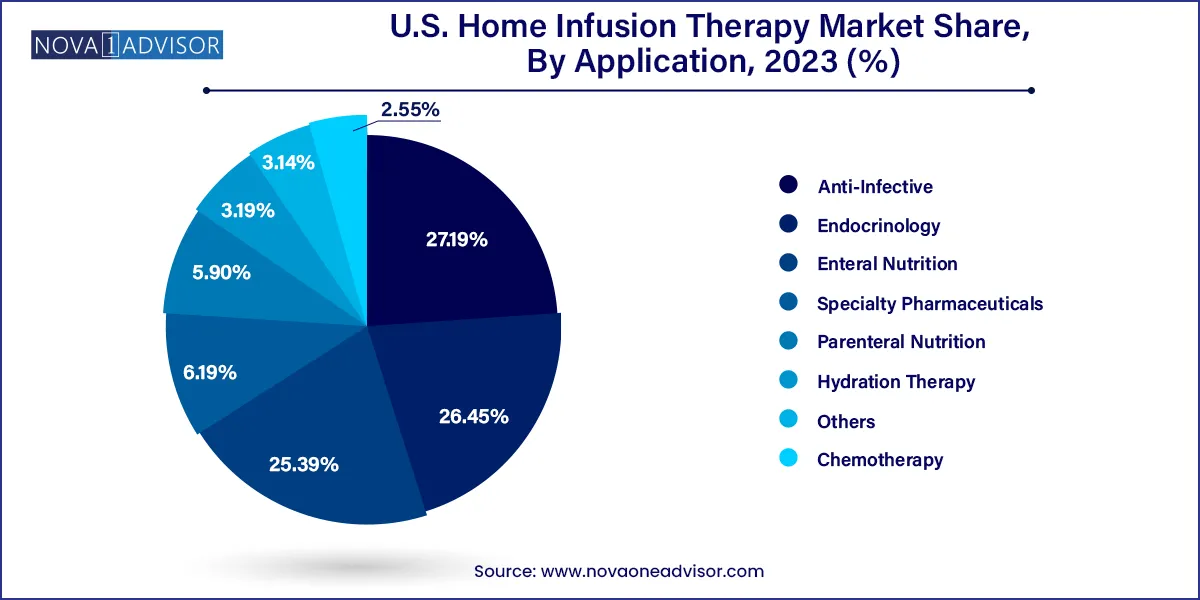
Chemotherapy is the fastest-growing application, as oncologists and infusion providers explore home-based cancer care options to reduce patient fatigue, hospitalization costs, and immune system exposure. Many chemotherapy regimens, especially for chronic and stable conditions like metastatic breast cancer or colon cancer, are now being safely delivered at home through portable infusion pumps or elastomeric devices. The ability to offer treatment in a familiar environment significantly enhances patient comfort and reduces caregiver burden. With cancer incidence rising and value-based care models gaining ground, home chemotherapy will continue to drive innovation and investment.
The United States represents the entire geographic scope of this market, and its evolution reflects the broader transformation in American healthcare delivery. Driven by patient-centered care, payer incentives, and technological maturity, the U.S. home infusion therapy market is one of the most advanced globally. The presence of large national providers such as Option Care Health, Coram CVS Specialty Infusion, and BioScrip (now part of Option Care) has created structured, standardized services across all 50 states.
Urban centers like New York, Los Angeles, and Chicago are witnessing high adoption due to advanced healthcare infrastructure and higher rates of chronic disease. Simultaneously, rural and suburban regions are emerging as high-potential zones, where hospitals and clinics are partnering with infusion providers to extend care beyond traditional settings. Payers, including Medicare Advantage and Medicaid Managed Care Organizations, are increasingly supportive of home infusion for cost containment and patient satisfaction purposes. The U.S. FDA and National Home Infusion Association (NHIA) continue to play pivotal roles in shaping safety, compliance, and industry best practices.
Some of the players profiled in the U.S. home infusion therapy industry focus on adopting growth strategies, such as mergers and acquisitions, new product launches, innovations in existing technologies, and more.
For instance, In March 2022, B. Braun acquired Intermedt Medizin & Technik GmbH to integrate a comprehensive range of products and services for dialysis therapy.
March 2025 – Option Care Health announced a strategic collaboration with a large national oncology network to expand home-based chemotherapy services across 15 states.
February 2025 – Baxter International unveiled its next-gen Amia Home Infusion System, incorporating voice assistance and data-sharing capabilities for parenteral nutrition patients.
January 2025 – Coram CVS Specialty Infusion Services launched a tele-infusion platform that connects patients with infusion nurses and pharmacists via real-time video consults and remote monitoring.
November 2024 – ICU Medical received FDA clearance for a wireless elastomeric pump with integrated dose-tracking for outpatient antimicrobial therapy.
September 2024 – Smiths Medical introduced a line of needleless safety connectors with antimicrobial surfaces to address catheter-related infection risks in the home setting.
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2033. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the U.S. Home Infusion Therapy market.
By Product
By Application